Adenine deaminase
In enzymology, an adenine deaminase (EC 3.5.4.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
- adenine + H2O hypoxanthine + NH3
| adenine deaminase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
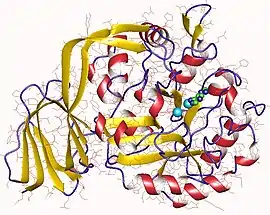 adenine deaminase monomer, Enterococcus | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 3.5.4.2 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9027-68-3 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are adenine and H2O, whereas its two products are hypoxanthine and NH3.
This enzyme belongs to the family of hydrolases, those acting on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, specifically in cyclic amidines. The systematic name of this enzyme class is adenine aminohydrolase. Other names in common use include adenase, adenine aminase, and ADase. This enzyme participates in purine metabolism.
Structural studies
As of late 2007, only one structure has been solved for this class of enzymes, with the PDB accession code 2ICS.
References
- Blauch M, Koch FC, Hane ME (1939). "A study of xanthine oxidase of rat blood". J. Biol. Chem. 130: 471–486.
- Heppel LA, Hurwitz J, Horecker BL (1957). "Adenine deaminase of Azotobacter vinelandii". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 (3): 630–633. doi:10.1021/ja01560a033.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
