Cartesian tree
In computer science, a Cartesian tree is a binary tree derived from a sequence of numbers; it can be uniquely defined from the properties that it is heap-ordered and that a symmetric (in-order) traversal of the tree returns the original sequence. Introduced by Vuillemin (1980) in the context of geometric range searching data structures, Cartesian trees have also been used in the definition of the treap and randomized binary search tree data structures for binary search problems. The Cartesian tree for a sequence may be constructed in linear time using a stack-based algorithm for finding all nearest smaller values in a sequence.
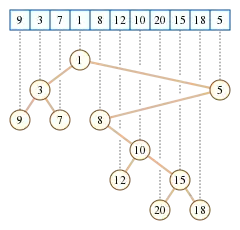
Definition
The Cartesian tree for a sequence of distinct numbers can be uniquely defined by the following properties:
- The Cartesian tree for a sequence has one node for each number in the sequence. Each node is associated with a single sequence value.
- A symmetric (in-order) traversal of the tree results in the original sequence. That is, the left subtree consists of the values earlier than the root in the sequence order, while the right subtree consists of the values later than the root, and a similar ordering constraint holds at each lower node of the tree.
- The tree has the heap property: the parent of any non-root node has a smaller value than the node itself.[1]
Based on the heap property, the root of the tree must be the smallest number in the sequence. From this, the tree itself may also be defined recursively: the root is the minimum value of the sequence, and the left and right subtrees are the Cartesian trees for the subsequences to the left and right of the root value. Therefore, the three properties above uniquely define the Cartesian tree.
If a sequence of numbers contains repetitions, the Cartesian tree may be defined by determining a consistent tie-breaking rule (for instance, determining that the first of two equal elements is treated as the smaller of the two) before applying the above rules.
An example of a Cartesian tree is shown in the figure above.
Range searching and lowest common ancestors
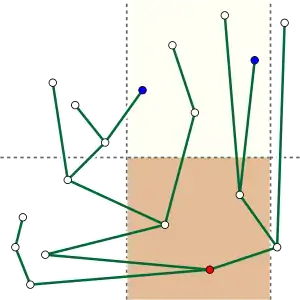
Cartesian trees may be used as part of an efficient data structure for range minimum queries, a range searching problem involving queries that ask for the minimum value in a contiguous subsequence of the original sequence.[2] In a Cartesian tree, this minimum value may be found at the lowest common ancestor of the leftmost and rightmost values in the subsequence. For instance, in the subsequence (12,10,20,15) of the sequence shown in the first illustration, the minimum value of the subsequence (10) forms the lowest common ancestor of the leftmost and rightmost values (12 and 15). Because lowest common ancestors may be found in constant time per query, using a data structure that takes linear space to store and that may be constructed in linear time,[3] the same bounds hold for the range minimization problem.
Bender & Farach-Colton (2000) reversed this relationship between the two data structure problems by showing that lowest common ancestors in an input tree could be solved efficiently applying a non-tree-based technique for range minimization. Their data structure uses an Euler tour technique to transform the input tree into a sequence and then finds range minima in the resulting sequence. The sequence resulting from this transformation has a special form (adjacent numbers, representing heights of adjacent nodes in the tree, differ by ±1) which they take advantage of in their data structure; to solve the range minimization problem for sequences that do not have this special form, they use Cartesian trees to transform the range minimization problem into a lowest common ancestor problem, and then apply the Euler tour technique to transform the problem again into one of range minimization for sequences with this special form.
The same range minimization problem may also be given an alternative interpretation in terms of two dimensional range searching. A collection of finitely many points in the Cartesian plane may be used to form a Cartesian tree, by sorting the points by their x-coordinates and using the y-coordinates in this order as the sequence of values from which this tree is formed. If S is the subset of the input points within some vertical slab defined by the inequalities L ≤ x ≤ R, p is the leftmost point in S (the one with minimum x-coordinate), and q is the rightmost point in S (the one with maximum x-coordinate) then the lowest common ancestor of p and q in the Cartesian tree is the bottommost point in the slab. A three-sided range query, in which the task is to list all points within a region bounded by the three inequalities L ≤ x ≤ R and y ≤ T, may be answered by finding this bottommost point b, comparing its y-coordinate to T, and (if the point lies within the three-sided region) continuing recursively in the two slabs bounded between p and b and between b and q. In this way, after the leftmost and rightmost points in the slab are identified, all points within the three-sided region may be listed in constant time per point.[4]
The same construction, of lowest common ancestors in a Cartesian tree, makes it possible to construct a data structure with linear space that allows the distances between pairs of points in any ultrametric space to be queried in constant time per query. The distance within an ultrametric is the same as the minimax path weight in the minimum spanning tree of the metric.[5] From the minimum spanning tree, one can construct a Cartesian tree, the root node of which represents the heaviest edge of the minimum spanning tree. Removing this edge partitions the minimum spanning tree into two subtrees, and Cartesian trees recursively constructed for these two subtrees form the children of the root node of the Cartesian tree. The leaves of the Cartesian tree represent points of the metric space, and the lowest common ancestor of two leaves in the Cartesian tree is the heaviest edge between those two points in the minimum spanning tree, which has weight equal to the distance between the two points. Once the minimum spanning tree has been found and its edge weights sorted, the Cartesian tree may be constructed in linear time.[6]
Treaps
Because a Cartesian tree is a binary tree, it is natural to use it as a binary search tree for an ordered sequence of values. However, defining a Cartesian tree based on the same values that form the search keys of a binary search tree does not work well: the Cartesian tree of a sorted sequence is just a path, rooted at its leftmost endpoint, and binary searching in this tree degenerates to sequential search in the path. However, it is possible to generate more-balanced search trees by generating priority values for each search key that are different than the key itself, sorting the inputs by their key values, and using the corresponding sequence of priorities to generate a Cartesian tree. This construction may equivalently be viewed in the geometric framework described above, in which the x-coordinates of a set of points are the search keys and the y-coordinates are the priorities.
This idea was applied by Seidel & Aragon (1996), who suggested the use of random numbers as priorities. The data structure resulting from this random choice is called a treap, due to its combination of binary search tree and binary heap features. An insertion into a treap may be performed by inserting the new key as a leaf of an existing tree, choosing a priority for it, and then performing tree rotation operations along a path from the node to the root of the tree to repair any violations of the heap property caused by this insertion; a deletion may similarly be performed by a constant amount of change to the tree followed by a sequence of rotations along a single path in the tree.
If the priorities of each key are chosen randomly and independently once whenever the key is inserted into the tree, the resulting Cartesian tree will have the same properties as a random binary search tree, a tree computed by inserting the keys in a randomly chosen permutation starting from an empty tree, with each insertion leaving the previous tree structure unchanged and inserting the new node as a leaf of the tree. Random binary search trees had been studied for much longer, and are known to behave well as search trees (they have logarithmic depth with high probability); the same good behavior carries over to treaps. It is also possible, as suggested by Aragon and Seidel, to reprioritize frequently-accessed nodes, causing them to move towards the root of the treap and speeding up future accesses for the same keys.
Efficient construction
A Cartesian tree may be constructed in linear time from its input sequence. One method is to simply process the sequence values in left-to-right order, maintaining the Cartesian tree of the nodes processed so far, in a structure that allows both upwards and downwards traversal of the tree. To process each new value x, start at the node representing the value prior to x in the sequence and follow the path from this node to the root of the tree until finding a value y smaller than x. The node x becomes the right child of y, and the previous right child of y becomes the new left child of x. The total time for this procedure is linear, because the time spent searching for the parent y of each new node x can be charged against the number of nodes that are removed from the rightmost path in the tree.[4]
An alternative linear-time construction algorithm is based on the all nearest smaller values problem. In the input sequence, one may define the left neighbor of a value x to be the value that occurs prior to x, is smaller than x, and is closer in position to x than any other smaller value. The right neighbor is defined symmetrically. The sequence of left neighbors may be found by an algorithm that maintains a stack containing a subsequence of the input. For each new sequence value x, the stack is popped until it is empty or its top element is smaller than x, and then x is pushed onto the stack. The left neighbor of x is the top element at the time x is pushed. The right neighbors may be found by applying the same stack algorithm to the reverse of the sequence. The parent of x in the Cartesian tree is either the left neighbor of x or the right neighbor of x, whichever exists and has a larger value. The left and right neighbors may also be constructed efficiently by parallel algorithms, so this formulation may be used to develop efficient parallel algorithms for Cartesian tree construction.[7]
Another linear-time algorithm for Cartesian tree construction is based on divide-and-conquer. In particular, the algorithm recursively constructs the tree on each half of the input, and then merges the two trees by taking the right spine of the left tree and left spine of the right tree (both of which are paths whose root-to-leaf order sorts their values from smallest to largest) and performs a standard merging operation, replacing these two paths in two trees by a single path that contains the same nodes. In the merged path, the successor in the sorted order of each node from the left tree is placed in its right child, and the successor of each node from the right tree is placed in its left child, the same position that was previously used for its successor in the spine. The left children of nodes from the left tree and right children of nodes from the right tree are left unchanged. The algorithm is also parallelizable since on each level of recursion, each of the two sub-problems can be computed in parallel, and the merging operation can be efficiently parallelized as well.[8]
Application in sorting
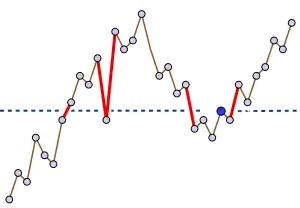
Levcopoulos & Petersson (1989) describe a sorting algorithm based on Cartesian trees. They describe the algorithm as based on a tree with the maximum at the root, but it may be modified straightforwardly to support a Cartesian tree with the convention that the minimum value is at the root. For consistency, it is this modified version of the algorithm that is described below.
The Levcopoulos–Petersson algorithm can be viewed as a version of selection sort or heap sort that maintains a priority queue of candidate minima, and that at each step finds and removes the minimum value in this queue, moving this value to the end of an output sequence. In their algorithm, the priority queue consists only of elements whose parent in the Cartesian tree has already been found and removed. Thus, the algorithm consists of the following steps:
- Construct a Cartesian tree for the input sequence
- Initialize a priority queue, initially containing only the tree root
- While the priority queue is non-empty:
- Find and remove the minimum value x in the priority queue
- Add x to the output sequence
- Add the Cartesian tree children of x to the priority queue
As Levcopoulos and Petersson show, for input sequences that are already nearly sorted, the size of the priority queue will remain small, allowing this method to take advantage of the nearly-sorted input and run more quickly. Specifically, the worst-case running time of this algorithm is O(n log k), where k is the average, over all values x in the sequence, of the number of consecutive pairs of sequence values that bracket x. They also prove a lower bound stating that, for any n and k = ω(1), any comparison-based sorting algorithm must use Ω(n log k) comparisons for some inputs.
History
Cartesian trees were introduced and named by Vuillemin (1980). The name is derived from the Cartesian coordinate system for the plane: in Vuillemin's version of this structure, as in the two-dimensional range searching application discussed above, a Cartesian tree for a point set has the sorted order of the points by their x-coordinates as its symmetric traversal order, and it has the heap property according to the y-coordinates of the points. Gabow, Bentley & Tarjan (1984) and subsequent authors followed the definition here in which a Cartesian tree is defined from a sequence; this change generalizes the geometric setting of Vuillemin to allow sequences other than the sorted order of x-coordinates, and allows the Cartesian tree to be applied to non-geometric problems as well.
Notes
- In some references, the ordering is reversed, so the parent of any node always has a larger value and the root node holds the maximum value.
- Gabow, Bentley & Tarjan (1984); Bender & Farach-Colton (2000).
- Harel & Tarjan (1984); Schieber & Vishkin (1988).
- Gabow, Bentley & Tarjan (1984).
- Hu (1961); Leclerc (1981)
- Demaine, Landau & Weimann (2009).
- Berkman, Schieber & Vishkin (1993).
- Shun & Blelloch (2014).
References
- Bender, Michael A.; Farach-Colton, Martin (2000), "The LCA problem revisited", Proceedings of the 4th Latin American Symposium on Theoretical Informatics, Springer-Verlag, Lecture Notes in Computer Science 1776, pp. 88–94.
- Berkman, Omer; Schieber, Baruch; Vishkin, Uzi (1993), "Optimal doubly logarithmic parallel algorithms based on finding all nearest smaller values", Journal of Algorithms, 14 (3): 344–370, doi:10.1006/jagm.1993.1018.
- Demaine, Erik D.; Landau, Gad M.; Weimann, Oren (2009), "On Cartesian trees and range minimum queries", Automata, Languages and Programming, 36th International Colloquium, ICALP 2009, Rhodes, Greece, July 5-12, 2009, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 5555, pp. 341–353, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-02927-1_29, hdl:1721.1/61963, ISBN 978-3-642-02926-4.
- Fischer, Johannes; Heun, Volker (2006), "Theoretical and Practical Improvements on the RMQ-Problem, with Applications to LCA and LCE", Proceedings of the 17th Annual Symposium on Combinatorial Pattern Matching, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 4009, Springer-Verlag, pp. 36–48, doi:10.1007/11780441_5, ISBN 978-3-540-35455-0
- Fischer, Johannes; Heun, Volker (2007), "A New Succinct Representation of RMQ-Information and Improvements in the Enhanced Suffix Array.", Proceedings of the International Symposium on Combinatorics, Algorithms, Probabilistic and Experimental Methodologies, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 4614, Springer-Verlag, pp. 459–470, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-74450-4_41, ISBN 978-3-540-74449-8
- Gabow, Harold N.; Bentley, Jon Louis; Tarjan, Robert E. (1984), "Scaling and related techniques for geometry problems", STOC '84: Proc. 16th ACM Symp. Theory of Computing, New York, NY, USA: ACM, pp. 135–143, doi:10.1145/800057.808675, ISBN 0-89791-133-4.
- Harel, Dov; Tarjan, Robert E. (1984), "Fast algorithms for finding nearest common ancestors", SIAM Journal on Computing, 13 (2): 338–355, doi:10.1137/0213024.
- Hu, T. C. (1961), "The maximum capacity route problem", Operations Research, 9 (6): 898–900, doi:10.1287/opre.9.6.898, JSTOR 167055.
- Leclerc, Bruno (1981), "Description combinatoire des ultramétriques", Centre de Mathématique Sociale. École Pratique des Hautes Études. Mathématiques et Sciences Humaines (in French) (73): 5–37, 127, MR 0623034.
- Levcopoulos, Christos; Petersson, Ola (1989), "Heapsort - Adapted for Presorted Files", WADS '89: Proceedings of the Workshop on Algorithms and Data Structures, Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 382, London, UK: Springer-Verlag, pp. 499–509, doi:10.1007/3-540-51542-9_41.
- Seidel, Raimund; Aragon, Cecilia R. (1996), "Randomized Search Trees", Algorithmica, 16 (4/5): 464–497, doi:10.1007/s004539900061.
- Schieber, Baruch; Vishkin, Uzi (1988), "On finding lowest common ancestors: simplification and parallelization", SIAM Journal on Computing, 17 (6): 1253–1262, doi:10.1137/0217079.
- Shun, Julian; Blelloch, Guy E. (2014), "A Simple Parallel Cartesian Tree Algorithm and its Application to Parallel Suffix Tree Construction", ACM Transactions on Parallel Computing, 1: 1–20, doi:10.1145/2661653.
- Vuillemin, Jean (1980), "A unifying look at data structures", Communications of the ACM, New York, NY, USA: ACM, 23 (4): 229–239, doi:10.1145/358841.358852.
