Montpelier, Vermont
Montpelier (/mɒntˈpiːliər/)[6] is the capital city of the U.S. state of Vermont and the seat of Washington County. The site of Vermont's state government, it is the least populous state capital in the United States.[7] The population was 7,855 as of the 2010 census. However, the daytime population grows to about 21,000, due to the large number of jobs within city limits.[8] The Vermont College of Fine Arts and New England Culinary Institute are located in the municipality. It was named after Montpellier, a city in the south of France.[9]
Montpelier | |
|---|---|
State capital and city | |
 The Vermont State House, Montpelier's best-known landmark | |
 Flag  Seal | |
 Location in Washington County in Vermont | |
 Montpelier Location in the United States  Montpelier Location within Vermont | |
| Coordinates: 44°15′34″N 72°34′33″W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| County | Washington |
| Region | New England |
| Settled | 1787 |
| Incorporated (village) | 1818 |
| Incorporated (city) | 1895 |
| Named for | Montpellier, France |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Anne Watson[1] |
| • City Manager | William J. Fraser |
| Area | |
| • Total | 10.25 sq mi (26.54 km2) |
| • Land | 10.05 sq mi (26.04 km2) |
| • Water | 0.19 sq mi (0.50 km2) |
| Elevation | 525 ft (160 m) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 7,855 |
| • Estimate (2019)[3] | 7,372 |
| • Density | 733.17/sq mi (283.07/km2) |
| Demonym(s) | Montpelierite |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (EST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| ZIP codes | 05601-05604, 05609, 05620, 05633 |
| Area code(s) | 802 |
| FIPS code | 50-46000[4] |
| GNIS feature ID | 1461834[5] |
| Interstates | |
| U.S. Highways | |
| State Routes | |
| Website | Official website |
History
.jpg.webp)
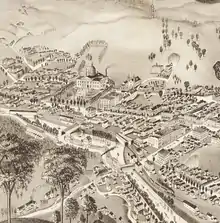

Between 1600 and 1800, European settlers began to arrive in the region.[10] Soon after, war, disease, and dispersal virtually destroyed the Native American settlements. However, evidence suggests some Native Americans remained in the area as late as the mid-1800s.[10]
Originally charted on August 14, 1781, the Town of Montpelier was granted municipal powers by the "Governor, Council and General Assembly of the Freemen of the State of Vermont".[11] The first permanent settlement began in May 1787, when Colonel Jacob Davis and General Parley Davis arrived from Charlton, Massachusetts. General Davis surveyed the land, while Colonel Davis cleared forest and erected a large log house on the west side of the North Branch of the Winooski River. His family moved in the following winter.
Colonel Davis selected the name "Montpelier" after the French city of Montpellier, capital of the department of Hérault.[12] There was a general enthusiasm for things French as a result of the country's aid to the American colonies during the Revolutionary War.[13] The settlement grew quickly, and by 1791 the population reached 117.
The configuration of the early village was strongly influenced by geography. As early as 1799 a bridge was constructed across the Winooski River to Berlin.[10]
The Town's Charter was reissued on February 6, 1804, to include a boundary description of the lands granted to the Town's inhabitants and proprietors.[11] The confluence of the Winooski, North Branch and Dog Rivers provided a central point for the local population and commerce.
By 1805 the town had a population of 1,200. In that year the state legislature sought a permanent home. Montpelier was selected because of its central location and accessibility, and because local residents provided land and money. A humble State House was soon constructed on State Street.[10]
In 1825, the Marquis de Lafayette visited Montpelier on a triumphal tour of the United States, 50 years after the Revolutionary War.
The town developed into a center for manufacturing, especially after the Central Vermont Railway opened in Montpelier on June 20, 1849. In response to Montpelier's growth and changing demographics, on November 9, 1848, the General Assembly divided the original Town into two district municipal corporations. The towns of East Montpelier and Montpelier were created. Later on, in an attempt to modernize its form of government, the town was reconstituted as the Village of Montpelier.[11]
By 1858, the layout of the main streets paralleling the rivers was in place. The downtown street pattern has changed very little since that time.[10]
Ten thousand people turned out to greet Major General Philip Sheridan when he visited to address the fourth annual meeting of Vermont former Union officers. He particularly thanked Vermont veterans of the Civil War for their performance at the Battle of Cedar Creek.[14][15]
In 1875, a large fire destroyed many downtown buildings.[10]
The village had the first municipal water driven hydro system in Vermont in 1884. Water pressure generated sufficient electricity for streetlights.[16]
The first charter of Montpelier was granted in 1894, and was amended shortly thereafter in 1898, and again in 1900 and 1912. The first amendment permitted the city to annex a part of the Town of Berlin; the latter enactments amended the 1898 charter to deal with such matters as water works, the relationship between the city and the Washington County Grammar School, and composition of the City Council.[11]
The state proclaimed October 12, 1899, as "Dewey Day" to honor native son George Dewey, the hero of Battle of Manila Bay in the Spanish–American War. Thousands turned out from the state to his hometown of Montpelier for the celebration.[17] In 1899, Hubbard Park was established with a donation of land, known as "Hubbard Hill", bequeathed to the City of Montpelier by John Erastus Hubbard (1847–1899) with the intent to "preserve wilderness" for future generations. In 1911, additional land was donated and from 1915 to 1930 an observation tower was constructed on this donated land.
In 1927, after a particularly wet summer and fall, heavy rains began on the evening of November 2 that continued until the morning of November 4. The heaviest rain fell on November 3, when more than seven inches fell in a six-hour period. The prolonged heavy rains on top of the already saturated soil from the summer and fall proved to be more than the watercourses could handle. Brooks and rivers overflowed carrying trees and logs in their wake. Dams, bridges and embankments were destroyed. Buildings were submerged, farm animals drowned, and homes and barns were swept away. Rivers reached 13 feet or more above their normal depths. Flood waters gradually receded, leaving behind silt, gravel and debris. At least a foot of mud was left on the floors of downtown stores.[18]
At the time only two stores in Montpelier carried flood insurance. The staggering loss represented an average of $400 for every man, woman, and child in town – equivalent to roughly $5,760 in 2018 dollars. In the days following the flood, Vermont was widely praised for its recovery efforts. President Calvin Coolidge, in particular, hailed the “indomitable spirit” of Vermonters, of whom he was one.[18]
In response to the damage suffered by Montpelier and surrounding communities in the Great Flood of 1927, the Civilian Conservation Corps built the Wrightsville Dam during a period from 1933 to 1935. The resulting reservoir, Wrightsville Reservoir, required the disbandment and flooding of the village of Wrightsville, which contained at least 30 built structures at the time.
The City of Montpelier grew slowly in the late 19th and early 20th centuries during the period of intensive out-migration from the state to new lands in the West, or to industrial centers elsewhere in New England. Montpelier was already established as a government, market, service and industrial center in the region. When the automobile arrived, new state highways were routed to the city limits, and traffic then circulated through the original streets of the city. In 1954, a new bridge was constructed at Bailey Avenue which linked to an extension of Winooski Avenue, now Memorial Drive, and diverted some of the traffic from the downtown area.[10]
An early spring thaw in March 1992 caused an ice jam to form in the Winooski River downstream of the Bailey Avenue bridge in Montpelier. In less than an hour, water levels in the Winooski and North Branch rivers rose upstream of the ice jam and flooded downtown Montpelier. The damage shut down 120 businesses, left 50 residents without homes, disrupted the operations of state government, and caused upwards of $5 million in damage.[19]
Geography

Montpelier is located in the north-central area of Vermont.[20] The city center is a flat clay zone (elevation 520 ft/158 m), surrounded by hills and granite ledges. Towne Hill runs in a 2-mile (3.2 km) ridge (~900 ft/275 m) along the northern edge of the city.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the city has a total area of 10.3 square miles (27 km2), of which 10.2 square miles (26 km2) is land and 0.10% is water. The Winooski River flows west along the south edge of downtown village and is fed by several smaller tributaries that cut through residential districts. Montpelier has been subject to periodic flooding in the flat city center, with two major floods occurring in 1927 and in 1992.[21]
On its borders are the towns of Middlesex to the west, Berlin to the south, and East Montpelier to the north and east. Montpelier lies near the geographic center of the state.[22] Though it does not share a border, Montpelier is frequently associated with the nearby city of Barre, and the two are often referred to together as "Barre-Montpelier".
Climate
Montpelier features a humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb), with long, cold, and snowy winters, short springs and autumns, and warm, humid summers. From January to July, daily means range from 16.4 to 67.3 °F (−8.7 to 19.6 °C). In winter, lows fall below 0 °F or −17.8 °C on 24 mornings and daytime highs stay below freezing for the majority of afternoons from December to February. Snow is also frequent and remains on the ground for long stretches throughout the winter, though thaws are by no means infrequent. Average annual snowfall is 94.2 inches or 2.39 metres.[23] Summers are warm and often humid, with 2 or 3 days above 90 °F or 32.2 °C, but rarely reaching 95 °F or 35 °C.
Extremes have ranged from −34 °F or −36.7 °C in January 1981 to 97 °F or 36.1 °C, most recently recorded in July 1977.
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Record high °F (°C) | 64 (18) |
72 (22) |
84 (29) |
93 (34) |
93 (34) |
103 (39) |
100 (38) |
100 (38) |
100 (38) |
86 (30) |
76 (24) |
70 (21) |
103 (39) |
| Mean maximum °F (°C) | 49.3 (9.6) |
53.2 (11.8) |
63.1 (17.3) |
85.1 (29.5) |
87.3 (30.7) |
95.2 (35.1) |
94.5 (34.7) |
93.8 (34.3) |
91.1 (32.8) |
80.0 (26.7) |
65.4 (18.6) |
50.1 (10.1) |
98.2 (36.8) |
| Average high °F (°C) | 28.7 (−1.8) |
32.1 (0.1) |
42.4 (5.8) |
55.8 (13.2) |
68.8 (20.4) |
78.1 (25.6) |
82.8 (28.2) |
81.5 (27.5) |
75.2 (24.0) |
58.8 (14.9) |
46.0 (7.8) |
33.0 (0.6) |
56.9 (13.9) |
| Daily mean °F (°C) | 16.0 (−8.9) |
19.5 (−6.9) |
29.7 (−1.3) |
43.3 (6.3) |
54.9 (12.7) |
65.3 (18.5) |
70.4 (21.3) |
68.6 (20.3) |
61.8 (16.6) |
47.2 (8.4) |
36.5 (2.5) |
23.5 (−4.7) |
44.7 (7.1) |
| Average low °F (°C) | 4.1 (−15.5) |
6.9 (−13.9) |
16.8 (−8.4) |
30.7 (−0.7) |
40.8 (4.9) |
52.6 (11.4) |
57.9 (14.4) |
55.7 (13.2) |
48.2 (9.0) |
35.6 (2.0) |
27.0 (−2.8) |
13.9 (−10.1) |
32.5 (0.3) |
| Mean minimum °F (°C) | −15.5 (−26.4) |
−13.7 (−25.4) |
−2.5 (−19.2) |
18.5 (−7.5) |
27.3 (−2.6) |
38.7 (3.7) |
47.5 (8.6) |
44.3 (6.8) |
34.4 (1.3) |
22.0 (−5.6) |
11.9 (−11.2) |
−6.5 (−21.4) |
−19.3 (−28.5) |
| Record low °F (°C) | −28 (−33) |
−28 (−33) |
−24 (−31) |
9 (−13) |
22 (−6) |
33 (1) |
42 (6) |
43 (6) |
24 (−4) |
18 (−8) |
0 (−18) |
−18 (−28) |
−28 (−33) |
| Average precipitation inches (mm) | 2.69 (68) |
2.91 (74) |
3.08 (78) |
3.18 (81) |
3.12 (79) |
4.42 (112) |
5.00 (127) |
3.57 (91) |
3.19 (81) |
4.13 (105) |
3.42 (87) |
4.49 (114) |
44.85 (1,139) |
| Average snowfall inches (cm) | 19.75 (50.2) |
10.48 (26.6) |
13.19 (33.5) |
1.50 (3.8) |
0.00 (0.00) |
0.00 (0.00) |
0.00 (0.00) |
0.00 (0.00) |
0.00 (0.00) |
0.00 (0.00) |
3.97 (10.1) |
12.50 (31.8) |
61.39 (156) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.01 in.) | 12.8 | 12.4 | 11.8 | 11.5 | 11.1 | 13.0 | 11.4 | 9.9 | 9.3 | 12.8 | 12.1 | 16.6 | 163.7 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.1 in.) | 7.0 | 5.8 | 3.5 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.5 | 5.0 | 23.7 |
| Mean daily sunshine hours | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 9 | 8 | 6 | 5 | 3 | 3 | 6 |
| Mean daily daylight hours | 9.3 | 10.5 | 12.0 | 13.5 | 14.8 | 15.5 | 15.1 | 14.0 | 12.5 | 11.0 | 9.6 | 8.9 | 12.2 |
| Average ultraviolet index | 1 | 2 | 3 | 5 | 7 | 8 | 8 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 4 |
| Source 1: NOAA[24] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather Atlas[25] | |||||||||||||
See or edit raw graph data.
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1800 | 890 | — | |
| 1810 | 1,877 | 110.9% | |
| 1820 | 2,308 | 23.0% | |
| 1830 | 1,193 | −48.3% | |
| 1840 | 3,725 | 212.2% | |
| 1850 | 2,310 | −38.0% | |
| 1860 | 2,411 | 4.4% | |
| 1870 | 3,023 | 25.4% | |
| 1880 | 3,219 | 6.5% | |
| 1890 | 4,160 | 29.2% | |
| 1900 | 6,266 | 50.6% | |
| 1910 | 7,856 | 25.4% | |
| 1920 | 7,125 | −9.3% | |
| 1930 | 7,837 | 10.0% | |
| 1940 | 8,006 | 2.2% | |
| 1950 | 8,559 | 6.9% | |
| 1960 | 8,782 | 2.6% | |
| 1970 | 8,609 | −2.0% | |
| 1980 | 8,241 | −4.3% | |
| 1990 | 8,247 | 0.1% | |
| 2000 | 8,035 | −2.6% | |
| 2010 | 7,855 | −2.2% | |
| 2019 (est.) | 7,372 | [3] | −6.1% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[26][27] | |||
Along with Barre, the city forms a small micropolitan area in the center of the state; together they are known as the twin cities.
As of the census[4] of 2010, there were 7,855 people, 3,739 households, and 1,940 families residing in the city. The population density was 784.0 people per square mile (302.7/km2). There were 3,899 housing units at an average density of 380.4 per square mile (146.9/km2). The racial makeup of the city was 93.7% White, 1.0% African American, 0.3% Native American, 2.2% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 0.39% from other races, and 2.2% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 2.1% of the population.
There were 3,739 households, out of which 26.0% had children under the age of 18 years living with them, 38.5% were married couples living together, 10.1% had a female householder with no husband present, and 48.1% were non-families. 39.4% of all households were made up of individuals, and 13.1% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.09 and the average family size was 2.84.
In the city, the population was spread out, with 21.3% under the age of 18, 8.6% from 18 to 24, 28.2% from 25 to 44, 27.1% from 45 to 64, and 14.9% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 40 years. For every 100 females, there were 84.2 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 82.0 males.
Personal income
The median income for a household in the city was $37,513, and the median income for a family was $51,818. Males had a median income of $35,957 versus $29,442 for females. The per capita income for the city was $22,599. About 7.2% of families and 9.8% of the population were below the poverty line, including 12.9% of those under age 18 and 5.7% of those age 65 or over.
Economy

Government, higher education, insurance and tourism are principal businesses.[28]
Industry
Since the city's establishment as capital in 1805, the primary business in Montpelier has been government, and by the mid-19th century government and life and fire insurance. Companies based in Montpelier include the National Life Group.
Located in Montpelier are the New England Culinary Institute, the annual Green Mountain Film Festival and the headquarters of several insurance companies. The majority of businesses in the downtown area, mostly retail, are locally owned.
Montpelier is the only state capital in the United States of America that does not have a McDonald's.[29] However, there is a McDonald's location in nearby Berlin, Vermont.
Tourism
The Vermont History Museum, operated in The Pavilion by the Vermont Historical Society, is an attraction.
Arts and culture

- Kellogg-Hubbard Library—with a copy of the Parthenon Frieze[30]
- Lost Nation Theater[31]
- Montpelier Theatre Guild[32]
- Vermont History Museum—in The Pavilion[33]
- Vermont State House
- T. W. Wood Gallery & Arts Center[34]
- Capital City Concerts[35]
- An annual local vernacular culture phenomenon, the Valentine Phantom, a tradition of covering downtown storefronts and public buildings with red hearts each February 14, began in Montpelier in the 1990s.
Sports
The Vermont Mountaineers of the New England Collegiate Baseball League play at the Montpelier Recreation Field.
Parks and recreation

The city has three city nature centers. Hubbard Park rises behind the state capitol building and extends along the ridge line towards the north past the pool to the stump dump.[37] Accessible from Cummings Street off State Route 12, the North Branch River Park is the second-largest park in the city.[38] The Mill Pond Park is located along State Route 12 approximately a 0.25 miles (0.40 km) from the cemetery and features boat access to the North Branch river, as well as benches and short-term parking.[39] The North Branch Nature Center is located at the northern end of town and includes 17 acres (6.9 ha) of protected land as well as a community nature center. A bridge from the North Branch Nature Center connects the land to the North Branch River Park on the opposite side of the North Branch River.[40] In recent years, North Branch River Park has significantly expanding its mountain biking trails, making it a hub for area mountain bikers of all ages. The first mountain bike trail in North Branch River Park was constructed and opened in 2005 as part of a partnership between the Montpelier Area Mountain Bike Association and the Montpelier Parks Department. Since that time, 4 additional miles of trails have been added. A pump track is also currently under construction.
Government
Montpelier's government maintains a city council, city manager, and mayor. The city council consists of a mayor and six members each elected from districts with each district electing two members for two year terms. The mayor is elected in a citywide vote to a two-year term. The council appoints the city manager who is the chief administrative officer of the city.
The city provides municipal services for its residents and businesses. These include local law enforcement, firefighting, planning and zoning regulation, and provision for potable drinking water and wastewater.
Education
- Public schools include:
- Montpelier High School
- Main Street Middle School[41]
- Union Elementary School[42]
- River Rock School is a private school serving kindergarten through 8th grade students.[43]
- A campus of the Community College of Vermont
- New England Culinary Institute, a for-profit career college
- Union Institute & University Vermont campus, offers a Master of Education program through a low-residency (online) program[44]
- Vermont College of Fine Arts is a low-residency graduate school offering Masters of Fine Arts degrees in visual arts, writing, and writing for children and young adults[45]
Infrastructure
Transportation

Montpelier has become one of Vermont's most readily accessible cities and towns, as Vermont's founders deliberately placed the capital near the geographic center of the state.[46][47]
Roads
The city is located along Interstate 89. East–west U.S. Route 2 and north–south Vermont Route 12 are two other principal routes that intersect in Montpelier. Both I-89 and U.S. 2 provide a direct link to Burlington and the populous Lake Champlain Valley in the northwestern corner of the state. U.S. Route 302 has its western terminus in Montpelier, connecting it with the nearby city of Barre and points east.
Rail
Amtrak, the national passenger rail system, provides daily service from its station at Montpelier Junction in the neighboring town of Berlin, on the route known as the "Vermonter", operating between St. Albans, Vermont and Washington, D.C.
Bus
Greyhound and Megabus operate buses that serve Montpelier. The Green Mountain Transit Authority (GMTA) operates a local bus network throughout the micropolitan area, with stops in Montpelier and Barre, including nearby Waterbury, the Vermont State House, the Ben & Jerry's factory, and the local Berlin Mall. GMTA and its sister bus company in Burlington, the Chittenden County Transportation Authority (CCTA), operate a series of LINK commuter buses with stops in Montpelier, Burlington, Richmond, and Waterbury.
Air
Air travelers in private planes can use the Edward F. Knapp State Airport in Berlin to access Montpelier. The Burlington International Airport in Chittenden County is the closest commercial air service, located 35 miles (56 km) northwest of Montpelier.
Other
Two shared-use paths for walking and bicycling connect to Montpelier: the Cross Vermont Trail and the Central Vermont Regional Path. Montpelier's downtown is relatively compact and pedestrian-friendly, with sidewalks and crosswalks throughout the downtown area.
Notable people
See also
- Athenwood and the Thomas W. Wood Studio - historic buildings in Montpelier
- Christ Episcopal Church - historic church in Montpelier
- Saint Augustine's Church - historic church in Montpelier
References
- "City Council & Mayor". City of Montpelier, Vermont. Retrieved 10 January 2020.
- "2019 U.S. Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved August 7, 2020.
- "Population and Housing Unit Estimates". United States Census Bureau. May 24, 2020. Retrieved May 27, 2020.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved 2008-01-31.
- "Montpelier". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey.
- "the definition of Montpelier".
- Smallest capital city plans big MLK celebration Archived 2011-07-26 at the Wayback Machine. Retrieved 2010-04-23.
- A Study and Analysis of the Fiscal Impacts of Growth in the City of Montpelier
- "Washington County". Virtual Vermont. Archived from the original on 13 July 2017. Retrieved 9 September 2017.
- "About Montpelier | Montpelier, VT". www.montpelier-vt.org. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- "Charter of the City of Montpelier". www.montpelier-vt.org/DocumentCenter/View/1454/City-Charter-PDF. Archived from the original on 2018-05-24.
- Federal Writers' Project of the Works Progress Administration for the State of Vermont (1996). Vermont: A guide to the Green Mountain State. The Stephen Greene Press. p. 117.
- Swift, Esther Munroe (1977). Vermont Place Names: Footprints of History. Houghton Mifflin. pp. 451–454. ISBN 0-8289-0291-7.
- Coffin, Howard (6 May 2013). Something Abides: Discovering the Civil War in Today's Vermont. The Countryman Press. ISBN 9781581577778 – via Google Books.
- Huegenin, Joan (May 18, 2016). "Reunion Society of Vermont Officers". Journal of the Northeast Kingdom Civil War Roundtable: 7–8.
- Barg, Lori (9 August 2009). "Power from the plumbing". =Burlington Free Press. Burlington, Vermont. pp. 5D.
- "George Dewey (1837–1917) Family Papers, 1844–1901 MS 125" (PDF). Retrieved April 14, 2013.
- "The Flood of '27, 1927 - Vermont Historical Society". vermonthistory.org. Retrieved 2018-05-24.
- "Vermont's capital braces for possible river flooding".
- "US Gazetteer files: 2010, 2000, and 1990". United States Census Bureau. 2011-02-12. Retrieved 2011-04-23.
- C. B. Hall (March 7, 2014). "The Rivers and Montpelier". The Bridge. Archived from the original on December 8, 2015. Retrieved November 27, 2015.
- "Montpelier". Virtual Vermont. Archived from the original on July 13, 2017. Retrieved November 27, 2015.
Montpelier's proximity to the geographic center of the state was a principal deciding factor.
- NWS Burlington Forecast Office
- "NOWData - NOAA Online Weather Data". NOAA. Retrieved June 21, 2020.
- "Monthly weather forecast and climate: Montpelier, VT". Weather Atlas. Retrieved June 21, 2020.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- "Vermont History Explorer". Retrieved August 7, 2015.
- "Montpelier: Economy-Major Industries". City.com. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- Jones, Meghan. "This is the only US state capital that doesn't have a McDonald's". Business Insider. Reader's Digest. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- "Home - Kellogg Hubbard Library".
- "Lost Nation Theater - Home".
- "Montpelier Theatre Guild". Archived from the original on 2008-09-19.
- "Home - Vermont Historical Society".
- "T.W. Wood Gallery, Vermont - Welcome".
- "Capital City Concerts – Montpelier Vermont's Premiere Classical Concert Series". Retrieved April 14, 2013.
- "Park Features – Montpelier, Vermont". City of Montpelier, Vermont.
- "Hubbard Park – Montpelier, VT".
- "North Branch River Park – Montpelier, VT".
- "Mill Pond Park – Montpelier, VT".
- "North Branch Nature Center – Homepage".
- http://www.mpsvt.org/msms/
- Union Elementary School
- Ryan, River Rock School, Rob. "River Rock School: Handcrafted Education in Central Vermont".
- Union Institute and University of Vermont Center M.Ed. Program
- Vermont College of Fine Arts
- "Vermont Geography from NETSTATE".
- "Vermont Capitol - Montpelier, VT - Capitol Buildings on Waymarking.com".
Further reading
- Coolidge, A. J. & Mansfield, J. B. (1859). A History and Description of New England. Boston, Massachusetts: A.J. Coolidge. p. 9.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Montpelier, Vermont. |
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Montpelier. |
| Wikisource has the text of the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica article Montpelier. |