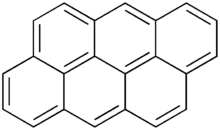
Anthanthrene
Anthanthrene is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon.[1] According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer, as of 2006 there was "limited evidence in experimental animals" that it is a carcinogen.[2]
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Dibenzo[def,mno]chrysene | |
| Other names
Anthanthren; Dibenzo[cd,jk]pyrene
Hexacyclo[8.8.4.03,21.06,22.012,20.015,19]docosa-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17,19,21-hendecaene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.351 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C22H12 | |
| Molar mass | 276.33 g/mol |
| Appearance | Golden yellow solid |
| Melting point | 261 °C (502 °F; 534 K) |
| Insoluble | |
| -204.2·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
References
- Clar, E. (1964). Polycyclic Hydrocarbons. New York: Academic Press.
- "PAHs: IARC Working Group, 2006". Carcinogenic Risk In Occupational Settings.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
