Dihydroquinine
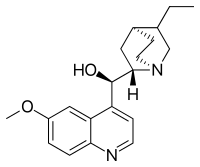
Dihydroquinine, also known as hydroquinine,[1] is an organic compound and as a cinchona alkaloid closely related to quinine. The specific rotation is −148° in ethanol. A derivative of this molecule is used as chiral ligand in the AD-mix for Sharpless dihydroxylation.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(R)-[(2S,4S,5R)-5-ethyl-1-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octan-2-yl]-(6-methoxyquinolin-4-yl)methanol | |
| Other names
(8α,9R)-10,11-Dihydro-6'-methoxycinchonan-9-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.578 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H26N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 326.440 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 173–175 °C |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
See also
References
- "Dihydroquinine chemical information". ChemIndustry.com.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.