Batcher odd–even mergesort
Batcher's odd–even mergesort is a generic construction devised by Ken Batcher for sorting networks of size O(n (log n)2) and depth O((log n)2), where n is the number of items to be sorted. Although it is not asymptotically optimal, Knuth concluded in 1998, with respect to the AKS network that "Batcher's method is much better, unless n exceeds the total memory capacity of all computers on earth!"[1]
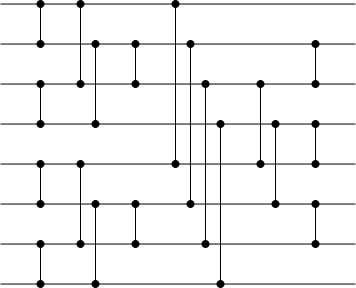 Visualization of the odd–even mergesort network with eight inputs | |
| Class | Sorting algorithm |
|---|---|
| Data structure | Array |
| Worst-case performance | parallel time |
| Best-case performance | parallel time |
| Average performance | parallel time |
| Worst-case space complexity | non-parallel time |
It is popularized by the second GPU Gems book,[2] as an easy way of doing reasonably efficient sorts on graphics-processing hardware.
Pseudocode
Various recursive and iterative schemes are possible to calculate the indices of the elements to be compared and sorted. This is one iterative technique to generate the indices for sorting n elements:
# note: the input sequence is indexed from 0 to (n-1)
for p = 1, 2, 4, 8, ... # as long as p < n
for k = p, p/2, p/4, p/8, ... # as long as k >= 1
for j = mod(k,p) to (n-1-k) with a step size of 2k
for i = 0 to k-1 with a step size of 1
if floor((i+j) / (p*2)) == floor((i+j+k) / (p*2))
compare and sort elements (i+j) and (i+j+k)
Non-recursive calculation of the partner node index is also possible.[3]
See also
References
- D.E. Knuth. The Art of Computer Programming, Volume 3: Sorting and Searching, Second Edition. Addison-Wesley, 1998. ISBN 0-201-89685-0. Section 5.3.4: Networks for Sorting, pp. 219–247.
- https://developer.nvidia.com/gpugems/GPUGems2/gpugems2_chapter46.html
- "Sorting network from Batcher's Odd-Even merge: partner calculation". Renat Bekbolatov. Retrieved 7 May 2015.
External links
- Odd–even mergesort at fh-flensburg.de
- Odd-even mergesort network generator Interactive Batcher's Odd-Even merge-based sorting network generator.