Beyer, Peacock and Company
Beyer, Peacock and Company was an English railway locomotive manufacturer with a factory in Openshaw, Manchester. Founded by Charles Beyer, Richard Peacock and Henry Robertson, it traded from 1854 until 1966. The company exported locomotives, and machine tools to service them, throughout the world.
| Industry | Locomotive manufacturing |
|---|---|
| Founded | 1854 England |
| Founders | Charles Beyer Richard Peacock Henry Robertson |
| Defunct | 1966 |
| Headquarters | Greater Manchester |
Areas served | Africa, South America, Asia, Australia and South Pacific |
| Products | Locomotives and machine tools |
Founders
German-born Charles Beyer had undertaken engineering training related to cotton milling in Dresden before moving to England in 1831 aged 21. He secured employment as a draughtsman at Sharp, Roberts and Company's Atlas works in central Manchester, which manufactured cotton mill machinery and had just started building locomotives for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. There he was mentored by head engineer and prolific inventor of cotton mill machinery, Richard Roberts. By the time he resigned 22 years later he was well established as the company's head engineer; he had been involved in producing more than 600 locomotives.
Richard Peacock had been chief engineer of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway's locomotive works in Gorton when he resigned in 1854, confident in his ability to secure orders to build locomotives. Beyer’s resignation presented Peacock with a partnership opportunity. However, the business at the outset (Beyer, Peacock & Co.) was a legal partnership and the partners were therefore liable for debts should the business fail; in a mid-Victorian economic climate of boom and bust, it was a risky venture. Beyer could raise £9,524 (nearly £900,000 in 2015) and Peacock £5,500, but they still required a loan from Charles Geach (founder of the Midland Bank and first treasurer to the Institution of Mechanical Engineers), of which Beyer and Peacock had been founding members. Soon afterwards, however, Geach died, the loan was recalled, and the whole project nearly collapsed. Thomas Brassey came to the rescue, persuading Henry Robertson to provide a £4,000 loan in return for being the third (sleeping) partner.[1] It was not until 1883 that the company was incorporated as a private limited company and renamed Beyer, Peacock & Co. Ltd. In 1902 it took on its final form as a public limited company.[2][note 1]
During the Great Depression, faced with competition from tramways and electric railways, the company began to look for alternatives so that they were not dependent on one product. In 1932 they acquired their first company and in 1949 formed a joint company with Metropolitan-Vickers to build locomotives other than steam. By 1953 Beyer, Peacock had acquired more than five subsidiary companies; two others followed five years later. In 1958 Beyer, Peacock (Hymek) Ltd was formed.[2]
Gorton Foundry
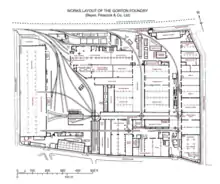
Beyer and Peacock started building their Gorton Foundry in 1854 two miles east from the centre of Manchester at Openshaw on a 12-acre site, on the opposite (south) side of the Manchester, Sheffield and Lincolnshire Railway (MS&LR) line from Peacock's previous works.[note 2] The site was chosen because land was cheaper than in the city, allowing ample room to expand, and there was a good water supply from an MS&LR reservoir. At the Foundry, Beyer designed and manufactured machine tools needed to build the locomotives, and oversaw locomotive design and production. Peacock dealt with the business side, often travelling to continental Europe to secure orders.[3]
In July 1855 the first locomotive, built for the Great Western Railway, left Gorton Foundry. Between 1854 and 1868 the company built 844 locomotives, of which 476 were exported. The company sold mainly to the British colonies, Southern Africa and South America; it never broke into the North American market.[2]
During the First World War Beyer, Peacock manufactured artillery; in August 1915 Gorton Works was put under government control with production switching almost entirely to the war effort, especially heavy field artillery. During the Second World War, the company was again brought under government control but continued to build locomotives throughout the war.[2]
Condensing locomotives for underground railways
.jpg.webp)
A technological innovation that strengthened the company's reputation was the world's first successful condensing[note 3] locomotive design for London's first underground railway – the Metropolitan Railway A Class 4-4-0 tank engine. Between 1864 and 1886, 148 were built for various railways; most operated until the lines' electrification in 1905. The locomotives' main designer, Hermann Ludwig Lange (1837–92), was a native of Beyer's home town, Plauen, Saxony (now Germany) who had undertaken an apprenticeship followed by engineering training. Beyer had invited him to England in 1861 and employed him for the first year in the company workshops, then as a draughtsman under his direction. He became chief draughtsman in 1864 or 1865. After Beyer's death in 1876, he became chief engineer and co-manager of the company.[1][4]
Beyer-Garratt articulated locomotives
_--_side_elevation.png.webp)
An articulated locomotive design that became renowned in the 20th century was another innovation, the Beyer-Garratt articulated locomotive (generically known as a "Garratt"), invented by Herbert William Garratt, who was granted a patent in 1908; Beyer, Peacock had sole rights of manufacture in Britain. After the patents ran out in 1928, the company began to use the name "Beyer-Garratt" to distinguish their locomotives.[2] They became widely used throughout Africa, South America, Asia, Australia and the South Pacific, where difficult terrain and lightly laid, tightly curved track, usually narrow-gauge, severely limited the weight and power output of conventional locomotives. In Garratt's design, two girders holding a boiler[note 4] and a cab were slung between two "engine" units, each with cylinders, wheels and motion. The weight of the locomotive was therefore spread over a considerable distance. Both engine units were topped by water tanks. The unit adjoining the cab end also held a fuel bunker.[5][6]
Between 1909 and 1958, Beyer, Peacock built more than a thousand Garratts;[7] significant types are listed below. Among them, three of the most significant are preserved (see the "Preserved steam locomotives" table below):
- first: the Tasmanian Government Railways K class, built in 1909 for the North East Dundas Tramway of western Tasmania
- most powerful: the East African Railways 59 class of 1955
- last: the South African Railways NG G16 class locomotive of 1958.[8]
Diesel and electric locomotives
In the decade following 1954, the company built four types of diesel-powered locomotives and two electric types, listed below.
Decline and closure
The late 1950s saw a rapid transformation in locomotive manufacture. In 1955 British Railways decided to switch from steam to diesel traction and by then overseas railways had done the same. A major problem the company soon faced was that it had chosen to make diesel-hydraulic locomotives when the Western Region had opted for lightweight locomotives with hydraulic transmission under the British Railways Modernisation Plan of 1955; but British Railways opted for diesel-electrics.[note 5] The company all but closed down the Gorton Foundry at the end of 1958.[2]
In 1966, after 112 years of operation, all production ceased at Gorton Foundry.[2] During that time, the company had built nearly 8,000 locomotives.[7]
As of 2012 the building that housed the former boiler shop, tender shop and bolier mounting shop – 550 feet (167 metres) in length – remained in use as part of the Hammerstone Road Depot of Manchester City Council.
Gallery
- (click to enlarge)
 0-4-2 locomotive built for the Madras Railway in 1860 at the Gorton Foundry
0-4-2 locomotive built for the Madras Railway in 1860 at the Gorton Foundry NSWGR Z12 class locomotive no. 1210 of 1878 at Canberra, Australia in 2011
NSWGR Z12 class locomotive no. 1210 of 1878 at Canberra, Australia in 2011
 Experimental Ljungström turbine condenser locomotive in 1927; it was developed with the LMS Railway
Experimental Ljungström turbine condenser locomotive in 1927; it was developed with the LMS Railway 4-6-0 locomotive no. 2 of the State Saw Mills (of Western Australia), similar to the WAGR G class, in the 1940s
4-6-0 locomotive no. 2 of the State Saw Mills (of Western Australia), similar to the WAGR G class, in the 1940s South Australian Railways 400 class no. 405 in "builder's photo" livery in 1953
South Australian Railways 400 class no. 405 in "builder's photo" livery in 1953.jpg.webp) Builder's plate on preserved NSWGR AD60 class locomotive no. 6029 of 1953
Builder's plate on preserved NSWGR AD60 class locomotive no. 6029 of 1953 Fittings and controls on the 1952 NSWGR AD60 class Beyer-Garratt
Fittings and controls on the 1952 NSWGR AD60 class Beyer-Garratt British Rail Class 35 Hymek diesel-hydraulic locomotive of 1961
British Rail Class 35 Hymek diesel-hydraulic locomotive of 1961
Classes of locomotives
Non-articulated
List shows delivery year(s), railway and locomotive class, wheel arrangement (Whyte notation) and number in order.
- 1859 Victorian Railways J class (1859) 2-2-2, later 2-4-0
- 1859 Victorian Railways P class 0-6-0
- 1861 Victorian Railways B class 2-4-0 (19)
- 1861 Victorian Railways O class 0-6-0 (11)
- 1864–1885 Metropolitan Railway A class 4-4-0T
- 1869 South Australian Railways G class 2-4-0T (5)
- 1869 Holdfast Bay Railway Company 2-4-0T (later, became South Australian Railways G class) (3)
- 1871–1886 District Railway 4-4-0T
- 1873–1926 Various locomotives for the Isle of Man Railway 2-4-0T
- 1874 Victorian Railways F class 2-4-0 (pattern engine)
- 1874 Victorian Railways T class 0-6-0 (pattern engine)
- 1875 South Australian Railways J class 0-6-0 (2)
- 1876 South Australian Railways U class 2-6-0T (8)
- 1876 South Australian Railways V class 0-4-4T (4)
- 1877–1882 South Australian Railways W class 2-6-0 (35)
- 1878 NSWGR Z12 class|New South Wales Government Railways Z12 class 4-4-0
- 1879 South Australian Railways L class 4-4-0 (4)
- 1879–1884 South Australian Railways K class 0-6-4T (18)
- 1879 Victorian Railways M class 4-4-0T (pattern engine)
- 1879 Victorian Railways 'Old' R class 0-6-0 (pattern engine + 3)
- 1880 Holdfast Bay Railway Company (later, became South Australian Railways Gd class) 0-4-4WT (2)
- 1884 South Australian Railways P class 2-4-0T (6)
- 1884 Victorian Railways 'Old' A class 4-4-0
- 1885–1898 South Australian Railways Y class 2-6-0
- 1885–1907 Tasmanian Government Railways C class 2-6-0 (27)
- 1888–1907 Silverton Tramway Y class 2-6-0; two 2-6-2 (50)
- 1889 Western Australian Government Railways G class 4-6-0 (7)
- 1897 Glenelg Railway Company 4-4-0T (later, became South Australian Railways Ge class) (2)
- 1898 Tobu Railway B1 class 4-4-0 (12 locos)[9]
- 1902 Victorian Railways DD class 4-6-0 (20)
- 1912, 1915 Silverton Tramway A class 4-6-0 (4)
- 1921 Rhymney Railway R class 0-6-2T (6)
- 1922 Dublin and South Eastern Railway nos 15 & 16) 2-6-0 (2)
- 1928 Great Eastern Railway class S69 (later, became London and North Eastern Railway class B12) 4-6-0
- 1931 Great Western Railway 5700 class 0-6-0PT (25)
- 1951–1952 Silverton Tramway W class 4-8-2 (4)
- 1951–1952 Western Australian Government Railways W class 4-8-2 (60)
- 1955 Western Australian Government Railways V class 2-8-2 (sub-contracted to Robert Stephenson and Hawthorns) (24)
Beyer-Garratt (articulated)
List shows delivery year(s), railway and locomotive class, wheel arrangement (Whyte notation) and number in order.
- 1909 Tasmanian Government Railways K class
- 1910 Darjeeling Himalayan Railway D class
- 1911 Western Australian Government Railways M class 2-6-0+0-6-2 (6)
- 1913 Western Australian Government Railways Ms class 2-6-0+0-6-2 (7)
- 1925 London and North Eastern Railway class U1
- 1926 Victorian Railways G class
- 1927 London, Midland and Scottish Railway Garratt
- 1928 New Zealand Railways G class
- 1928 South African Railways GL class
- 1936–1939 Fyansford Cement Works Railway (nos 1&2)
- 1939 South African class NG G16
- 1940–1952 Rhodesia Railways 15th class
- 1949 East African Railways 56 class
- 1951 Queensland Railways Beyer-Garratt class
- 1951 South Australian Railways 400 class 4-8-2+2-8-4 (10)
- 1952–1954, 1957 New South Wales Government Railways AD60 class 4-8-4+4-8-4 (42)
- 1954-68 Rhodesia Railways 20th class
- 1955 East African Railways 59 class
- 1956 South African Railways GMA/M Class
Steam turbine
Diesel
- 1954–56 Western Australian Government Railways X class
- 1961–63 British Rail Class 35
- 1962 British Rail Class 25
- 1964 British Rail Class 17 (as sub-contractor to (Clayton Equipment Company)
Electric
- 1956–58 New South Wales 46 class
- 1960–62 British Rail Class 82
Preserved locomotives
Click "Show" to display.
| Preserved diesel locomotives built by Beyer, Peacock | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7911 | 1962 | British Railways | D7017 | BR Class 35 Hymek | Bo-Bo | West Somerset Railway | ||
| 7912 | 1962 | British Railways | D7018 | BR Class 35 Hymek | Bo-Bo | West Somerset Railway | ||
| 7923 | 1962 | British Railways | D7029 | BR Class 35 Hymek | Bo-Bo | Severn Valley Railway | ||
| 7980 | 1963 | British Railways | D7076 | BR Class 35 Hymek | Bo-Bo | East Lancs Railway | ||
| ? | 1964 | British Railways | D8568 | British Rail Class 17 | Bo-Bo | Chinnor and Princes Risborough Railway | ||
| 8038 | 1965 | British Railways | D7628, 25278 Sybilla | BR Class 25 | Bo-Bo | North Yorkshire Moors Railway - Operational | ||
| 8039 | 1965 | British Railways | D7629, 25279 | BR Class 25 | Bo-Bo | Great Central Railway (Nottingham) - Operational | ||
| 8043 | 1965 | British Railways | D7633, 25283 | BR Class 25 | Bo-Bo | Dean Forest Railway - Operational | ||
| Preserved electric locomotives built by Beyer, Peacock | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP No. | Built | Company built for | Locomotive number(s) | Class | Wheel arrangement | Preserved at | ||
| 1956 | NSWGR | 4601 | 46 Class | Co-Co | Valley Heights Locomotive Depot Heritage Museum | |||
| 1956 | NSWGR | 4602 | 46 Class | Co-Co | Dorrigo Steam Railway & Museum | |||
| 1956 | NSWGR | 4615 | 46 Class | Co-Co | Junee Roundhouse Museum on permanent loan from the Sydney Electric Train Society | |||
| 1956 | NSWGR | 4627 | 46 Class | Co-Co | Sydney Electric Train Society | |||
| 1956 | NSWGR | 4638 | 46 Class | Co-Co | NSW Rail Museum, Broadmeadow Locomotive Depot[10] | |||
| 1961 | British Railways | E3054, 82008 | BR Class 82 | Bo-Bo | Barrow Hill Engine Shed | |||
Notes
- The public company was incorporated as Beyer, Peacock & Co. (1902) Ltd; the "(1902)" was dropped in 1903.
- The two works were adjacent, on either side of the line between the present-day stations of Ashburys and Gorton.
- By condensing steam, little of it emanated from the locomotives, and using coke (later, "smokeless" Welsh coal) greatly reduced smoke pollution.
- Significant in the performance of the boiler, hence power output, was that the Garratt's firebox was no longer confined to the narrow space between a locomotive's frame but was constrained only by the much greater distance between girders.
- Beyer Peacock (Hymek) Ltd was formed as a joint venture between Bristol Siddeley Engines, which was licensed to build Maybach engines, and Stone-Platt Industries, licensed to build Mekydro transmissions.
References
- Bruce, J. Graeme (1971). Steam to silver. London: London Transport. ISBN 9780853290124.
- "Beyer Peacock & Co Ltd". Science Museum Group. Science Museum Group. 2019. Retrieved 8 January 2020.
- Hills, R.L.; Patrick, D. (1982). Beyer, Peacock: Locomotive builders to the world. Glossop: Transport Publishing Co. ISBN 0903839415.
- "Hermann Ludwig Lange". Grace's Guide to British industrial history. Grace's Guide Project. 2019. Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- Walker, Rosanne (18 August 2011). "Garratt, Herbert William (1864-1913)". Encyclopedia of Australian Science. The University of Melbourne eScholarship Research Centre. Retrieved 2 January 2020.
- "Beyer-Garratt". Encyclopedia Britannica. Encyclopedia Britannica. 2019. Retrieved 4 January 2020.
- Atkins (1999), p. 104.
- Paxton, Leith; Bourne, David (1985). Locomotives of the South African Railways (1st ed.). Cape Town: Struik. pp. 109–110. ISBN 0869772112.
- Tobu Museum exhibit guide Archived 22 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine Retrieved on 11 March 2009 (in Japanese).
- 'Veteran electric finds new home as in-traffic units face uncertain future'. Railway Digest. July 1998. p. 10.
Select bibliography
- Atkins, P. (1999). The golden age of steam locomotive building. Atlantic. pp. 66–67. ISBN 978-0906899878.
- Durrant, A.E. (1981). Garratt locomotives of the world (rev. and enl. ed.). David & Charles. ISBN 0715376411.
- Hills, Richard L.; Patrick, D. (1982). Beyer, Peacock, locomotive builders to the world. Glossop: Transport Publishing Co. ISBN 0-903839-41-5.
- Lowe, James W. (1989) [1975]. "Beyer, Peacock & Company". British steam locomotive builders. London: Guild Publishing. pp. 59–64. ISBN 0900404213.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Beyer, Peacock and Company. |