Andermatt
Andermatt (Romansh: ![]() Ursera ) is a mountain village and municipality in the canton of Uri in Switzerland. At an altitude of 1437 meters above sea level, Andermatt is located at the center of the Saint-Gotthard Massif and the historical center cross of north-south and east-west traverses of Switzerland. It is some 28 km (17 mi) south of Altdorf, the capital of Uri.
Ursera ) is a mountain village and municipality in the canton of Uri in Switzerland. At an altitude of 1437 meters above sea level, Andermatt is located at the center of the Saint-Gotthard Massif and the historical center cross of north-south and east-west traverses of Switzerland. It is some 28 km (17 mi) south of Altdorf, the capital of Uri.
Andermatt | |
|---|---|
 Andermatt looking east towards the Oberalp Pass with cable car (to Gemsstock) bottom station in front and Rossbodenstock (2836m) in the back (8 Feb 2003) | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Andermatt 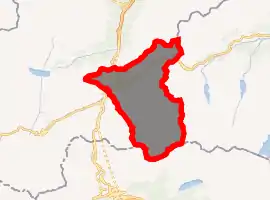
| |
 Andermatt 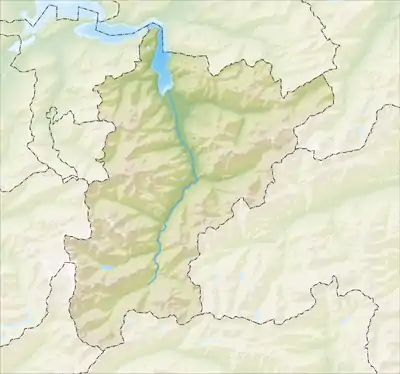 Andermatt | |
| Coordinates: 46°37′N 8°35′E | |
| Country | Switzerland |
| Canton | Uri |
| District | n.a. |
| Government | |
| • Executive | Gemeinderat with 5 members |
| • Mayor | Präsidentin Yvonne Baumann |
| • Parliament | none (Offene Dorfgemeinde) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 62.26 km2 (24.04 sq mi) |
| Elevation (Church) | 1,437 m (4,715 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 2,999 m (9,839 ft) |
| Lowest elevation (Schöllenen) | 1,289 m (4,229 ft) |
| Population (2018-12-31)[2] | |
| • Total | 1,390 |
| • Density | 22/km2 (58/sq mi) |
| Demonym(s) | German: Andermatter(in) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (Central European Time) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (Central European Summer Time) |
| Postal code(s) | 6490 |
| SFOS number | 1202 |
| Localities | Andermatt, Gurschen, Unteralp, Nätschen, Oberalp, Alp Rossboden |
| Surrounded by | Airolo (TI), Göschenen, Gurtnellen, Hospental, Tujetsch (GR) |
| Website | www SFSO statistics |
Geography


Andermatt is in the Urseren valley, on the headwaters of the river Reuss and surrounded by the Adula Alps. Immediately to the north of Andermatt, the Reuss flows through the steeply descending Schöllenen Gorge (or the Schöllenen) to Göschenen and further down the Reuss Valley to the north. It then flows, near Altdorf, into the Urnersee, part of Lake Lucerne. In the other three directions, the valley is linked by three Alpine passes: the Oberalp Pass (6,706 ft; 2,044 m.) to the east, the St Gotthard Pass (6,909 ft; 2,106 m.) to the south and the Furka Pass (7,992 ft; 2,436 m.) to the west.[3]
Andermatt has an area, as of 2006, of 62.2 km2 (24.0 sq mi). Of this area, 40.8% is used for agricultural purposes, while 5.5% is forested. Of the rest of the land, 1.7% is settled (buildings or roads) and the remainder (52%) is non-productive (rivers, glaciers or mountains).[4] In the 1993/97 land survey, 0.4% of the total land area was heavily forested, while 5.1% is covered in small trees and shrubbery. Of the agricultural land, 4.3% is used for orchards or vine crops and 36.5% is used for alpine pastures. Of the settled areas, 0.5% is covered with buildings, and 1.1% is transportation infrastructure. Of the unproductive areas, 0.5% is unproductive standing water (ponds or lakes), 1.0% is unproductive flowing water (rivers), 30.9% is too rocky for vegetation, and 19.7% is other unproductive land.[5]
Transport
Andermatt serves as a crossroads between southern Switzerland and the north as well as between eastern Switzerland (i.e. Graubünden/Grisons) and western Switzerland, (i.e. Valais, Bern and the Swiss Romande). The village is connected by three Alpine passes: the Oberalp Pass (6,706 ft; 2,044 m.) to the east connecting the Surselva in the canton of Graubünden, the St Gotthard Pass (6,909 ft; 2,106 m.) to the south connecting with the Valle Leventina in canton of Ticino, and the Furka Pass (7,992 ft; 2,436 m.) to the west connecting with the Obergoms in canton of Valais. To the north the steeply descending Schöllenen Gorge links Andermatt with Göschenen and is the location of the famous Devil's Bridge.[3]
Since the opening of the Schöllenen route, around 1200, Andermatt has been on the Gotthard route.
The town is served by a Matterhorn Gotthard Bahn (MGB) owned and operated railway station. The station is connected with Brig and Visp (Valais) and with the western terminus of the Rhaetian Railway at Disentis/Mustér (Grisons). There is also a very short branch line, the Schöllenenbahn, nowadays part of MGB, between Andermatt and Göschenen, at the northern end of the Gotthard Rail Tunnel, connecting with the Gotthard railway line.
History


Archaeological finds dating back to 4000 BC indicate that the Urseren was already populated in the Neolithic period. During Roman times this Alpine valley was probably inhabited by some Helvetic Celtic tribes. However, the origins of Andermatt can only be traced back to Alemannic tribes, the Walsers, who established settlements in the area, where the current town of Andermatt is situated.

The parish of Andermatt was not mentioned until 1203; it was held by the Benedictine Disentis Abbey. This first mention refers to it as de Prato. In 1290 it was mentioned as A der Matte.[6] In 1649, with the emergence of an independent Swiss Confederation, the ecclesiastical rights of the Disentis monastery were revoked in favour of civil legislation.
In the Flight of the Earls, Irish earls lost a fortune in gold at the Devil's Bridge crossing ravine on St Patrick's Day 1608. It has never been recovered and is known as the Lost Treasure of the St Gotthard Pass.[7]
Nearby Schöllenen Gorge is the site of a memorial commemorating the 1799 campaign of the Russian general Alexander Suvorov.
Between 1818-1831 the nearby St Gotthard Pass was made accessible to stagecoaches. As the last resort before the pass, Andermatt flourished economically and became a popular spa town.
The opening, in 1881, of the St Gotthard railway tunnel, however, reversed its fortunes as the tunnel runs immediately beneath the town, connecting the Central Swiss town Göschenen with Airolo in Ticino. Some Andermattians who worked on the tunnel were killed during its construction. A strike by the tunnel workers, furthermore, was put down by military force, killing a further four workers.
Since 1885, Andermatt has been a garrison town of the Swiss Federal Army. Here the infrastructure for the High Command of the Swiss Federal Army in an event of war was built. Today it is location of a Training Centre of the Swiss army.
Plans to build a series of reservoirs in the valley of Andermatt, the Urseren, encountered fierce resistance by the locals in 1946 and were abandoned four years later.[8] A huge reservoir was built instead in the next valley, the Göschenertal.[9]
Several avalanches, in particular in the winter of 1951 and 1975 have caused havoc in some residential areas of Andermatt, killing the inhabitants of the houses affected.

By the 1930s the town's income from tourism had seriously declined, and many of the Ursental's hotels were abandoned or changed use. The Grand Hotel Bellevue, which was built by the aristocratic Müller family from neighbouring Hospental (who at one time or another owned many other hotels nearby including the Hotel Furkablick and Hotel Furka Passhöhe - as well as hotels in Flüelen, Alpnachstad, Herisau and Neuchâtel) was converted in the 1970s into apartments, but by 1990 had been abandoned and was demolished with explosives. By the turn of the 21st century, as an alternative to the expensive skiing resorts in the Grisons (Graubünden) at St Moritz and Gstaad, Andermatt's fortunes again revived and the town has seen considerable expansion and is currently undergoing much speculative building.
Demographics
Andermatt has a population (as of 31 December 2019) of 1,433.[10] As of 2007, 10.0% of the population was made up of foreign nationals. Over the last 10 years the population has decreased at a rate of -8.8%. Most of the population (as of 2000) speaks German (95.2%), with Portuguese being second most common (1.0%) and Italian being third (0.9%).[4] As of 2007 the gender distribution of the population was 50.8% male and 49.2% female.[11]
In Andermatt about 75.2% of the population (between age 25-64) have completed either non-mandatory upper secondary education or additional higher education (either university or a Fachhochschule).[4]
Andermatt has an unemployment rate of 0.9%. As of 2005, there were 51 people employed in the primary economic sector and about 22 businesses involved in this sector. 90 people are employed in the secondary sector and there are 13 businesses in this sector. 599 people are employed in the tertiary sector, with 78 businesses in this sector.[4]
| Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1799 | 605 |
| 1850 | 677 |
| 1900 | 818 |
| 1950 | 1,231 |
| 1970 | 1,589 |
| 2000 | 1,282 |
| 2008 | 1,242 |
| 2010 | 1,304 |
| 2014 | 1,408 |
Climate
Between 1961 and 1990 Andermatt had an average of 147.3 days of rain per year and on average received 1,422 mm (56.0 in) of precipitation. The wettest month was April, with an average of 135 mm (5.3 in) of precipitation and an average of 14 days with precipitation. The month with the most days of precipitation was May, with an average of 14.1, but with only 128 mm (5.0 in) of precipitation. The driest month of the year was February with an average of 106 mm (4.2 in) of precipitation over 14 days.[12] According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Andermatt has a Marine West Coast climate, abbreviated "Cfb" on climate maps.[13]
| Climate data for Andermatt (1981-2010) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −4.7 (23.5) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
−0.4 (31.3) |
3.2 (37.8) |
7.9 (46.2) |
10.9 (51.6) |
13.1 (55.6) |
12.8 (55.0) |
9.5 (49.1) |
6.0 (42.8) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−3.5 (25.7) |
4.2 (39.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −8.1 (17.4) |
−7.9 (17.8) |
−4.2 (24.4) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
3.8 (38.8) |
6.5 (43.7) |
8.8 (47.8) |
8.5 (47.3) |
5.5 (41.9) |
2.3 (36.1) |
−3.0 (26.6) |
−6.6 (20.1) |
0.4 (32.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 121 (4.8) |
115 (4.5) |
122 (4.8) |
125 (4.9) |
146 (5.7) |
132 (5.2) |
126 (5.0) |
132 (5.2) |
148 (5.8) |
124 (4.9) |
144 (5.7) |
116 (4.6) |
1,552 (61.1) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 114.8 (45.2) |
113.9 (44.8) |
94.7 (37.3) |
71.2 (28.0) |
24.6 (9.7) |
2.2 (0.9) |
0.1 (0.0) |
0 (0) |
2.1 (0.8) |
22 (8.7) |
85.9 (33.8) |
102.5 (40.4) |
634 (250) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 11.9 | 11.0 | 13.4 | 13.1 | 13.7 | 13.4 | 12.6 | 12.4 | 10.6 | 10.5 | 11.8 | 12.2 | 146.6 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 1.0 cm) | 11.8 | 11.3 | 11.1 | 7.7 | 2.5 | 0.3 | 0 | 0 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 8.4 | 12.2 | 68.3 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 76 | 75 | 75 | 74 | 73 | 75 | 75 | 76 | 77 | 74 | 77 | 77 | 75 |
| Source: MeteoSwiss [14] | |||||||||||||
Skiing
Andermatt has two main ski areas in the winter. Nätschen is a mountain located on the north-east side of Andermatt. Gemsstock is a mountain located on the southern side of Andermatt. Both areas are accessible by ski lifts running up from the village, and have valley runs which are open until around mid-March. Additionally, Nätschen is accessible by the railway. There are plans to overhaul the ski areas, and connect Nätschen with the neighbouring slopes of Oberalp, which are currently only accessible by train, however they are a part of the whole ski area.
Andermatt's mountains are popular for their off-piste, deep snow characteristics.
Future

Orascom Hotels and Development are expanding Andermatt village into a large resort, doubling the size of Andermatt. These plans will include having:
- 6 new 4-5 star hotels
- Just under 500 new apartments
- Up to 30 new villas
- An 18-hole golf course
- A new leisure centre
- Over twice the amount of ski slopes currently available
Media
The gas station Aurora, near the Gemsstock departure, appears in the James Bond movie Goldfinger. Bond fills up his Aston Martin there after a car chase on the Furka pass.
In November 2012 Andermatt appeared on the British television series The Gadget Show, where presenters Jason Bradbury and Pollyanna Woodward were testing electric bicycles, scooters, and several mobile phone photo editing applications, on the hills of Nätschen.[15]
Notable people
- Felix Maria Diogg (1762–1834), Classicism portrait painter
- Bernhard Russi (born August 20, 1948), ski champion and Winter Olympia Gold medallist
Gallery
 A view of Andermatt from Nätschen looking west through the Urseren towards Hospental in front below the Pizzo d'Orsino/Winterhorn (2661 m) and the Furka Pass (2429 m) in the back (August 2007)
A view of Andermatt from Nätschen looking west through the Urseren towards Hospental in front below the Pizzo d'Orsino/Winterhorn (2661 m) and the Furka Pass (2429 m) in the back (August 2007) The Unteralpreuss flowing through Andermatt
The Unteralpreuss flowing through Andermatt Andermatt from Pazolastock/Piz Nurschalas (2739 m) looking west through the Urseren towards the Bernese Alps with the Finsteraarhorn (4274 m) in the middle
Andermatt from Pazolastock/Piz Nurschalas (2739 m) looking west through the Urseren towards the Bernese Alps with the Finsteraarhorn (4274 m) in the middle The Unteralpreuss flowing through Andermatt
The Unteralpreuss flowing through Andermatt Andermatt by Eduard Spelterini, ca. 1903
Andermatt by Eduard Spelterini, ca. 1903
References
- "Arealstatistik Standard - Gemeinden nach 4 Hauptbereichen". Federal Statistical Office. Retrieved 13 January 2019.
- https://www.pxweb.bfs.admin.ch/pxweb/fr/px-x-0102020000_201/-/px-x-0102020000_201.px/table/tableViewLayout2/?rxid=c5985c8d-66cd-446c-9a07-d8cc07276160; retrieved: 2 June 2020.
- "4 - Map sheet 4 SE" (Map). Andermat (2014 ed.). 1:200'000. National Map 1:200'000. Wabern, Switzerland: Federal Office of Topography – swisstopo. ISBN 978-3-302-00004-6. Retrieved 2017-07-05 – via map.geo.admin.ch.
- Swiss Federal Statistical Office Archived 2016-01-05 at the Wayback Machine accessed 08-Sep-2009
- Canton Uri - Ground use statistics Archived 2011-07-07 at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 8 September 2009
- Andermatt in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Hume to unveil Swiss monument to Irish earls Archived 2011-07-10 at the Wayback Machine The Epoch Times, February 28-March 12, 2008
- «Krawallnacht» rettet Andermatt vor dem Untergang |Neue Zürcher Zeitung, February 15, 2016
- Fritz Ringwald, Das Kraftwerk Göschenen : Geographische Studie über die Nutzbarmachung der Reuss, Geographica Helvetica 18 no. 4, 1963, pp. 305-314
- "Ständige und nichtständige Wohnbevölkerung nach institutionellen Gliederungen, Geburtsort und Staatsangehörigkeit". bfs.admin.ch (in German). Swiss Federal Statistical Office - STAT-TAB. 31 December 2019. Retrieved 6 October 2020.
- Uri Population statistics Archived 2011-07-07 at the Wayback Machine (in German) accessed 8 September 2009
- "Temperature and Precipitation Average Values-Table, 1961-1990" (in German, French, and Italian). Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology - MeteoSwiss. Archived from the original on 27 June 2009. Retrieved 8 May 2009..
- Climate Summary for Andermatt
- "Climate Norm Value Tables". Climate diagrams and normals from Swiss measuring stations. Federal Office of Meteorology and Climatology (MeteoSwiss). Archived from the original on 14 May 2013. Retrieved 23 January 2013. The weather station elevation is 1442 meters above sea level.
- "The Gadget Show - Switzerland". 8 January 2013
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Andermatt. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Andermatt. |
- Andermatt in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
