Catholic emancipation
Catholic emancipation or Catholic relief was a process in the kingdoms of Great Britain and Ireland, and later the combined United Kingdom in the late 18th century and early 19th century, that involved reducing and removing many of the restrictions on Roman Catholics introduced by the Act of Uniformity, the Test Acts and the penal laws. Requirements to abjure (renounce) the temporal and spiritual authority of the pope and transubstantiation placed major burdens on Roman Catholics.
| General |
|---|
| Early |
| Medieval |
| Early Modern |
| Eighteenth century to present |
The penal laws started to be dismantled from 1766. The most significant measure was the Roman Catholic Relief Act 1829, which removed the most substantial restrictions on Roman Catholicism in the United Kingdom.
Initial reliefs
In Canada, British since 1763, the Quebec Act of 1774 ended some restrictions on Roman Catholics, so much so that it was criticized in the Petition to George III submitted in October 1774 by the First Continental Congress of the Thirteen Colonies.[1]
In Great Britain and, separately, in Ireland, the first Relief Act, called the "Papists Act", was passed in 1778; subject to an oath renouncing Stuart claims to the throne and the civil jurisdiction of the pope, it allowed Roman Catholics to own property and to inherit land. Reaction against this led to riots in Scotland in 1779 and then the Gordon Riots in London on 2 June 1780.
Further relief was given by an Act of 1782 allowing the establishment of Roman Catholic schools and bishops. The British Roman Catholic Relief Act 1791 was adopted by the Irish Parliament in 1792–93. Since the electoral franchise at the time was largely determined by property, this relief gave the votes to Roman Catholics holding land with a rental value of £2 a year. They also started to gain access to many middle-class professions from which they had been excluded, such as the legal profession, grand jurors, universities and the lower ranks of the army and judiciary.
Act of Union with Ireland 1800
The issue of greater political emancipation was considered in 1800 at the time of the Act of Union between Great Britain and Ireland: it was not included in the text of the Act because this would have led to greater Irish Protestant opposition to the Union. Non-conformists also suffered from discrimination at this time, but it was expected to be a consequence given the proportionately small number of Roman Catholics in the United Kingdom as a whole.
William Pitt the Younger, the Prime Minister, had promised emancipation to accompany the Act. No further steps were taken at that stage, however, in part because of the belief of King George III that it would violate his Coronation Oath. Pitt resigned when the King's opposition became known, as he was unable to fulfill his pledge. Catholic emancipation then became a debating point rather than a major political issue.
The increasing number of Irish Catholics serving in the British army led to the army giving freedom of worship to Catholic soldiers in 1811.[2] Their contribution in the Napoleonic wars may have contributed to the support of Wellington (himself Irish-born, though Protestant) for emancipation.

Developments of the 1820s
In 1823, Daniel O'Connell started a campaign for emancipation by establishing the Catholic Association. In 1828 he stood for election in County Clare in Ireland and was elected even though he could not take his seat in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom. He repeated this feat in 1829.
O'Connell's manoeuvres were important, but the decisive turning point came with the change in public opinion in Britain in favour of emancipation. Politicians understood the critical importance of public opinion. They were influenced as well by the strong support for the measure by the Whigs in the House of Lords and by the followers of Lord Grenville (1759–1834). The increasing strength of public opinion, as expressed in the newspapers and elections over a twenty-year period, overcame religious bias and deference to the crown, first in the House of Commons and then in the House of Lords. Every member of parliament elected after 1807, with one exception, announced his support for Emancipation. Despite this, the votes in the House of Lords were consistently negative, in part because of the king's own opposition. The balance of opinion in the House of Lords shifted abruptly in 1828–29 in response to public opinion, especially reflecting fear of a religious civil war in Ireland. In 1828 the Sacramental Test Act removed the barrier that required certain public officials to be members of the established Church.
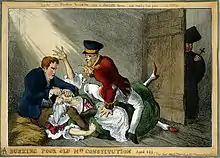
Finally, the Duke of Wellington and Sir Robert Peel changed positions and passed the Roman Catholic Relief Act of 1829. This removed many of the remaining substantial restrictions on Roman Catholics throughout the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. However, at the same time the minimum property qualification for voters was increased, rising from a rental value of forty shillings (£2) per annum to £10 per annum, substantially reducing the number of those entitled to vote, although after 1832 the threshold was again lowered in successive Reform Acts. The major beneficiaries were the Roman Catholic middle classes, who could now enter careers in the higher civil service and in the judiciary. The year 1829 is therefore generally regarded as marking the chief moment of Emancipation in Britain and Ireland.[3]
The obligation, however, to pay tithes to the established Anglican church in Ireland remained, resulting in the Tithe War of the 1830s, and many other minor disabilities remained. A series of further reforms were introduced over time.
Continuing disabilities: Acts of Settlement 1701 and 1705
The Act of Settlement and the Bill of Rights 1689 provisions on the monarchy still discriminate against Roman Catholics. The Bill of Rights requires a new monarch to swear a coronation oath to maintain the Protestant religion and asserts that "it hath been found by experience that it is inconsistent with the safety and welfare of this Protestant Kingdom to be governed by a Papist Prince".
The Act of Settlement (1701) went further, limiting the succession to the heirs of the body of Sophia of Hanover, provided that they do not "professe the Popish religion", "marry a Papist", "be reconciled to or ... hold Communion with the See or Church of Rome".
A Roman Catholic heir can therefore only inherit the throne by changing religious allegiance. Ever since the Papacy recognized the Hanoverian dynasty in January 1766, none of the immediate royal heirs has been a Roman Catholic, and thereby disallowed by the Act. Many more distantly related potential Roman Catholic heirs are listed on the line of succession to the British throne. Section 2 of the Succession to the Crown Act 2013, and similar provisions in the law of other signatories to the Perth Agreement, allow marriage by such an heir to a Roman Catholic.
Political results
The slowness of liberal reform between 1771 and 1829 led to much bitterness in Ireland, which underpinned Irish nationalism until recent times. Fresh from his success in 1829, O'Connell launched his Repeal Association in the 1830s and 1840s, hoping but failing to repeal the Acts of Union 1800.
It was not until the 1920s that the last of the disabilities were removed from the statute book by MP Francis Blundell.[4]
Comparative reforms in Europe
The Persecution of Huguenots under Louis XV had diminished by 1764. The dechristianization of France in 1790–1801, the anti-Catholic Kulturkampf in Germany in the 1870s and the progress of Jewish emancipation present interesting comparisons of toleration at the European level. Protestant sentiments in Ireland, on the other hand, were greatly alarmed by the possibility of Roman Catholic political influence on future governments, which brought about equally long-lasting bitter resistance by the Orange Order, alleging that "Home Rule was Rome Rule". Liberal rights came slowly to the Papal States as well, and well-publicised cases such as the Mortara affair were a concern to liberals in America and Europe in the 1860s.
Emancipation in Canada
Roman Catholics in Quebec had a grandfathered level of religious freedom, including the ability to serve in that colony's legislative body without having to take a Test Oath denouncing their faith. This policy continued in both successor provinces of Lower Canada and Upper Canada. The prohibitions and restrictions on Catholic participation in legislative affairs elsewhere in British North America applied until 1823, when Laurence Kavanagh was seated in the Nova Scotia House of Assembly as the first representative of Cape Breton Island and the first English-speaking Roman Catholic to serve in a legislature in the Atlantic provinces.
Emancipation in Newfoundland
The granting of Roman Catholic emancipation in Newfoundland was less straightforward than it was in Ireland, and this question had a significant influence on the wider struggle for a legislature. Almost from its first settlement, Newfoundland had a significant population of Roman Catholics, largely because George Calvert, 1st Baron Baltimore, was the founding proprietor of the Province of Avalon on Newfoundland's Avalon Peninsula. After Calvert himself converted to Rome in 1625, he migrated to Avalon, intending his colony there to serve as a refuge for his persecuted fellow-religionists. Newfoundland, however, like Calvert's other colony in the Province of Maryland, ultimately passed out of the Calvert family's control, and its Roman Catholic population became subject to essentially the same religious restrictions that applied in other areas under British control. In the period from 1770 to 1800, the Governors of Newfoundland had begun to relax restrictions on Roman Catholics, permitting the establishment of French and Irish missions. On visiting St. John's in 1786, Prince William Henry (the future King William IV) noted that "there are ten Roman Catholics to one Protestant",[5] and the Prince worked to counter the early relaxations of ordinances against this substantial majority.[6]
News of emancipation reached Newfoundland in May 1829, and 21 May was declared a day of celebration. In St. John's there was a parade and a thanksgiving Mass was celebrated at the Chapel, attended by the Benevolent Irish Society and the Catholic-dominated Mechanics' Society. Vessels in the harbour flew flags and discharged guns in salute.
Most people assumed that Roman Catholics would pass unhindered into the ranks of public office and enjoy equality with Protestants. But on 17 December 1829, the attorney general and supreme court justices decided that the Roman Catholic Relief Act did not apply to Newfoundland, because the laws repealed by the act had never applied there, being a colony and not part of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. As each governor's commission had been granted by royal prerogative and not by the statute laws of the British Parliament, Newfoundland had no choice but to be left with whatever existing local regulations discriminated against Roman Catholics.
On 28 December 1829 the St. John's Roman Catholic Chapel was packed with an emancipation meeting, where petitions were sent from O'Connell to the British Parliament, asking for full rights for Newfoundland Roman Catholics as British subjects. More than any previous event or regulation, the failure of the British government to grant emancipation renewed the strident claims by Newfoundland Reformers for a colonial legislature. There was no immediate reaction from London, but the question of Newfoundland was now before the British Colonial Office. It was not until May 1832 that the British Secretary of State for the Colonies formally stated that a new commission would be issued to Governor Cochrane to remove any and all Roman Catholic disabilities in Newfoundland.[7]
Related topics leading up to Catholic emancipation
- Gunpowder Plot 1605–1606
- Popish Recusants Act 1605
- Test Act 1673
- Declaration of Indulgence 1687
- Bill of Rights 1689
- Act of Toleration 1689
- Penal laws
- Education Act 1695
- Disarming Act 1695
- Marriage Act 1697
- Banishment Act 1697
- Registration Act 1704
- Popery Act 1704 and 1709
- Occasional Conformity Act 1711
- Disenfranchising Act 1728
- Roman Catholic Relief Bills 1778 and 1793
- Gordon Riots 1780
- Act of Union 1800
- Test Acts Repealed 1828
- Roman Catholic Relief Act 1829
Organisations:
References
- Petition to King George III.
- Hansard XIX, 11 March 1811. cc.350-356.
- Davis, 1999
- "The Lord Lieutenant". Merseyside Lieutenancy. Retrieved 11 May 2018.
- Memorial University, Note 87: PWH to King, 21 September 1786, Later Correspondence of George III, Vol. 1, 251.
- Newfoundland, Memorial University of. "Department of Religious Studies". Memorial University of Newfoundland. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- John P. Greene, Between Damnation and Starvation: Priests and Merchants in Newfoundland Politics, 1745–1855 (1999).
Further reading
- Davis, Richard W. "The House of Lords, the Whigs and Catholic Emancipation 1806–1829," Parliamentary History, March 1999, Vol. 18 Issue 1, pp 23–43
- Greene, John P. Between Damnation and Starvation: Priests and Merchants in Newfoundland Politics, 1745–1855 (1999).
- Keenan, Desmond. The Grail of Catholic Emancipation 1793 to 1829 (2002)
- Liedtke, Rainer, and Stephan Wendehorst, eds. The Emancipation of Catholics, Jews and Protestants: Minorities and the Nation-State in Nineteenth-Century Europe (1999)
- Linker, R. W. "The English Roman Catholics and Emancipation: The Politics of Persuasion," Journal of Ecclesiastical History, April 1976, Vol. 27 Issue 2, pp 151–180
- O'Ferrall, Fergus. Catholic Emancipation: Daniel O'Connell and the Birth of Irish Democracy, 1820–30 (1987)
- Reynolds, James A. The Catholic Emancipation Crisis in Ireland, 1823–1829 (1970)
- Ward, Bernard. The Eve of Catholic Emancipation, Vol. 3 (2010)
