7 Iris
Iris (minor planet designation: 7 Iris) is a large main-belt asteroid and perhaps remnant planetesimal orbiting the Sun between Mars and Jupiter. It is the fourth-brightest object in the asteroid belt. It is classified as an S-type asteroid, meaning that it has a stony composition.
 Iris imaged by the Very Large Telescope in 2017[1] | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | John Russell Hind |
| Discovery date | August 13, 1847 |
| Designations | |
| (7) Iris | |
| Pronunciation | /ˈaɪərɪs/[2] |
Named after | Īris |
| Main belt | |
| Adjectives | Iridian /aɪˈrɪdiən/[3] |
| Orbital characteristics[4] | |
| Epoch 27 April 2019 (JD 2458600.5) | |
| Aphelion | 2.937 AU (439.4 Gm) |
| Perihelion | 1.834 AU (274.4 Gm) |
| 2.385 AU (356.8 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.2312 |
| 3.68 a (1345.375 d) | |
Average orbital speed | 19.03 km/s |
| 140.420° | |
| Inclination | 5.524° |
| 259.563° | |
| 145.265° | |
| Proper orbital elements[5] | |
Proper semi-major axis | 2.3862106 AU |
Proper eccentricity | 0.2125516 |
Proper inclination | 6.3924857° |
Proper mean motion | 97.653672 deg / yr |
Proper orbital period | 3.6865 yr (1346.493 d) |
Precession of perihelion | 38.403324 arcsec / yr |
Precession of the ascending node | −46.447128 arcsec / yr |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 268 km × 234 km × 180 km ± (5 km × 4 km × 6 km)[1] 225 km × 190 km × 190 km[6] |
Mean diameter | 214±5 km[1] 200±10 km (IRAS)[4] |
| 538460 km2[lower-alpha 1] | |
| Volume | 37153500 km3[lower-alpha 1] |
| Mass | (1.375±0.13)×1019 kg[1] |
Mean density | 2.7±0.3 g/cm3[1] |
Equatorial surface gravity | 0.08 m/s² |
Equatorial escape velocity | 0.131 km/s |
| 7.138843 h (0.2974518 d)[1] | |
Equatorial rotation velocity | 25.4 m/s[lower-alpha 1] |
| 0.277 | |
| Temperature | ~171 K max: 275 K (+2°C) |
| S | |
| 6.7[7][8] to 11.4 | |
| 5.51 | |
| 0.32" to 0.07" | |
Discovery and name
Iris was discovered on August 13, 1847, by J. R. Hind from London, UK. It was Hind's first asteroid discovery and the seventh asteroid to be discovered overall.
Iris was named after the rainbow goddess Iris in Greek mythology, who was a messenger to the gods, especially Hera. Her quality of attendant of Hera was particularly appropriate to the circumstances of discovery, as Iris was spotted following 3 Juno by less than an hour of right ascension (Juno is the Roman equivalent of Hera).
Characteristics
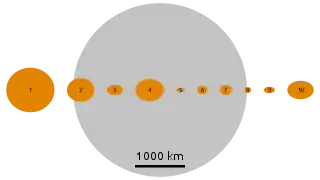
Geology
Iris is an S-type asteroid. The surface is bright and is probably a mixture nickel-iron metals and magnesium- and iron-silicates. Its spectrum is similar to that of L and LL chondrites with corrections for space weathering,[9] so it may be an important contributor of these meteorites. Planetary dynamics also indicates that it should be a significant source of meteorites.[10]
Among the S-type asteroids, Iris ranks fifth in geometric mean diameter after Eunomia, Juno, Amphitrite and Herculina. Its shape is consistent with an oblate spheroid with a large equatorial excavation, suggesting it is a remnant planetesimal. No collisional family can be associated with Iris, likely because the excavating impact occurred early in the history of the Solar System, and the debris has since dispersed.[1]
Brightness

Iris's bright surface and small distance from the Sun make it the fourth-brightest object in the asteroid belt after Vesta, Ceres, and Pallas. It has a mean opposition magnitude of +7.8, comparable to that of Neptune, and can easily be seen with binoculars at most oppositions. At typical oppositions it marginally outshines the larger though darker Pallas.[11] But at rare oppositions near perihelion Iris can reach a magnitude of +6.7 (last time on October 31, 2017 reaching a magnitude of +6.9),[7] which is as bright as Ceres ever gets.
Surface features
A study by Hanus et al. using data from the VLT's SPHERE instrument names eight craters 20 to 40 km in diameter, and seven recurring features who remain nameless due to a lack of consistency and their occurrence on the edge of Iris. The names are Greek names of colors, corresponding to the rainbow as the sign of Iris. It is unknown whether these names are under consideration by the IAU. All 8 features are craters, the natures of the remaining 7 features are unknown, and they are labeled A through G.[1]
| Feature | Pronunciation | Greek | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chloros | /ˈkloʊrɒs/ | χλωρός | 'green' |
| Chrysos | /ˈkraɪsɒs/ | χρῡσός | 'gold' |
| Cirrhos | /ˈsɪrɒs/ | κιρρός | 'orange'[lower-alpha 2] |
| Cyanos | /ˈsaɪənɒs/ | κύανος | 'blue' |
| Erythros | /ˈɛrɪθrɒs/ | ἐρυθρός | 'red' |
| Glaucos | /ˈɡlɔːkɒs/ | γλαυκός | 'grey'[lower-alpha 3] |
| Porphyra | /ˈpɔːrfɪrə/ | πορφύρα | 'purple' |
| Xanthos | /ˈzænθɒs/ | ξανθός | 'yellow' |
Rotation
Iris has a rotational period of 7.14 hours. Iris's north pole points towards the ecliptic coordinates (λ, β) estimated to be (18°, +19°) with a 4° uncertainty (Viikinkoski et al. 2017) or (19°, +26°) with a 3° uncertainty (Hanuš et al. 2019). This gives an axial tilt of xx°, so that on much of each hemisphere, the sun does not set during summer, and does not rise during winter. On an airless body this gives rise to very large temperature differences.
Observations
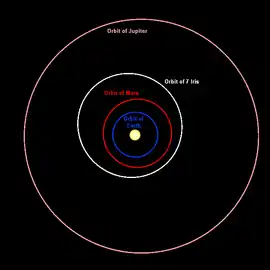
Iris was observed occulting a star on May 26, 1995, and later on July 25, 1997. Both observations gave a diameter of about 200 km.
See also
Notes
References
- Hanuš, J.; Marsset, M.; Vernazza, P.; Viikinkoski, M.; Drouard, A.; Brož, M.; et al. (24 April 2019). "The shape of (7) Iris as evidence of an ancient large impact?". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 624 (A121). arXiv:1902.09242. Bibcode:2018DPS....5040406H. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201834541.
- "iris". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- "iridian". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 7 Iris" (2018-03-27 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 17 June 2019.
- "AstDyS-2 Iris Synthetic Proper Orbital Elements". Department of Mathematics, University of Pisa, Italy. Retrieved 1 October 2011.
- Kaasalainen, M.; et al. (2002). "Models of twenty asteroids from photometric data" (PDF). Icarus. 159 (2): 369. Bibcode:2002Icar..159..369K. doi:10.1006/icar.2002.6907.
- Donald H. Menzel & Jay M. Pasachoff (1983). A Field Guide to the Stars and Planets (2nd ed.). Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin. pp. 391. ISBN 0-395-34835-8.
- "Bright Minor Planets 2006". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 21 May 2008.
- Y. Ueda et al. Surface Material Analysis of the S-type Asteroids: Removing the Space Weathering Effect from Reflectance Spectrum, 34th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, March 17–21, 2003, League City, Texas, abstract no.2078 (2003).
- Migliorini, F.; et al. (1997). "(7) Iris: a possible source of ordinary chondrites?". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 321: 652. Bibcode:1997A&A...321..652M.
- Odeh, Moh'd. "The Brightest Asteroids". Jordanian Astronomical Society. Archived from the original on 13 August 2007. Retrieved 16 July 2007.
- "cirrhosis". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
External links
- Shape model deduced from lightcurve (M. Kaasalainen 2002)
- 2011-Feb-19 Occultation (Durech Model) / (2011 Asteroidal Occultation Results for North America)
- "Discovery of Iris", MNRAS 7 (1847) 299
- JPL Ephemeris
- "Elements and Ephemeris for (7) Iris". Minor Planet Center. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. (displays Elong from Sun and V mag for 2011)
- 7 Iris at AstDyS-2, Asteroids—Dynamic Site
- 7 Iris at the JPL Small-Body Database

