Basuto Gun War
The Gun War, also known as the Basuto War, was an 1880-1881 conflict in the British territory of Basutoland (present-day Lesotho) in Southern Africa, fought between Cape Colony forces and nationalist Basotho chiefs over the right of the Basotho people to bear arms. Although a military stalemate, the final settlement favored the Basotho and led to the splitting of Basutoland from the Cape Colony.
| Gun War | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the South African Wars (1879-1915) | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Basuto Nationalists | |||||||
Background
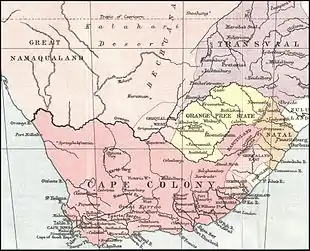
Basutoland—home of the Basotho people—had been under the nominal control of the Cape Colony (of the British Empire) since 1871 (it was a British protectorate from 1868 until 1871), but the territory remained essentially autonomous in the early years of colonial rule, with traditional Basotho authorities wielding effective power. Only in the late 1870s did Cape authorities attempt to consolidate power over the region and enforce its laws. Basutoland, an independent state until 1868, chafed under the new restrictions and attempts to reduce the authority of its chiefs.
Matters came to a head in 1879, when Governor Henry Bartle Frere reserved part of Basutoland for white settlement and demanded that all natives surrender their firearms to Cape authorities under the 1879 Peace Protection Act.
Outbreak of fighting
The Cape government of Sir John Gordon Sprigg set April 1880 as the date for surrendering weapons. Although some Basotho with great reluctance were willing to surrender their guns, the majority refused; government attempts to enforce the law brought fighting by September.
Within months, most Basotho chiefs were in open rebellion. Colonial Cape forces sent to put down the rebellion suffered heavy casualties, as the Basotho had obtained serviceable firearms from the Orange Free State and enjoyed a natural defensive advantage in their country's mountainous terrain. The rebels relied primarily on guerrilla warfare, ambushing isolated units to negate the British/Cape superiority in firepower. In October, Basotho forces ambushed a mounted column of colonial cavalry (1st Regiment, Cape Mounted Yeomanry) at Qalabani near Mafeteng), killing 39. The defeat of an experienced and well-armed cavalry column discouraged Cape authorities.[1]
Resolution
The costs of the war when added to the earlier war with the Xhosa and renewed troubles in the Transkei were dragging the Cape Colony towards bankruptcy. The war was also becoming increasingly unpopular, and the Sprigg government was replaced by the Thomas Scanlen government.
A peace treaty was signed with Basotho chiefs in 1881, in which colonial authorities conceded most of the points in dispute. The land remained in Basotho hands and the nation enjoyed unrestricted access to firearms in exchange for a national one-time indemnity of 5000 cattle.
However, unrest continued and it quickly became clear that Cape Town could not control the territory. In 1884, the British government returned the territory to Crown colony status as Basutoland, granting internal self-government in the process. With effective power once again firmly with the chiefs, the conflict subsided.[2]
Notes
- "BASUTOLAND ROLL OF HONOUR 1851 - 1881 - South African Military History Society - Journal". samilitaryhistory.org.
- "Basuto Gun War". Archived from the original on 2011-07-06.
References
- Dutton, Roy (2010). Forgotten heroes : Zulu & Basuto Wars : including complete medal roll 1877-8-9. Prenton [England]: InfoDial. ISBN 9780955655449.