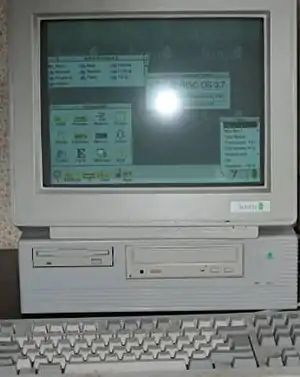
Acorn A7000
The A7000 and A7000+ were Acorn Computers' entry level computers based on the RiscPC architecture. Launched in 1995,[1] they replaced some of the models of the Acorn Archimedes range,[4] being considered a successor to the A5000 and fitting into Acorn's range between the A4000 and Risc PC600. Unlike the Risc PC, the A7000 had been "designed with the rigours of school life in mind", aiming for "a 7-year classroom lifespan".[5] After the breakup of Acorn Computers in 1998, Castle Technology bought the rights to continue production of the A7000+.[6] The A7000 used the ARM7500 system on chip which combined the separate ARM CPU, MMU, VIDC20 video chip and IOMD IO controller of the RiscPC into a single chip.[1]
| Developer | Acorn Computers |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Acorn Computers |
| Release date | 1995[1] |
| Operating system | RISC OS |
| CPU | 32 MHz ARM7500 |
| Memory | 4–132 MiB RAM |
| Dimensions |
|
| Successor | A7000+ |
| Related articles | RiscPC |
 | |
| Developer | Acorn Computers |
|---|---|
| Manufacturer | Acorn Computers, Castle Technology[2] |
| Release date | 1995[3] |
| Operating system | RISC OS |
| CPU | 48–56 MHz ARM7500FE |
| Memory | 8–136 MiB RAM |
| Dimensions |
|
| Successor | Phoebe, Iyonix PC, A9home |
| Related articles | RiscPC |
History
The A7000 was launched in 1995, featuring a 32 MHz ARM7500 processor.[1] The more advanced A7000+ was launched in 1997, featuring a 48 MHz ARM7500FE processor.[3] When Acorn Computers was broken up in 1998 Castle Technology bought the rights to continue A7000+ production.[6]
Specifications and technical details
| Acorn A7000 [7] | Acorn A7000+ [8] | Castle A7000+ | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CPU | ARM7500 @ 32 MHz | ARM7500FE @ 48 MHz | ARM7500FE @ 56 MHz | The FE in the ARM7500FE identifier indicates integrated floating point hardware. |
| Memory type | 4 MiB FPM | 8 MiB EDO | RAM mounted on motherboard. Additionally 1 SIMM slot, supporting an additional 128 MiB. | |
| Video subsystem | VIDC20 controller | Video controller integrated into ARM7500 core, display memory is shared with main memory. | ||
| Expansion | One Eurocard-sized Podule support in common with Archimedes-series machines. | One internal network card socket. | ||
| Case | One 3.5 inch bay, with floppy drive, one 5.25 inch bay for a CD-ROM drive. | Only one of a CD-ROM/DVD-ROM drive or a Eurocard Podule could be fitted. | ||
| Ports | RS-232 Serial, DB25 Parallel, PS/2 keyboard, PS/2 mouse, 3.5mm headphone audio out, DE15 VGA | 8P8C 10Base-T network (optional). | ||
| Dimensions | HxWxD: 102 × 357 × 283 mm | |||
| Operating system | RISC OS 3.60 | RISC OS 3.71. | RISC OS 4 is available as a replacement. Alternatively NetBSD[9] or ARM Linux (historically).[10] | |
Modifications
A user modification (dubbed the A7KP) to rehouse an A7000+ as a portable weighing 5 lb (2.3 kg) was seen in 2011.[11]
References
- Chris's Acorns - Acorn A7000
- "Acorn announces distribution deal with Castle Technology for RISC based products". Acorn Computers Ltd (Press release). Acorn Computers Ltd. 1998-10-12. Archived from the original on May 6, 1999. Retrieved 2011-01-06.
(October 12th 1998), Cambridge, UK-Acorn announced today that it has completed negotiations with Castle Technology for them to distribute Acorn products.
- Chris's Acorns - Acorn A7000+
- Enhancements and diversification - Online Media, Risc PC updates and handhelds (1994 to 1996) – Technical history of Acorn of RPC700 and A7000
- "The A7000" (PDF). Acorn in 1995. Beebug Limited. 1995. pp. 4–6. Retrieved 31 January 2021.
- Chris's Acorns - Castle A7000+
- Acorn Risc Technologies - A7000 Factsheet
- Acorn Clan Newsletter - A7000+
- NetBSD acorn/32 project page
- ARM Linux - Overview of Acorn Machines
- Heater, Brian (June 23, 2011). "The Acorn A7000+ portable mod is what your MacBook looks like in an alternate universe". Engadget. Retrieved February 27, 2012.
[Acorn's] late-period A7000+ desktop has now seen a successful second life at the hands of a British modder as the A7KP. The Acorn's innards have been stuffed into a five pound (relatively) portable setup.
External links
- Technical history of Acorn
- Exciting times - the StrongARM Risc PC and the A7000+ (1996 to 1997) – Technical history of Acorn of StrongARM and A7000+
- Chris's Acorns - Castle Technology
- Castle announce the A7000+ Odyssey
