Conosa
Conosa is a grouping of Amoebozoa. It is subdivided into three groups – Archamoebae, Variosea (paraphyletic) and Mycetozoa (polyphyletic).[1][2]
| Conosa | |
|---|---|
 | |
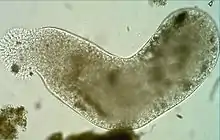
| Dictyostelium discoideum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Phylum: | Amoebozoa |
| Subphylum: | Conosa Cavalier-Smith, 1998 |
| Infraphyla | |
In some classifications, the mycetozoan Myxogastria and Dictyostelia are united in Macromycetozoa.
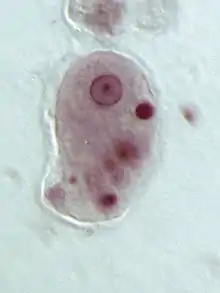
Conosa includes the species Dictyostelium discoideum and Entamoeba histolytica, among others.[3]
References
- Cavalier-Smith T (August 1998). "A revised six-kingdom system of life". Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 73 (3): 203–66. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.1998.tb00030.x. PMID 9809012. Archived from the original on 2012-12-05.
- Bapteste E, Brinkmann H, Lee JA, et al. (February 2002). "The analysis of 100 genes supports the grouping of three highly divergent amoebae: Dictyostelium, Entamoeba, and Mastigamoeba". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (3): 1414–9. doi:10.1073/pnas.032662799. PMC 122205. PMID 11830664.
- Song J, Xu Q, Olsen R, et al. (December 2005). "Comparing the Dictyostelium and Entamoeba genomes reveals an ancient split in the Conosa lineage". PLoS Comput. Biol. 1 (7): e71. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0010071. PMC 1314882. PMID 16362072.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.