Battle of Glasgow, Missouri
The Battle of Glasgow was fought on October 15, 1864, in and near Glasgow, Missouri as part of Price's Raid during the American Civil War. In late 1864, Confederate leadership in the Trans-Mississippi Theater planned a campaign into the state of Missouri, in hopes of drawing Union troops from more important theaters east of the Mississippi River. Major General Sterling Price commanded the expedition, and initially hoped to capture St. Louis, although an early defeat at the Battle of Pilot Knob led him to abandon this plan. After the strength of the Union garrison at Jefferson City convinced Price to cancel a planned attempt to capture the place, he led his army into the pro-Confederate region of Little Dixie, where recruiting efforts were successful.
| Battle of Glasgow | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Trans-Mississippi Theater of the American Civil War | |||||||
 The route of Price's Raid - top left, in red | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Chester Harding, Jr. |
John Bullock Clark Jr. Joseph O. Shelby | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 550–800 | c. 1,825 | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 43 killed or wounded, over 600 paroled | c. 50 | ||||||
However, many of these new recruits were unarmed. After learning of a Union weapons cache at Glasgow, Price sent Brigadier General John B. Clark Jr. with two brigades on a side raid to capture it. The Union garrison of Glasgow was commanded by Colonel Chester Harding, and was mostly composed of militia and men of the 43rd Missouri Infantry Regiment. At 05:00 on October 15, Confederate artillery opened fire on the Union position, although the main attack did not begin until about 08:00. Harding's men were driven back into the town itself, and surrendered at 13:30 after burning 50,000 rations to prevent them from falling into Confederate hands. Clark's men paroled the Union soldiers, captured 1,000 overcoats and 1,200 weapons, and burned a steamboat. The Confederate column rejoined Price's main army the next day. On October 23, the Confederates were decisively defeated at the Battle of Westport. Price's men retreated, but were harried for much of the way by Union pursuit; the retreat eventually reached Texas, although the pursuit did not follow that far.
Context
At the start of the American Civil War in 1861, the state of Missouri was a slave state, but did not secede. However, the state was politically divided: Governor Claiborne Fox Jackson and the Missouri State Guard (MSG) supported secession and the Confederate States of America, while Brigadier General Nathaniel Lyon and the Union Army supported the United States and opposed secession.[1] Under Major General Sterling Price, the MSG defeated Union armies at the battles of Wilson's Creek and Lexington in 1861, but by the end of the year, Price and the MSG were restricted to the southwestern portion of the state. Meanwhile, Jackson and a portion of the state legislature voted to secede and join the Confederate States of America, while another element of the legislature voted to reject secession, essentially giving the state two governments.[2] In March 1862, a Confederate defeat at the Battle of Pea Ridge in Arkansas gave the Union control of Missouri,[3] and Confederate activity in the state was largely restricted to guerrilla warfare and raids throughout 1862 and 1863.[4]
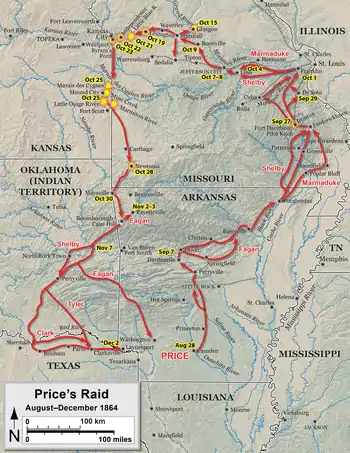
By the beginning of September 1864, events in the eastern United States, especially the Confederate defeat in the Atlanta campaign, gave Abraham Lincoln, who supported continuing the war, an edge in the 1864 United States presidential election over George B. McClellan, who favored ending the war. At this point, the Confederacy had very little chance of winning the war.[5] Meanwhile, in the Trans-Mississippi Theater, the Confederates had defeated Union attackers during the Red River campaign in Louisiana, which took place from March through May. As events east of the Mississippi River turned against the Confederates, General Edmund Kirby Smith, Confederate commander of the Trans-Mississippi Department, was ordered to transfer the infantry under his command to the fighting in the Eastern and Western Theaters. However, this proved to be impossible, as the Union Navy controlled the Mississippi River, preventing a large scale crossing. Despite having limited resources for an offensive, Smith decided that an attack designed to divert Union troops from the principal theaters of combat would have an equivalent effect to the proposed transfer of troops, through decreasing the Confederates' numerical disparity east of the Mississippi. Price and the Confederate Governor of Missouri, Thomas Caute Reynolds, suggested that an invasion of Missouri would be an effective offensive; Smith approved the plan and appointed Price to command the offensive. Price expected that the offensive would create a popular uprising against Union control of Missouri, divert Union troops away from the principal theaters of combat (many of the Union troops previously defending Missouri had been transferred out of the state, leaving the Missouri State Militia to be the state's primary defensive force), and aid McClellan's chance of defeating Lincoln in the election.[6] On September 19, Price's column, named the Army of Missouri, entered the state.[7]
Prelude
_(14761985221).jpg.webp)
When it entered the state, Price's force was composed of about 13,000 cavalrymen. However, several thousand of these men were poorly armed, and all 14 of the army's cannons were smaller than was standard at the time, limiting their range and effectiveness.[8] Countering Price was the Union Department of Missouri, under the command of Major General William S. Rosecrans, who had fewer than 10,000 men on hand, many of whom were militiamen.[9] In late September, the Confederates encountered a small Union force holding Fort Davidson near the town of Pilot Knob. Attacks against the post in the Battle of Pilot Knob on September 27 failed, and the Union garrison abandoned the fort that night. Price had suffered hundreds of casualties in the battle, and decided to divert the aim of his advance from St. Louis to Jefferson City.[10] Price's army was accompanied by a sizable wagon train, which significantly slowed its movement. The train was used to carry the supplies and forage collected by the Confederates from the towns they went through.[11] The delays caused by this slow progress enabled Union forces to reinforce Jefferson City, whose garrison was increased from 1,000 men to 7,000 between October 1 and October 6.[12] In turn, Price determined that Jefferson City was too strong to attack, and began moving westwards along the course of the Missouri River.[13]
The vanguard of Price's army reached Boonville on October 9. Boonville was part of a pro-Confederate area known as Little Dixie, and many men, including Bloody Bill Anderson and his guerillas, joined the Confederates; Price detached Anderson to operate north of the main body to harass the Northern Missouri Railroad.[14] Meanwhile, Union troops were following Price. One body was to the east of Boonville at Rocheport, and another, under Brigadier General John B. Sanborn, was to the south at California.[15] On the 11th, Sanborn moved north and skirmished with the Confederates, who abandoned the town the next day and continued west in the direction of Marshall.[16] While the new recruits added to the numerical strength of Price's army, a significant proportion of them were unarmed. Late on the 12th, Price learned of rumors that a substantial store of weapons was held by the Union garrison of Glasgow, which was across the Missouri River and 20 miles (32 km) from Boonville.[17] On October 14, Price authorized two raids away from his main body for the purpose of taking supplies. One under Brigadier General[lower-alpha 1] M. Jeff Thompson, commander of Shelby's Iron Brigade, was sent to Sedalia, which it quickly captured on October 15. The second was led by Brigadier General John B. Clark Jr. and was directed towards Glasgow.[19]
Battle
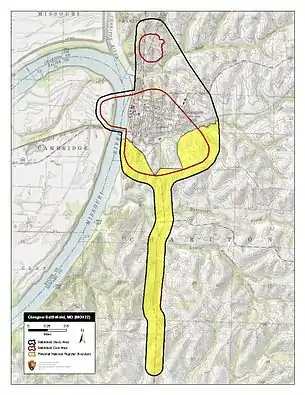
Clark's column consisted of 1,700 men in his own brigade and that of Colonel Sidney D. Jackman, as well as part of Harris's Missouri Battery. Clark and Jackman were selected for the operation, as they were local residents. The column crossed the Missouri at Arrow Rock on the 14th. After hearing rumors that the garrison of Glasgow had a "tin-clad boat", Clark asked Price for more artillery. Since the river at Glasgow was narrow enough for artillery to effectively fire across it, Price sent Shelby with 125 men and part of Collins's Missouri Battery to a point across the Missouri from Glasgow.[20] The Union garrison was initially a small force under the command of Captain John E. Mayo, but it had been reinforced on October 13 by part of the 43rd Missouri Infantry Regiment under the command of Colonel Chester Harding. The Missouri infantrymen had been temporarily stranded when the steamboats they were on ran aground. Once the ships were freed, they went downriver to Glasgow, where they unloaded the Missourians and supplies. One of the ships, Benton, returned to Jefferson City, while the other, West Wind, stayed at Glasgow. Contrary to the rumors heard by Clark, West Wind was both unarmored and unarmed.[21]
Harding, who was now in command of the garrison at Glasgow, had around 550 to 800 men available. Glasgow was a hilltop town, which provided some advantage to the defenders. The line was anchored by two unfinished fortifications, but the defenses between the fortifications were makeshift. Elements of the 43rd Missouri Infantry held east and west positions south of Glasgow, near points where roads crossed Greggs Creek. In between those two positions, a line of local militiamen were posted. North of the town, a group of cavalry, largely members of the Missouri State Militia held a position north of Bear Creek.[22][23] At around 05:00, Collins's Battery opened fire, aiming primarily for West Wind, visible campfires, and exposed streets in the town. This fire was largely ineffective, as was fire from the cavalry accompanying the cannons. Union sharpshooters were able to silence some of the Confederates by driving them away from the riverbank.[24][25]
Clark's force arrived later than Shelby expected.[26] By about 07:00, Clark's men finally arrived on the field. Jackman's men were aligned to the left, closer to the river, with most of the rest of the Confederate force to Jackman's right. The 3rd Missouri Cavalry Regiment held the extreme Confederate right. The 10th Missouri Cavalry Regiment was sent around the Union rear to attack Glasgow from the north.[24] Clark sent a surrender offer to Harding, using civilians to deliver the message instead of military personnel. The Union commander was confused by the nonstandard use of civilian messengers, and rejected the offer.[27] Clarks' main body south of town forced its way across Greggs Creek beginning around 08:00, although the Union defenders put up a hardy fight.[28] In his after-battle report, Harding stated that his men had been outflanked on both sides of their line.[29] The Union troops fell back into Glasgow proper, where they came under fire from the Confederate artillery on the opposite side of the river, which was more effective this time. Shelby ordered men across the river in a small boat to West Wind, hoping to use it as a ferry across the river. While the Confederates reached West Wind, the steamboat's engines had been rendered nonfunctional, and they were forced to return to Shelby as they came. Meanwhile, the 10th Missouri Cavalry's drive from the north had been stymied.[28]
Harding reported that the line within Glasgow was anchored on a promontory on one flank, and at a schoolhouse on the other.[29] Confederate troops closed in on the line. Clark described the distance between the lines as "short", while Harding estimated the distance at 30 yards (27 m) to 50 yards (46 m). House-to-house fighting ensued.[29][28] Having suffered 43 casualties, 11 of which were fatalities, Harding conducted a council of war, which resulted in the decision to surrender. Before surrendering, Union troops burned 50,000 rations in Glasgow's City Hall to prevent them from falling into Confederate hands. The fire spread, causing $130,000 worth of damage.[28] The surrender took place around 13:30, and its terms allowed captured Union officers to keep their horses and sidearms.[29] Harding and his men were paroled and escorted to a Union position on the Lamine River.[30]
Aftermath
The Glasgow victory significantly aided the morale of Price's army, which had been dented after Pilot Knob, and resulted in the capture of 1,200 weapons and 1,000 Union uniform overcoats.[29][30] The regular Confederate troops did not loot in Glasgow,[31] although guerrilla William C. Quantrill and his men robbed a bank on October 16.[30] Confederate casualties have been estimated at around 50, while over 600 Union soldiers were paroled, in addition to the battle losses.[13] Confederate soldiers burned West Wind.[32] Clark rejoined the Confederate army on October 16, and the combined force continued moving west towards Kansas City, where men of the Kansas State Militia and the Union Army of the Border were forming.[13]
The Confederates fought and won three minor battles over the next several days: Second Lexington on the 19th, Little Blue River on October 21, and Second Independence on the 22nd. October 23 saw a significant Confederate defeat during the Battle of Westport at the hands of Union Major General Samuel R. Curtis. Price's men began retreating, but suffered three consecutive defeats on October 25, at the battles of Marais des Cygnes, Mine Creek, and Marmiton River. Mine Creek, in particular, was disastrous for the Confederates, as several cannons and 600 men were captured during the fighting. After one last action at the Second Battle of Newtonia on October 28, the Confederates retreated into Arkansas and then the Indian Territory; Union pursuit continued until the Arkansas River was reached on November 8. The Confederate retreat continued until Texas was reached. The campaign had cost Price more than two-thirds of his army.[33]
Notes
- Thompson's commission was in the Missouri State Guard, not the Confederate States Army.[18]
References
- Kennedy 1998, pp. 19–20.
- Kennedy 1998, pp. 20–25.
- Kennedy 1998, pp. 34–37.
- Kennedy 1998, pp. 377–379.
- Kennedy 1998, p. 343.
- Collins 2016, pp. 27–28.
- Collins 2016, p. 37.
- Collins 2016, p. 39.
- Collins 2016, p. 41.
- Kennedy 1998, pp. 380–382.
- Collins 2016, p. 53.
- Collins 2016, p. 54.
- Kennedy 1998, p. 382.
- Collins 2016, p. 59.
- Collins 2016, p. 60.
- Collins 2016, p. 62.
- Sinisi 2020, p. 127.
- Warner 1987, p. xviii.
- Collins 2016, p. 63.
- Sinisi 2020, pp. 127–128.
- Sinisi 2020, pp. 128–130.
- Sinisi 2020, pp. 130–131.
- Collins 2016, pp. 64–65.
- Collins 2016, p. 64.
- Sinisi 2020, pp. 131–132.
- Sinisi 2020, p. 132.
- Sinisi 2020, pp. 132–133.
- Sinisi 2020, p. 133.
- Collins 2016, p. 65.
- Sinisi 2020, p. 134.
- "Glasgow, Missouri". civilwaronthewesternborder.org. Kansas City Public Library. Retrieved 5 November 2020.
- "Remove Hull of Missouri River Steamer" (PDF). Plattsmouth Semi-Weekly Journal. November 21, 1921. p. 5. Retrieved 5 November 2020.
- Kennedy 1998, pp. 382–386.
Sources
- Collins, Charles D., Jr. (2016). Battlefield Atlas of Price's Missouri Expedition of 1864 (PDF). Fort Leavenworth, Kansas: Combat Studies Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-940804-27-9.
- Kennedy, Frances H., ed. (1998). The Civil War Battlefield Guide (2nd ed.). Boston/New York: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0-395-74012-5.
- Sinisi, Kyle S. (2020) [2015]. The Last Hurrah: Sterling Price's Missouri Expedition of 1864 (paperback ed.). Lanham, Maryland: Rowman & Littlefield. ISBN 978-1-5381-4151-9.
- Warner, Ezra J. (1987) [1959]. Generals in Gray (Louisiana Paperback ed.). Baton Rouge, Louisiana: Louisiana State University Press. ISBN 978-0-8071-3150-3.

