Anterior clinoid process
In the sphenoid bone, the posterior border, smooth and rounded, is received into the lateral fissure of the brain; the medial end of this border forms the anterior clinoid process, which gives attachment to the tentorium cerebelli;[1] it is sometimes joined to the middle clinoid process by a spicule of bone, and when this occurs the termination of the groove for the internal carotid artery is converted into a foramen (carotico-clinoid).
| Anterior clinoid process | |
|---|---|
 Upper and posterior surfaces of sphenoid bone (anterior clinoid process visible at top left) | |
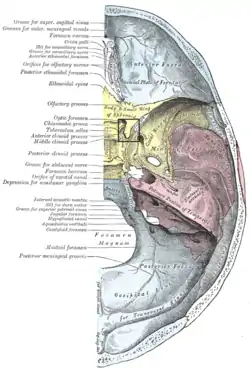 Upper surface of the base of the skull (label for anterior clinoid process visible at center left. Sphenoid bone is yellow.) | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Processus clinoideus anterior |
| TA98 | A02.1.05.022 |
| TA2 | 607 |
| FMA | 54693 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
Etymology
The anterior and posterior clinoid processes surround the sella turcica like the four corners of a four poster bed. Cline is Greek for bed. –oid, as usual, indicates a similarity to.[1] The term may also come from the Greek root klinein or the Latin clinare, both meaning "sloped" as in "inclined".
Additional images
 Anterior clinoid process
Anterior clinoid process
Petroclinoid ligament
The petroclinoid ligament is a fold of dura mater. It extends between the posterior clinoid process and anterior clinoid process and the petrosal part of the temporal bone of the skull.
See posterior clinoid process page for full information on this ligament.
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 151 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- "Anterior clinoid process of the sphenoid bone". AnatomyExpert. Retrieved 20 March 2013.
External links
- "Anatomy diagram: 34257.000-2". Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator. Elsevier. Archived from the original on 2013-06-22.
- Anatomy photo:22:os-0910 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center