Companhia Paulista de Trens Metropolitanos
Companhia Paulista de Trens Metropolitanos (CPTM) (English: São Paulo Metropolitan Trains Company) is a rapid transit and commuter rail company owned by the São Paulo State Department for Metropolitan Transports. It was created on May 28, 1992 from several railroads that already existed in Greater São Paulo, Brazil.
.svg.png.webp) | |||
 | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Owner | São Paulo Government, Mixed Economy | ||
| Locale | Greater São Paulo | ||
| Transit type | Rapid transit and commuter rail | ||
| Number of lines | 7 | ||
| Number of stations | 94 | ||
| Daily ridership | 3,000,000 (2019) | ||
| Annual ridership | 863,300,000 (2018)[1] | ||
| Chief executive | Pedro Tegon Moro | ||
| Headquarters | Rua Boa Vista, 185, Centro | ||
| Website | www | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | May 28, 1992 | ||
| Operator(s) | |||
| Number of vehicles | 213 (2018) | ||
| Headway | 4′ to 35′ | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 273.0 kilometres (169.6 mi) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,600 mm (5 ft 3 in) | ||
| Electrification | 3,000 V DC catenary | ||
| Average speed | 60 km/h (37 mph) | ||
| Top speed | 90 km/h (56 mph) | ||
| |||
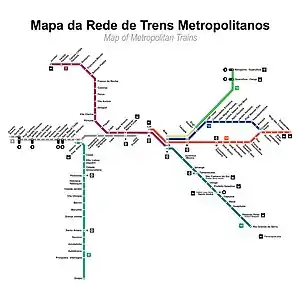
Part of the Greater São Paulo rail network, CPTM has 94 stations in seven lines, with a total length of 273.0 kilometres (169.6 mi). The system carries about 3 million passengers a day. On December 7, 2018, CPTM set a weekday ridership record with 3,221,035 trips.[2]
History
Most of railways now run by CPTM were built between 1860 and 1957 by the São Paulo Railway (lines 7 and 10), Estrada de Ferro Sorocabana (lines 8 and 9) and Estrada de Ferro Central do Brasil (lines 11 and 12). These railways were eventually incorporated into the state-owned Rede Ferroviária Federal (RFFSA) in 1957 and Ferrovia Paulista S.A. (FEPASA) 1971. Finally, in 1992 the urban sections of RFFSA and FEPASA merged, forming CPTM.
Between the end of the 1990s and the early 2000s, CPTM began the conversion of some metropolitan lines to provide a service similar to rapid transit and better integrate with the São Paulo Metro. Most of the stations where either rebuilt or modernized and new trains were purchased allowing the headway of lines to be as low as four minutes in some lines. This experience started in Line E in the year 2000, in the stretch known as "East Express", serving the east end of São Paulo City and running parallel to Line 3 - Red.
The proposed Trens Intercidades regional railway project is considering using Line 7 tracks for providing service to neighboring cities of Jundiaí, Campinas and Americana.[3][4]
In 2018, CPTM opened Line 13, the first line completely built and operated by the company. This line connects Line 12 to the São Paulo–Guarulhos International Airport, with a special Express service connecting it to the central Luz station, and another service connecting it to the Brás station, both only operating on a specific schedule.[5]
Operation
CPTM operates seven lines in the Greater São Paulo area, identified by number and color. Most of these lines run on existing surface tracks that continue out of Greater São Paulo as MRS Logística intercity freight lines and share right of way with freight trains. The more lightly used outer sections of several lines have level crossings.
Service starts every day at 4 AM, when trains depart from each terminus, until the last train leaves at midnight. On Saturdays operation is extended until 1 AM.
The company charges a flat fare that can be paid either by magnetic ticket sold in the stations or with a rechargeable smartcard, and grants access to any of the rail lines on the Greater São Paulo, including lines operated by the São Paulo Metro.
Lines
| Line | Color | Terminus | Length | Stations | Daily ridership (Apr 2019)[6] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line 7 | Ruby | Brás ↔ Jundiaí | 62.7 kilometres (39.0 mi) | 19 | 473,400 |
| Line 8 | Diamond | Júlio Prestes ↔ Itapevi | 35.2 kilometres (21.9 mi) | 20 | 521,000 |
| Line 9 | Emerald | Osasco ↔ Grajaú | 31.8 kilometres (19.8 mi) | 18 | 613,000 |
| Line 10 | Turquoise | Brás ↔ Rio Grande da Serra | 34.9 kilometres (21.7 mi) | 14 | 391,000 |
| Line 11 | Coral | Luz ↔ Estudantes | 50.8 kilometres (31.6 mi) | 16 | 752,800 |
| Line 12 | Sapphire | Brás ↔ Calmon Viana | 38.8 kilometres (24.1 mi) | 13 | 272,000 |
| Line 13 | Jade | Engenheiro Goulart ↔ Aeroporto–Guarulhos | 12.2 kilometres (7.6 mi) | 3 | 13,300 |
Operational Extensions
| Line | Color | Terminals | Length | Stations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line 8 | Diamond | Itapevi ↔ Amador Bueno | 6.3 kilometres (3.9 mi) | 3 | Commute on this operational extension is free of charge, a fare being required to access the rest of the system on Itapevi station. |
Expansion
| Line | Color | Terminals | Length | Stations | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line 9 | Emerald | Grajaú ↔ Varginha | 4.36 kilometres (2.71 mi) | 2 | Under construction |
Express services
| Line | Color | Terminals | Length | Stations | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Line 13 | Jade (Airport Express)[7] | Luz ↔ Aeroporto-Guarulhos | 28.3 kilometres (17.6 mi) | 4 | |
| Line 10 | Turquoise (Expresso Linha 10[8]/Expresso Educação Linha 10[9]) | Tamanduateí ↔ Prefeito Celso Daniel-Santo André | 9.2 kilometres (5.7 mi) | 3 | |
| Line 10 | Turquoise (Expresso Linha 10+)[10] | Luz ↔ Prefeito Celso Daniel-Santo André | 17.7 kilometres (11.0 mi) | 5 |
Gallery
 Internal view of a 2000 Series CPTM train
Internal view of a 2000 Series CPTM train Luz Station.
Luz Station. CPTM 2070 Series train in Brooklin CBD.
CPTM 2070 Series train in Brooklin CBD. Ferraz de Vasconcelos Station.
Ferraz de Vasconcelos Station.
See also
References
- "RELATÓRIO INTEGRADO DA ADMINISTRAÇÃO 2018" (PDF). empresaspublicas.imprensaoficial.com.br. 8 March 2019. Retrieved 31 August 2020.
- https://www.cptm.sp.gov.br/a-companhia/BalancosDemonstrativos/Relat%c3%b3rio%20Integrado%20CPTM%202018.pdf
- "Trem Intercidades entre SP e Campinas pode ser um serviço expresso da Linha 7". Metrô CPTM (in Portuguese). 2019-01-16. Retrieved 2019-05-01.
- "Governo do estado surpreende com projeto de levar Linha 7-Rubi até Campinas". Metrô CPTM (in Portuguese). 2018-09-05. Retrieved 2019-05-01.
- "Aeroporto | CPTM". cptm.sp.gov.br. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- "A Companhia". CPTM (in Portuguese). 2019-10-15. Retrieved 2019-10-15.
- "CPTM oferece três diferentes opções para chegar ao Aeroporto de Guarulhos | CPTM". cptm.sp.gov.br. Retrieved 2020-05-21.
- "CPTM lança serviço Expresso Linha 10 | CPTM". www.cptm.sp.gov.br. Retrieved 2020-06-01.
- "CPTM inicia operação do Expresso Educação Linha 10 nesta segunda (10/02) | CPTM". www.cptm.sp.gov.br. Retrieved 2020-06-01.
- "CPTM lança trem expresso aos sábados entre Santo André e Luz, na Linha 10-Turquesa | CPTM". www.cptm.sp.gov.br. Retrieved 2020-06-01.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Companhia Paulista de Trens Metropolitanos. |
- (in Portuguese) Official page of the CPTM
- (in Portuguese) Secretaria dos Transportes Metropolitanos