Etterbeek
Etterbeek (French: [ɛtəʁbek]; Dutch: [ˈɛtərˌbeːk] (![]() listen)) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region (Belgium). It neighbours the municipalities of Auderghem, the City of Brussels, Ixelles, Schaerbeek, Woluwe-Saint-Lambert and Woluwe-Saint-Pierre. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch).
listen)) is one of the 19 municipalities of the Brussels-Capital Region (Belgium). It neighbours the municipalities of Auderghem, the City of Brussels, Ixelles, Schaerbeek, Woluwe-Saint-Lambert and Woluwe-Saint-Pierre. In common with all of Brussels' municipalities, it is legally bilingual (French–Dutch).
Etterbeek | |
|---|---|
 Etterbeek town hall | |
 Flag  Coat of arms | |
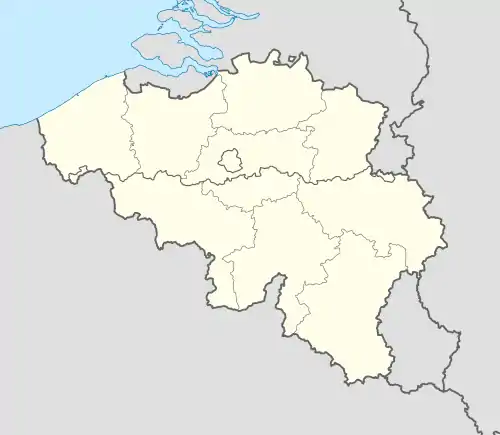 Etterbeek Location in Belgium
Etterbeek municipality in the Brussels-Capital Region 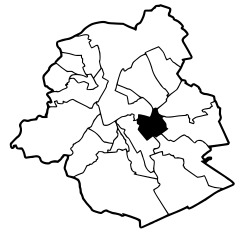 | |
| Coordinates: 50°50′N 04°23′E | |
| Country | Belgium |
| Community | Flemish Community French Community |
| Region | Brussels |
| Arrondissement | Brussels |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Vincent De Wolf (MR) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 3.15 km2 (1.22 sq mi) |
| Population (2018-01-01)[1] | |
| • Total | 47,786 |
| • Density | 15,000/km2 (39,000/sq mi) |
| Postal codes | 1040 |
| Area codes | 02 |
| Website | www.etterbeek.be |
The main university campus of Vrije Universiteit Brussel is called Campus Etterbeek, although it is geographically not within Etterbeek but in the adjacent municipality of Ixelles.
History
Origins and etymology
According to legend, St. Gertrude, daughter of Pippin of Landen, founded a chapel there in the 8th century. A document by Holy Roman Emperor Otto I, dated 966, mentions the church of Iatrebache. The name Ietrebecca – possibly from the Celtic root ett meaning "rapid movement" and the Dutch word beek meaning "stream" – is found for the first time in a document dated 1127. The current spelling appears eleven years later in 1138, around which time a newer and larger church was built.
Middle Ages
%252C_naar_Hans_Bol%252C_Jacob_Grimmer%252C_1530_-_1580.jpg.webp)
In the Middle Ages, Etterbeek was a rural hamlet mostly independent of Brussels, aside from taxation rights on beer given to Brussels around 1300 by John II, Duke of Brabant. The following two centuries counted several grievous moments: in 1489, Albert III, Duke of Saxony ravaged Etterbeek in his pursuit of the rebels who fought against Maximilian of Austria; in 1580, the village was destroyed again, this time by the iconoclasts during the Protestant Reformation wars. Peace returned under the reigns of Archdukes Albert and Isabella.
Barony and municipality
In 1673, Etterbeek gained its independence from neighbouring Sint-Genesius-Rode, when Charles II of Spain promoted it into a barony. The first baron was Don Diego-Henriquez de Castro, general treasurer of the Netherlands armies. The Castro house was sold in 1767 and can still be seen today as Etterbeek's oldest building.
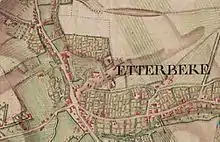
Under the French regime, Etterbeek was made into a commune, within the canton of Sint-Stevens-Woluwe. From then on, and especially after the Belgian Revolution of 1830 and the development of Brussels as a capital city, the population of Etterbeek grew quickly. In 1876, there were more than 10,000 inhabitants, in 1900 more than 20,000, and in 1910 more than 33,000. In the 1900s (decade), under the reign of Leopold II, construction boomed and changed the town's character with the addition of the broad avenues and residential areas that we know today.
Places of interest
- Two Roman Catholic churches are located in Etterbeek: the Church of Saint Anthony of Padua and the Church of Our Lady of the Sacred Heart. A third church – the Church of Saint Gertrude – was demolished in 1993, as it was in danger of collapsing.
- The Cauchie house was built in 1905 by the Art Nouveau architect, painter, and designer Paul Cauchie. Its facade is remarkable for its allegorical sgraffiti.
- Of a completely different character, the Barony house dates from 1680 and is the oldest building in the municipality.
- The Fondation René Carcan, a foundation and museum in René Carcan's old studio, was located in Etterbeek.
- Chaussée de Wavre/Waversesteenweg has, since 27 September 2014, featured a series of large scale Le Chat drawings by the Belgian cartoonist Philippe Geluck, who was born and raised in this neighbourhood. The 24 drawings extend over a total length of 120 metres (390 feet).[2]
- Etterbeek has a few green areas, including the Jean-Felix Hap garden. The better known Cinquantenaire park lies on the territory of both the City of Brussels and Etterbeek and Leopold Park borders the municipality's territory.

Barony house (1680) 
A typical Etterbeek street: Rue des Boers/Boerenstraat 
Cauchie house by Paul Cauchie (1905) 
Sgraffito panel in the Cauchie house 
Place Jourdan 
Jean Felix Hap garden
Transportation
Etterbeek is served by Etterbeek railway station but, like the neighbouring campus of the Vrije Universiteit Brussel, it is also located in Ixelles. Etterbeek currently has one rail station (Mérode) and three metro stations (Mérode, Thieffry and Pétillon).
Sports
- Etterbeek hosts two football clubs (R.R.C. Etterbeek and Armenia) playing in Belgian Provincial leagues at the Guy Thys stadium, thus named after the famous Belgian manager since 2003. He led Belgium national football team to fourth place at the 1986 FIFA World Cup.
- In the summer of 1996, the municipal swimming pool burnt down. It has now been rebuilt and is again open to the public.
Proposed redevelopment "Les Jardins de la Chasse"
A project is currently proposed to redevelop an area of Etterbeek near Avenue des Casernes/Kazernelaan. This project would result in the town hall and police station being relocated to new buildings in a central administrative centre on this site.[3] The new site is being called the Jardins de la Chasse in French or Tuinen van de Jacht in Dutch. Demolition of the former CPAS building on the site started in 2014,[4] and building of houses on the site started in 2016, with construction of the new town hall awaiting administrative approval.[5] Municipal offices are forecast to move to the new location in summer 2018. The site of the current town hall may in the future be used for further residential development.[4]
Events

Etterbeek hosts an annual medieval market. Previously held at the end of May on Avenue du 2ème Régiment de Lanciers/2de Lansiers Regimentlaan to the south of the municipality, in recent years it has taken place at the Cinquantenaire.
Notable residents
Born in Etterbeek:
- Jérôme d'Ambrosio (b. 1985), racing driver
- Jean Brachet (1909–1998), biochemist
- Monique De Wael a.k.a. Misha Defonseca (b. 1937), writer of Misha: A Mémoire of the Holocaust Years
- Pierre Deligne (b. 1944), Fields Medal-winning mathematician
- François Englert (b. 1932), Nobel Prize–winning physicist
- Giani Esposito (1930–1974), actor
- Lara Fabian (b. 1970), international singer
- Philippe Francq (b. 1961), comic book artist
- André Franquin (1924–1997), cartoonist, creator of Gaston and Marsupilami
- Philippe Geluck (b. 1954), comics writer and artist, creator of Le Chat[6]
- Georges Grün (b. 1962), football defender
- Georges Remi a.k.a. Hergé (1907–1983), comics writer and artist, creator of The Adventures of Tintin
- Arthur Maurice Hocart (1883–1939), anthropologist
- Daniel Hulet (1942–2011), cartoonist
- Roland Lethem (b. 1942), filmmaker and writer
- Alexandre de Merode (1934–2002), member of the International Olympic Committee (IOC)
- Constantin Meunier (1831–1905), painter and sculptor
- Amélie Nothomb (b. 1966), writer
- René Kalisky (1936–1981), playwright, novelist, essayist, journalist, historian
- Charles Picqué (b. 1948), politician, freemason, and mayor of Saint-Gilles
- Godelieve Quisthoudt-Rowohl (b. 1947), German politician
- Richard Makela a.k.a. Monsieur R (b. 1975), rap artist
- Andre Sapir (b. 1950), economist
- Stromae (b. 1985), singer
- Herman Van Rompuy (b. 1947), politician and first permanent President of the European Council
- Marouane Fellaini
Lived part of their life in Etterbeek:
- Jean Absil (1893–1974), composer and organist
- Jean-Baptiste Baronian (b. 1942), Belgian-Armenian writer
- René Carcan (1925–1993), engraver and sculptor
- Adrien de Gerlache (1866–1934), officer of the Belgian Navy and leader of the Belgian Antarctic Expedition
- W.F. Hermans (1921–1995), Dutch writer
- Edgar Pierre Jacobs (1904–1987), comic book artist, creator of Blake and Mortimer
- Gaston Salmon (1878–1917), épée fencer, Olympic champion
Buried in Etterbeek:
- Moise Tshombe (1919–1969), Congolese politician
International relations
Etterbeek is twinned with:
References
- "Wettelijke Bevolking per gemeente op 1 januari 2018". Statbel. Retrieved 9 March 2019.
- "Journal La Vie Etterbeekoise Octobre 2014" (pdf) (in French).
- "Les Jardins de la Chasse" (pdf) (in French). Retrieved 12 October 2008.
- Julien Thomas (22 September 2014). "Les Jardins de la Chasse verront le jour d'ici 2019" (in French). dh.be. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
- Patrice Leprince (1 February 2016). "Etterbeek: les Jardins de la Chasse se profilent" (in French). Le Soir. Retrieved 23 January 2017.
- "Journal La Vie Etterbeekoise Octobre 2014" (pdf) (in French).
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Etterbeek. |
- Official website of Etterbeek, in French and Dutch
