Caesium hexafluorocuprate(IV)
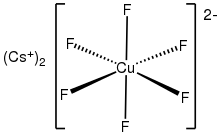
Caesium hexafluorocuprate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Cs
2CuF
6. It is a red solid that degrades upon contact with water. It was first prepared be heating CsCuCl
3 and caesium fluoride at 410°C under 350 atmospheres of fluorine:[2]
- 2 CsCuCl3 + 2 CsF + 5 F2 → 2 Cs2CuF6 + 3 Cl2
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Cesium hexafluorocuprate; Dicesium hexafluorocuprate | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Cs2CuF6 | |
| Molar mass | 443.35 g/mol |
| Appearance | Red orange solid[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The anion [CuF6]2- iss a rare example of a copper(IV) complex. In terms of its electronic structure, the anion has a low-spin d7 configuration. It is thus susceptible to Jahn-Teller distortion.[3]
Further reading
- Müller, Bernd G. (1987). "Fluoride mit Kupfer, Silber, Gold und Palladium". Angewandte Chemie. 99 (11): 1120–1135. doi:10.1002/ange.19870991105.
- Popova, T. V.; Aksenova, N. V. (2003). "Complexes of Copper in Unstable Oxidation States". Russian Journal of Coordination Chemistry. 29 (11): 743. doi:10.1023/B:RUCO.0000003432.39025.cc. S2CID 93464243.
References
- Jane E. Macintyre, ed. (1992). Dictionary of Inorganic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 3100. ISBN 9780412301209.
- Harnischmacher, Werner; Hoppe, Rudolf (1973). "Tetravalent Copper: Cs2[CuF6]". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 12 (7): 582–583. doi:10.1002/anie.197305822.
- Grannec, J.; Tressaud, A.; Hagenmuller, P. (1984). "Some physical properties of d-transition metal fluorides in unusual oxidation states". Journal of Fluorine Chemistry. 25: 83–90. doi:10.1016/S0022-1139(00)81198-7.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.