Eymoutiers
Eymoutiers (Occitan: Aimostier) is a commune in the Haute-Vienne department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region in western France.
Eymoutiers | |
|---|---|
 The church and surrounding buildings in Eymoutiers | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Eymoutiers 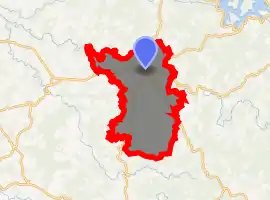
| |
 Eymoutiers  Eymoutiers | |
| Coordinates: 45°44′24″N 1°44′36″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Nouvelle-Aquitaine |
| Department | Haute-Vienne |
| Arrondissement | Limoges |
| Canton | Eymoutiers |
| Intercommunality | Portes de Vassivière |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | Mélanie Plazanet |
| Area 1 | 70.22 km2 (27.11 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 2,062 |
| • Density | 29/km2 (76/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 87064 /87120 |
| Elevation | 316–758 m (1,037–2,487 ft) |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
Inhabitants are known as Pelauds.
History
The foundation of Eymoutiers can be traced back to a church and a monastery associated with Saint Psalmodius (Psalmet), who had been a hermit in this area. A native of either Ireland or Scotland, Psalmodius became a hermit in a small cell in the forest of Grigeas or Grie, in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine near Eymoutiers. He acquired the name of Psalmodius (his original Celtic name is unknown) because he loved to sing psalms.[2][3]
When Psalmodius died, he was buried on the banks of the Vienne River. A church was built over his tomb; later a monastery was attached to it. The monastery was at the foot of the hill ("ayen-moutiers"), a description that turned into the place-name of Eymoutiers.
A settlement developed around the monastery and it fell under the jurisdiction of the bishop of Limoges. A bishop of Limoges built a castle here, but today no traces of it remain. In 1428, Eymoutiers became a bishopric on its own right. Thus free and independent, the city became a walled town.
Eymoutiers subsequently obtained a large Calvinist population. The city walls were destroyed during the Wars of Religion. In 1629, the Ursulines became established in the city on the order of Monseigneur François de La Fayette and a school for girls was established in the city. A school for boys was built later, in 1778, by Monseigneur Louis de Plessis d'Argentré.
At the beginning of the 16th century, Eymoutiers developed into a center for the tanning trade, which reached its apogee in the 18th century. The city had 20 tanneries by 1628, located on the banks of the Vienne. The inhabitants thus acquired the nickname of pelauds (skin-peelers). The local tanners formed a confraternity in the 17th century. It had religious and secular purposes. The brotherhood celebrated masses and did charity work, but also held 5 annual banquets for its members.
During World War II, the Maquis du Nouvelle-Aquitaine operated in Eymoutiers, and on March 13, 1943, French resistance leader Georges Guingouin sabotaged the viaduct of Bussy-Varache, on the Limoges-Ussel railway line.[4]
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- Alban Butler, The Lives of the Fathers, Martyrs, and Other Principal Saints (B. Dornin, 1821), 213.
- John O’Hanlon, Lives of the Irish Saints (Original from Oxford University, 1873. Digitized Aug 30, 2006), 658.
- http://perso.orange.fr/ecole.eymoutiers/Normal/guingouin.htm
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Eymoutiers. |