beta-Pinene
beta-Pinene (β-pinene) is a monoterpene, an organic compound found in plants. It is one of the two isomers of pinene, the other being α-pinene. It is colorless liquid soluble in alcohol, but not water. It has a woody-green pine-like smell.
 | |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
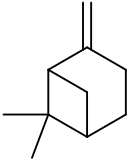
| IUPAC names
6,6-Dimethyl-2-methylidenebicyclo[3.1.1]heptane Pin-2(10)-ene | |||
| Other names
6,6-Dimethyl-2-methylenebicyclo[3.1.1]heptane 2(10)-Pinene Nopinene Pseudopinene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol) |
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.430 | ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID |
|||
| UNII | |||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C10H16 | |||
| Molar mass | 136.238 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.872 g/mL | ||
| Melting point | −61.54 °C; −78.77 °F; 211.61 K[1] | ||
| Boiling point | 165–167 °C; 329–332 °F; 438–440 K[2] | ||
| Thermochemistry | |||
Std enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
−6214.1±2.9 kJ/mol[3] | ||
| Hazards | |||
| R-phrases (outdated) | R10 R36 R37 R38 | ||
| S-phrases (outdated) | S26 S36 | ||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 36 °C (97 °F; 309 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
This is one of the most abundant compounds released by forest trees.[4] If oxidized in air, the allylic products of the pinocarveol and myrtenol family prevail.[5]
Sources
Many plants from many botanical families contain the compound, including:
See also
References
- http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?Name=beta-pinene&Units=SI&cTG=on&cIR=on&cTC=on&cTZ=on&cTP=on&cMS=on&cTR=on&cUV=on&cIE=on&cGC=on&cIC=on&cES=on&cDI=on&cSO=on visited on 01/29/2018
- https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/402753?lang=pt®ion=BR visited on 01/29/2018
- http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?Name=beta-pinene&Units=SI&cTG=on&cIR=on&cTC=on&cTZ=on&cTP=on&cMS=on&cTR=on&cUV=on&cIE=on&cGC=on&cIC=on&cES=on&cDI=on&cSO=on visited on 01/29/2018
- Geron, C., et al. (2000). A review and synthesis of monoterpene speciation from forests in the United States. Atmospheric Environment 34(11), 1761-81.
- Neuenschwander, U., et al. (2011). Peculiarities of β-pinene autoxidation. ChemSusChem 4(11), 1613-21.
- Li, R. and Z. T. Jiang. (2004). Chemical composition of the essential oil of Cuminum cyminum L. from China. Flavour and Fragrance Journal 19(4), 311-13.
- Wang, L., et al. (2009). Ultrasonic nebulization extraction coupled with headspace single drop microextraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for analysis of the essential oil in Cuminum cyminum L. Analytica Chimica Acta 647(1), 72-77.
- Tinseth, G. The Essential Oil of Hops: Hop Aroma and Flavor in Hops and Beer. Archived 2013-11-11 at the Wayback Machine Brewing Techniques January/February 1994. Accessed July 21, 2010.
- Hillig, Karl W (October 2004). "A chemotaxonomic analysis of terpenoid variation in Cannabis". Biochemical Systematics and Ecology. 32 (10): 875–891. doi:10.1016/j.bse.2004.04.004. ISSN 0305-1978.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
-(-)-beta-pinene-2D-projected-skeletal.png.webp)
-(%E2%88%92)-beta-pinene-from-xtal-3D-balls.png.webp)

