Bean
A bean is the seed of one of several genera of the flowering plant family Fabaceae, which are used as vegetables for human or animal food.[1] They can be cooked in many different ways,[2] including boiling, frying, and baking, and are used in many traditional dishes throughout the world.
.jpg.webp)



Terminology
The word "bean" and its Germanic cognates (e.g. German Bohne) have existed in common use in West Germanic languages since before the 12th century,[3] referring to broad beans, chickpeas, and other pod-borne seeds. This was long before the New World genus Phaseolus was known in Europe. After Columbian-era contact between Europe and the Americas, use of the word was extended to pod-borne seeds of Phaseolus, such as the common bean and the runner bean, and the related genus Vigna. The term has long been applied generally to many other seeds of similar form,[3][4] such as Old World soybeans, peas, other vetches, and lupins, and even to those with slighter resemblances, such as coffee beans, vanilla beans, castor beans, and cocoa beans. Thus the term "bean" in general usage can refer to a host of different species.[5]

Seeds called "beans" are often included among the crops called "pulses" (legumes),[3] although a narrower prescribed sense of "pulses" reserves the word for leguminous crops harvested for their dry grain. The term bean usually excludes legumes with tiny seeds and which are used exclusively for forage, hay, and silage purposes (such as clover and alfalfa). The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization defines "BEANS, DRY" (item code 176)[5] as applicable only to species of Phaseolus. However, in the past, several species, including Vigna angularis (adzuki bean), V. mungo (black gram), V. radiata (green gram), and V. aconitifolia (moth bean), were classified as Phaseolus and later reclassified, and general usage is not governed by that definition.[6][7]
Cultivation

Unlike the closely related pea, beans are a summer crop that needs warm temperatures to grow. Legumes are capable of nitrogen fixation and hence need less fertiliser than most plants. Maturity is typically 55–60 days from planting to harvest.[8] As the bean pods mature, they turn yellow and dry up, and the beans inside change from green to their mature colour. As a vine, bean plants need external support, which may take the form of special "bean cages" or poles. Native Americans customarily grew them along with corn and squash (the so-called Three Sisters),[9] with the tall cornstalks acting as support for the beans.
In more recent times, the so-called "bush bean" has been developed which does not require support and has all its pods develop simultaneously (as opposed to pole beans which develop gradually).[10] This makes the bush bean more practical for commercial production.

History


Beans are one of the longest-cultivated plants. Broad beans, also called fava beans, in their wild state the size of a small fingernail, were gathered in Afghanistan and the Himalayan foothills.[11] In a form improved from naturally occurring types, they were grown in Thailand from the early seventh millennium BCE, predating ceramics.[12] They were deposited with the dead in ancient Egypt. Not until the second millennium BCE did cultivated, large-seeded broad beans appear in the Aegean, Iberia and transalpine Europe.[13] In the Iliad (8th century BCE) there is a passing mention of beans and chickpeas cast on the threshing floor.[14]
Beans were an important source of protein throughout Old and New World history, and still are today.
The oldest-known domesticated beans in the Americas were found in Guitarrero Cave, an archaeological site in Peru, and dated to around the second millennium BCE.[15] However, genetic analyses of the common bean Phaseolus show that it originated in Mesoamerica, and subsequently spread southward, along with maize and squash, traditional companion crops.[16]
Most of the kinds commonly eaten fresh or dried, those of the genus Phaseolus, come originally from the Americas, being first seen by a European when Christopher Columbus, while exploring what may have been the Bahamas, found them growing in fields. Five kinds of Phaseolus beans were domesticated[17] by pre-Columbian peoples: common beans (P. vulgaris) grown from Chile to the northern part of what is now the United States, and lima and sieva beans (P. lunatus), as well as the less widely distributed teparies (P. acutifolius), scarlet runner beans (P. coccineus) and polyanthus beans (P. polyanthus)[18] One especially famous use of beans by pre-Columbian people as far north as the Atlantic seaboard is the "Three Sisters" method of companion plant cultivation:
- In the New World, many tribes would grow beans together with maize (corn), and squash. The corn would not be planted in rows as is done by European agriculture, but in a checkerboard/hex fashion across a field, in separate patches of one to six stalks each.
- Beans would be planted around the base of the developing stalks, and would vine their way up as the stalks grew. All American beans at that time were vine plants, "bush beans" having been bred only more recently. The cornstalks would work as a trellis for the beans, and the beans would provide much-needed nitrogen for the corn.
- Squash would be planted in the spaces between the patches of corn in the field. They would be provided slight shelter from the sun by the corn, would shade the soil and reduce evaporation, and would deter many animals from attacking the corn and beans because their coarse, hairy vines and broad, stiff leaves are difficult or uncomfortable for animals such as deer and raccoons to walk through, crows to land on, etc.
Dry beans come from both Old World varieties of broad beans (fava beans) and New World varieties (kidney, black, cranberry, pinto, navy/haricot).
Beans are a heliotropic plant, meaning that the leaves tilt throughout the day to face the sun. At night, they go into a folded "sleep" position.
Types

Currently, the world genebanks hold about 40,000 bean varieties, although only a fraction are mass-produced for regular consumption.[19]
| Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) | |
|---|---|
| Energy | 334 kJ (80 kcal) |
10.5 g | |
0.5 g | |
9.6 g | |
| |
| †Percentages are roughly approximated using US recommendations for adults. | |
Some bean types include:
- Vicia
- Vicia faba (broad bean or fava bean)

- Phaseolus
- Phaseolus acutifolius (tepary bean)
- Phaseolus coccineus (runner bean)
- Phaseolus lunatus (lima bean)
- Phaseolus vulgaris (common bean; includes the pinto bean, kidney bean, black bean, Appaloosa bean as well as green beans, and many others)
- Phaseolus polyanthus (a.k.a. P. dumosus, recognized as a separate species in 1995)
- Vigna
- Vigna aconitifolia (moth bean)
- Vigna angularis (adzuki bean)
- Vigna mungo (urad bean)
- Vigna radiata (mung bean)
- Vigna subterranea (Bambara bean or ground-bean)
- Vigna umbellata (ricebean)
- Vigna unguiculata (cowpea; also includes the black-eyed pea, yardlong bean and others)
- Cicer
- Cicer arietinum (chickpea or garbanzo bean)
- Pisum
- Pisum sativum (pea)
- Lathyrus
- Lathyrus sativus (Indian pea)
- Lathyrus tuberosus (tuberous pea)
- Lens
 Lentils
Lentils- Lens culinaris (lentil)
- Lablab
- Lablab purpureus (hyacinth bean)

- Glycine
- Glycine max (soybean)
- Psophocarpus
- Psophocarpus tetragonolobus (winged bean)

- Cajanus
- Cajanus cajan (pigeon pea)
- Mucuna
- Mucuna pruriens (velvet bean)
- Cyamopsis
- Cyamopsis tetragonoloba or (guar)
- Canavalia
- Canavalia ensiformis (jack bean)
- Canavalia gladiata (sword bean)
- Macrotyloma
- Macrotyloma uniflorum (horse gram)
- Lupinus (lupin)
- Lupinus mutabilis (tarwi)
- Lupinus albus (lupini bean)
- Arachis
- Arachis hypogaea (peanut)
Properties
Nutrients
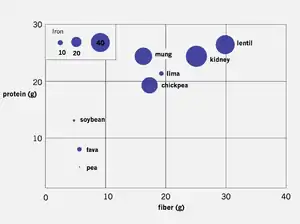
Beans are high in protein, complex carbohydrates, folate, and iron.[20] Beans also have significant amounts of fiber and soluble fiber, with one cup of cooked beans providing between nine and 13 grams of fiber.[20] Soluble fiber can help lower blood cholesterol.[21]
The Canadian government recommends that adults have up to two (female), and three (male) servings. 3/4 cup of cooked beans provide one serving.[22]
Antinutrients
Many types of bean contain significant amounts of antinutrients that inhibit some enzyme processes in the body. Phytic acid and phytates, present in grains, nuts, seeds and beans, interfere with bone growth and interrupt vitamin D metabolism. Pioneering work on the effect of phytic acid was done by Edward Mellanby from 1939.[23][24]
Flatulence
Many edible beans, including broad beans, navy beans, kidney beans and soybeans, contain oligosaccharides (particularly raffinose and stachyose), a type of sugar molecule also found in cabbage. An anti-oligosaccharide enzyme is necessary to properly digest these sugar molecules. As a normal human digestive tract does not contain any anti-oligosaccharide enzymes, consumed oligosaccharides are typically digested by bacteria in the large intestine. This digestion process produces gases such as methane as a byproduct, which are then released as flatulence.[25][26]
Processing the beans, such as by boiling, soaking, cooking, can leach the indigestible sugars from the beans and significantly reduce, if not entirely eliminate the problem. In addition enzyme pills are available.
Toxins
Some kinds of raw beans contain a harmful, tasteless toxin: the lectin phytohaemagglutinin, which must be removed by cooking. Red kidney beans are particularly toxic, but other types also pose risks of food poisoning. A recommended method is to boil the beans for at least ten minutes; undercooked beans may be more toxic than raw beans.[27]
Cooking beans, without bringing them to a boil, in a slow cooker at a temperature well below boiling may not destroy toxins.[27] A case of poisoning by butter beans used to make falafel was reported; the beans were used instead of traditional broad beans or chickpeas, soaked and ground without boiling, made into patties, and shallow fried.[28]
Bean poisoning is not well known in the medical community, and many cases may be misdiagnosed or never reported; figures appear not to be available. In the case of the UK National Poisons Information Service, available only to health professionals, the dangers of beans other than red beans were not flagged as of 2008.[28]
Fermentation is used in some parts of Africa to improve the nutritional value of beans by removing toxins. Inexpensive fermentation improves the nutritional impact of flour from dry beans and improves digestibility, according to research co-authored by Emire Shimelis, from the Food Engineering Program at Addis Ababa University.[29] Beans are a major source of dietary protein in Kenya, Malawi, Tanzania, Uganda and Zambia.[30]
Bacterial infection from bean sprouts
It is common to make beansprouts by letting some types of bean, often mung beans, germinate in moist and warm conditions; beansprouts may be used as ingredients in cooked dishes, or eaten raw or lightly cooked. There have been many outbreaks of disease from bacterial contamination, often by salmonella, listeria, and Escherichia coli, of beansprouts not thoroughly cooked,[31] some causing significant mortality.[32]
Production

The production data for legumes are published by FAO in three categories:
- Pulses dry: all mature and dry seeds of leguminous plants except soybeans and groundnuts.
- Oil crops: soybeans and groundnuts.
- Fresh vegetable: immature green fresh fruits of leguminous plants.
The following is a summary of FAO data.[33]
| crops [FAO code][34] |
1961 | 1981 | 2001 | 2015 | 2016 | Ratio 2016 /1961 |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Pulses (dry) [1726] | 40.78 | 41.63 | 56.23 | 77.57 | 81.80 | 2.01 | Per capita production had decreased. (Population increase was 2.4 ×) |
| Oil crops (dry) | |||||||
| Soybeans [236] | 26.88 | 88.53 | 177.02 | 323.20 | 334.89 | 12.46 | Drastic increase driven by the demand for animal feeds and oil. |
| Groundnuts, with shell [242] | 14.13 | 20.58 | 35.82 | 45.08 | 43.98 | 3.11 | |
| Fresh vegetables (80 - 90% water) | |||||||
| Beans, green [414] | 2.63 | 4.09 | 10.92 | 23.12 | 23.60 | 8.96 | |
| Peas, green [417] | 3.79 | 5.66 | 12.41 | 19.44 | 19.88 | 5.25 | |
Main crops of "Pulses, Total (dry)" are "Beans, dry [176]" 26.83 million tons, "Peas, dry [187]" 14.36 million tons, "Chick peas [191]" 12.09 million tons, "Cow peas [195]" 6.99 million tons, "Lentils [201]" 6.32 million tons, "Pigeon peas [197]" 4.49 million tons, "Broad beans, horse beans [181]" 4.46 million tons. In general, the consumption of pulses per capita has been decreasing since 1961. Exceptions are lentils and cowpeas.

| Country | 2016 | Share | Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 81.80 | 100% | ||
| 1 | India | 17.56 | 21.47% | |
| 2 | Canada | 8.20 | 10.03% | |
| 3 | Myanmar | 6.57 | 8.03% | |
| 4 | China | 4.23 | 5.17% | |
| 5 | Nigeria | 3.09 | 3.78% | |
| 6 | Russia | 2.94 | 3.60% | |
| 7 | Ethiopia | 2.73 | 3.34% | |
| 8 | Brazil | 2.62 | 3.21% | |
| 9 | Australia | 2.52 | 3.09% | |
| 10 | USA | 2.44 | 2.98% | |
| 11 | Niger | 2.06 | 2.51% | |
| 12 | Tanzania | 2.00 | 2.45% | |
| Others | 24.82 | 30.34% |
The world leader in production of Dry Beans (Phaseolus spp).[36] is Myanmar (Burma), followed by India and Brazil. In Africa, the most important producer is Tanzania.[37]
| Country | Production (tonnes) |
Footnote |
|---|---|---|
| 3,800,000 | F | |
| 3,630,000 | ||
| 2,936,444 | A | |
| 1,400,000 | * | |
| 1,294,634 | ||
| 1,150,000 | F | |
| 1,110,668 | ||
| 529,265 | F | |
| 461,000 | * | |
| 438,236 | ||
| World | 23,139,004 | A |
No symbol = official figure, P = official figure, F = FAO estimate, * = Unofficial/Semi-official/mirror data, C = Calculated figure A = Aggregate (may include official, semi-official or estimates)
Source: UN Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)[38]
See also
References
- "Beans and peas are unique foods | ChooseMyPlate". www.choosemyplate.gov. Retrieved 24 January 2020.
- Clark, Mellisa. "How to Cook Beans". New York Times Cooking. New York Times. Retrieved 3 January 2020.
- Merriam-Webster, Merriam-Webster's Collegiate Dictionary, Merriam-Webster
- Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, archived from the original on 25 September 2015, retrieved 3 May 2016.
- "Definition And Classification Of Commodities (See Chapter 4)". FAO, United Nations. 1994.
- Merriam-Webster BEAN
- Encyclopedia Britannica Bean
- Shurtleff, William; Aoyagi, Akiko (1 October 2013). Early Named Soybean Varieties in the United States and Canada: Extensively Annotated Bibliography and Sourcebook. Soyinfo Center. ISBN 9781928914600. Retrieved 18 November 2017 – via Google Books.
- Schneider, Meg. New York Yesterday & Today. Voyageur Press. ISBN 9781616731267. Retrieved 18 November 2017 – via Google Books.
- "The Germination Of a Bean" (PDF). Microscopy-uk.org.uk. Retrieved 18 November 2017.
- Kaplan, pp. 27 ff
- Gorman, CF (1969). "Hoabinhian: A pebble-tool complex with early plant associations in southeast Asia". Science. 163 (3868): 671–3. Bibcode:1969Sci...163..671G. doi:10.1126/science.163.3868.671. PMID 17742735. S2CID 34052655.
- Daniel Zohary and Maria Hopf Domestication of Plants in the Old World Oxford University Press, 2012, ISBN 0199549060, p. 114.
- "And as in some great threshing-floor go leaping From a broad pan the black-skinned beans or peas." (Iliad xiii, 589).
- Chazan, Michael (2008). World Prehistory and Archaeology: Pathways through Time. Pearson Education, Inc. ISBN 978-0-205-40621-0.
- Bitocchi, Elena; Nanni, Laura; Bellucci, Elisa; Rossi, Monica; Giardini, Alessandro; Zeuli, Pierluigi Spagnoletti; Logozzo, Giuseppina; Stougaard, Jens; McClean, Phillip; Attene, Giovanna; Papa, Roberto (3 April 2012). "Mesoamerican origin of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) is revealed by sequence data". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 109 (14): E788–E796. doi:10.1073/pnas.1108973109. PMC 3325731. PMID 22393017.
- Kaplan, p. 30: Domestication, besides involving selection for larger seed size, also involved selection for pods that did not curl and open when ripe, scattering the beans they contained..
- Kaplan, p. 30
- Laura McGinnis and Jan Suszkiw, ARS. Breeding Better Beans. Agricultural Research magazine. June 2006.
- Mixed Bean Salad (information and recipe) from The Mayo Clinic Healthy Recipes Archived 15 October 2008 at the Wayback Machine. Accessed February 2010.
- Dietary fiber: Essential for a healthy diet. MayoClinic.com (17 November 2012). Retrieved on 2012-12-18.
- "How Many Food Guide Servings of Meat and Alternatives Do I Need? - Canada.ca". Hc-sc.gc.ca. Retrieved 18 November 2017.
- Harrison, DC; Mellanby, E (October 1939). "Phytic acid and the rickets-producing action of cereals". Biochem. J. 33 (10): 1660–1680.1. doi:10.1042/bj0331660. PMC 1264631. PMID 16747083.
- Ramiel Nagel (26 March 2010). "Living With Phytic Acid - Weston A Price". The Weston A Price Foundation. Retrieved 23 January 2016.
- Harold McGee (2003). Food and Cooking. Simon & Schuster. p. 486. ISBN 978-0684843285.
Many legumes, especially soy, navy and lima beans, cause a sudden increase in bacterial activity and gas production a few hours after they're consumed. This is because they contain large amounts of carbohydrates that human digestive enzymes can't convert into absorbable sugars. These carbohydrates therefore leave the upper intestine unchanged and enter the lower reaches, where our resident bacterial population does the job we are unable to do.
- Peter Barham (2001). The Science of Cooking. Springer. p. 14. ISBN 978-3-540-67466-5.
we do not possess any enzymes that are capable of breaking down larger sugars, such as raffinose etc. These 3, 4 and 5 ring sugars are made by plants especially as part of the energy storage system in seeds and beans. If these sugars are ingested, they can't be broken down in the intestines; rather, they travel into the colon, where various bacteria digest them – and in the process produce copious amounts of carbon dioxide gas
- "Foodborne Pathogenic Microorganisms and Natural Toxins Handbook: Phytohaemagglutinin". Bad Bug Book. United States Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on 9 July 2009. Retrieved 11 July 2009.
- Vicky Jones (15 September 2008). "Beware of the beans: How beans can be a surprising source of food poisoning". The Independent. Retrieved 23 January 2016.
- Shimelis, Emire Admassu; Rakshit, Sudip Kumar (2008). "Influence of natural and controlled fermentations on α-galactosides, antinutrients and protein digestibility of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.)". International Journal of Food Science & Technology. 43 (4): 658–665. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2621.2006.01506.x. ISSN 1365-2621.
- Summary: Fermentation 'improves nutritional value of beans' (Sub Saharan Africa page, Science and Development Network website). Paper: Influence of natural and controlled fermentations on α-galactosides, antinutrients and protein digestibility of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.)
- "Sprouts: What You Should Know". Foodsafety.gov. Retrieved 23 January 2016.
- "Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC): Update on outbreak in the EU (27 July 2011, 11:00)". European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. 27 July 2011. Archived from the original on 15 March 2017.
- FAO STAT Production /Crops
- see Legume#Commodity Classification
- all legumes dry
- Dry Beans does not include broad beans, dry peas, chickpea, lentil
- FAO Pulses and Derived Products
- "Major Food And Agricultural Commodities And Producers – Countries By Commodity". Fao.org. Archived from the original on 6 September 2015. Retrieved 2 February 2015.
Bibliography
- Kaplan, Lawrence (2008). "Legumes in the History of Human Nutrition". In DuBois, Christine; Tan, Chee-Beng; Mintz, Sidney (eds.). The World of Soy. NUS Press. pp. 27–. ISBN 978-9971-69-413-5. Retrieved 18 December 2012.
External links
| Look up bean in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Beans. |
- Everett H. Bickley Collection, 1919–1980 Archives Center, National Museum of American History, Smithsonian Institution.
- Discovery Online: The Skinny On Why Beans Give You Gas
- Fermentation improves nutritional value of beans
- Cook's Thesaurus on Beans