Limoges
Limoges (/lɪˈmoʊʒ/,[2][3] also US: /liːˈ-/,[2][4] French: [limɔʒ] (![]() listen);[2] Occitan: Lemòtges, locally Limòtges [liˈmɔdzes]) is a city and commune, the capital of the Haute-Vienne department and was the administrative capital of the former Limousin region in west-central France. Situated on the first western foothills of the Massif Central, Limoges is crossed by the Vienne River, of which it was originally the first ford crossing point.
listen);[2] Occitan: Lemòtges, locally Limòtges [liˈmɔdzes]) is a city and commune, the capital of the Haute-Vienne department and was the administrative capital of the former Limousin region in west-central France. Situated on the first western foothills of the Massif Central, Limoges is crossed by the Vienne River, of which it was originally the first ford crossing point.
Limoges
| |
|---|---|
Prefecture and commune | |
 City Hall | |
 Coat of arms | |
Location of Limoges 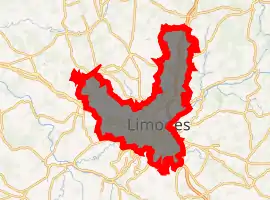
| |
 Limoges  Limoges | |
| Coordinates: 45°50′07″N 1°15′45″E | |
| Country | France |
| Region | Nouvelle-Aquitaine |
| Department | Haute-Vienne |
| Arrondissement | Limoges |
| Canton | Limoges-1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 |
| Intercommunality | CU Limoges Métropole |
| Government | |
| • Mayor (2020–2026) | Emile-Roger Lombertie |
| Area 1 | 77.45 km2 (29.90 sq mi) |
| Population (2017-01-01)[1] | 132,175 |
| • Density | 1,700/km2 (4,400/sq mi) |
| • Metro (2015) | 283,823 |
| Time zone | UTC+01:00 (CET) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC+02:00 (CEST) |
| INSEE/Postal code | 87085 /87000 |
| Elevation | 209–431 m (686–1,414 ft) (avg. 294 m or 965 ft) |
| Website | www.ville-limoges.fr |
| 1 French Land Register data, which excludes lakes, ponds, glaciers > 1 km2 (0.386 sq mi or 247 acres) and river estuaries. | |
The second most populated town in the New Aquitaine region after Bordeaux, a university town, an administrative centre and intermediate services with all the facilities of a regional metropolis, its has an urban area of 283,557 inhabitants in 2016, making it the sixth in South-West France and the 38th in the whole country.The inhabitants of the city are called the Limougeauds.
Founded around 10 BC under the name of Augustoritum, it became an important Gallo-Roman city. In the Middle Ages Limoges becomes a large city, strongly marked by the cultural influence of the Abbey of Saint-Martial, within the Duchy of Aquitaine, whose dukes are invested and crowned in this city. From the 12th century onwards, its enamels were exported throughout the Christian world. In 1765, during the industrial revolution, the discovery of a deposit of kaolin in the Saint-Yrieix-la-Perche region enabled the development of the Limoges porcelain industry, which would make Limoges world-famous. Sometimes nicknamed "the red city" or "the Rome of socialism" because of its tradition of voting on the left and the workers' events it experienced from the 19th to the beginning of the 20th century.
Since the 1990s, the city has also been associated with its basketball club, Limoges CSP, which has won several French championships and the European championship in 1993. Because of its heritage policy, it has held the label "City of Art and History" since 2008. A city with a tradition of butchery, home to one of the world leaders in electrical equipment for the building industry, it is also well positioned in the luxury goods industry. Known and recognised as the "capital of the arts of fire" because of the ever-present presence of the great porcelain houses, its art workshops working with enamel or stained glass. This specificity has led it to join the UNESCO Creative Cities Network in 2017 in the thematic category "Crafts and Popular Arts".
History
Ancient and medieval history
Scarce remains of pre-urban settlements have been found in the area of Limoges. The capital of the Gaulish people of the Lemovices, who lived in the area, was probably either near Villejoubert, some kilometres south-east of Saint-Léonard-de-Noblat, or St Gence, just west of Limoges.
The city proper was founded as Augustoritum by the Romans, around 10 BC: "rito-" is Gaulish for "ford". The foundation was part of the reorganization of the province by the emperor Augustus, hence the new name. The Roman city included an amphitheatre measuring 136 x 115 metres, a theatre, a forum, baths and several sanctuaries. According to tradition, a temple consecrated to Venus, Diana, Minerva and Jupiter was located near the modern cathedral. The city was on the typical Roman square plan, with two main streets crossing in the centre. It had a Senate and a currency of its own, a sign of its importance in the imperial age. Later, like many towns and cities in Gaul, it was renamed after the tribe (here the Lemovices) whose chief town it was; "Lemovices" subsequently evolved into "Limoges", and "Lemovicinus" for the area around changed into "Limousin".
Limoges was evangelized by Saint Martial, who came to the city around 250 with two companions, Alpinianus and Austriclinienus. However, in the late 3rd century it was increasingly abandoned, due to unsafe conditions created by the invasions of various Germanic tribes. The population was concentrated instead in a more easily fortifiable site, the modern Puy Saint-Étienne, which is the centre of the modern Limoges. Starting from the construction of the Abbey of St. Martial (9th century), another settlement grew around the tomb of the saint, while a third area, next to the residence of the viscount (the future Castle of Saint Martial), seems to have been populated from the 10th century.
Starting from the 11th century, thanks to the presence of the Abbey of St. Martial and its large library, Limoges became a flourishing artistic centre. It was home to an important school of medieval music composition, which is usually called the St. Martial School; its most famous member was the 13th-century troubadour Bertran de Born.

In the 13th century, at the peak of its splendour, central Limoges consisted of two fortified settlements.
- The town proper, with a new line of walls encompassing the Vienne River, inhabited mainly by clerks and workers. It has a bridge on the Vienne river named after Saint-Étienne, built by the bishops, and a developed port. Sacked in 1370, it never recovered entirely.
- The castle, with 12 meter-high walls, including the abbey and controlled by the abbot, sometimes in contrast with the bishop-ruled town ("la Cité"). Traces of the walls can still be seen in the city centre. Outside the lines of walls were the popular quarters.
In 1370, Limoges was occupied by Edward, the Black Prince, who massacred some 300 residents, "perhaps a sixth of the normal population", with another 60 members of the garrison of 140 dead as well.[6]
Modern history

The porcelain industry started to develop, favoured by the presence of kaolinite which was discovered near Limoges in 1768[7] (near St Yrieix, south-west of Limoges). Many of the inhabitants became employed in the new sector or in connected activities (including the lumbering of wood needed for firing the porcelain) in manufacture and exporting needed for European distribution of Limoges Boxes, dinnerware, and other porcelain wares. Because the Limousin region has had a long history of breeding (Baronet sheep and Limousine cows), the leather industry also settled in and around Limoges along the banks of the Vienne–the river providing the necessary water and power. Factories in Limoges and St Junien still produce luxury leather shoes, gloves, and bags.
The city and castle were united in 1792 to form the single city of Limoges. During the French Revolution several religious edifices, considered symbols of the Ancien Régime, were destroyed by the population: these included the Abbey of St. Martial itself.
In the 19th century Limoges saw strong construction activity, which included the destruction and rebuilding of much of the city centre. The unsafe conditions of the poorer population is highlighted by the outbreak of several riots, including that of July–November 1830 and April 1848. The first French confederation of workers, Confédération Générale du Travail (CGT) (General Confederation of Labour), was created in Limoges in 1895.
In early 1905 strikes began in another local industry, shoe factories soon followed in the porcelain factories. Barricades were built, the army intervened. There would be two casualties: a horse and a young porcelain worker, Camille Vardelle.
During World War II, many Jews from Alsace were evacuated to and around Limoges.
Sports
The city is one of France's basketball capitals. The Palais des Sports de Beaublanc, has been host for international basketball events such as the EuroBasket 1983 and serves as home court for the professional team CSP Limoges (Cercle St Pierre). Since 1983, the club has been French champion 11 times (1983, 1984, 1985, 1988, 1989, 1990, 1993, 1994, 2000, 2014, 2015) and 5 European titles (1982, 1983, 2000 (Korac Cup), 1988 (FIBA Saporta Cup), 1993 (Euroleague)). It was the first French club team to become European champion in a collective sport.[8][9] The team currently plays in Pro A, the French first basketball professional league.
Limoges Hand 87 is a French handball team based in Limoges, France, which is currently playing in the Division 2 of Ligue Nationale de Handball.
Limoges FC is the major city football team, currently playing in Championnat National 3 (Group A). Their home games are played at Stade St. Lazare. Limoges played in Division 1 from 1958 to 1961.
USA Limoges is an amateur rugby union club, based in Limoges. Currently competing in Fédérale 1, the top level of the French amateur rugby pyramid and one level below the professional leagues.
Climate
Limoges experiences an oceanic climate (Köppen climate classification Cfb) common to much of Western France. Most precipitation occurs between October and February. On 27 December 1999, winds reached 148 km/h. On average, the city undergoes 41 days of frost and seven days of snow each winter. In June, July and August, precipitation tends to come only from violent thunderstorms coming from the Bay of Biscay.
| Climate data for Limoges (LIG), elevation: 402 m (1,319 ft), 1981–2010 normals, extremes 1973–present | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 17.0 (62.6) |
23.1 (73.6) |
24.7 (76.5) |
27.8 (82.0) |
29.8 (85.6) |
36.2 (97.2) |
37.9 (100.2) |
37.2 (99.0) |
32.6 (90.7) |
27.3 (81.1) |
22.9 (73.2) |
18.3 (64.9) |
37.9 (100.2) |
| Average high °C (°F) | 6.9 (44.4) |
8.3 (46.9) |
11.5 (52.7) |
14.1 (57.4) |
18.0 (64.4) |
21.4 (70.5) |
23.9 (75.0) |
23.8 (74.8) |
20.4 (68.7) |
16.1 (61.0) |
10.4 (50.7) |
7.6 (45.7) |
15.2 (59.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 4.2 (39.6) |
5.0 (41.0) |
7.7 (45.9) |
10.0 (50.0) |
13.8 (56.8) |
17.0 (62.6) |
19.3 (66.7) |
19.1 (66.4) |
16.0 (60.8) |
12.5 (54.5) |
7.4 (45.3) |
4.9 (40.8) |
11.4 (52.5) |
| Average low °C (°F) | 1.5 (34.7) |
1.7 (35.1) |
3.9 (39.0) |
5.9 (42.6) |
9.5 (49.1) |
12.6 (54.7) |
14.6 (58.3) |
14.5 (58.1) |
11.7 (53.1) |
9.0 (48.2) |
4.5 (40.1) |
2.2 (36.0) |
7.7 (45.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −19.2 (−2.6) |
−15.0 (5.0) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−4.7 (23.5) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
4.0 (39.2) |
7.2 (45.0) |
5.4 (41.7) |
2.6 (36.7) |
−2.6 (27.3) |
−7.2 (19.0) |
−10.6 (12.9) |
−19.2 (−2.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 91.9 (3.62) |
79.8 (3.14) |
78.7 (3.10) |
90.8 (3.57) |
95.7 (3.77) |
77.5 (3.05) |
65.6 (2.58) |
75.0 (2.95) |
74.1 (2.92) |
93.4 (3.68) |
101.3 (3.99) |
99.7 (3.93) |
1,023.5 (40.30) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 1.0 mm) | 13.5 | 11.0 | 11.3 | 12.4 | 12.6 | 9.4 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 9.6 | 12.1 | 13.2 | 12.8 | 134.9 |
| Average snowy days | 4.6 | 3.8 | 2.7 | 2.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 1.7 | 3.0 | 18.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 85 | 80 | 76 | 71 | 75 | 73 | 71 | 72 | 75 | 80 | 82 | 84 | 77 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 86.0 | 104.0 | 156.8 | 167.7 | 204.9 | 227.4 | 238.2 | 231.0 | 191.5 | 133.3 | 81.4 | 77.6 | 1,899.8 |
| Source 1: Meteo France[10][11] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Infoclimat.fr (relative humidity 1961–1990)[12] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
In 2017, the population of the commune proper was 132,175, and of the Limoges urban area 283,556.[13] Inhabitants of Limoges are called limougeauds in French.[14]
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1968 | 133,019 | — |
| 1975 | 143,725 | +1.11% |
| 1982 | 140,418 | −0.33% |
| 1990 | 133,486 | −0.63% |
| 1999 | 133,994 | +0.04% |
| 2007 | 138,882 | +0.45% |
| 2012 | 136,221 | −0.39% |
| 2017 | 132,175 | −0.60% |
| Source: INSEE[15] | ||
Main sights



- The Crypt of Saint Martial, 10th century, including the tomb of the bishop who evangelized the city[16] It was discovered in the 1960s while building an underground parking lot (place de la république).
- Remains of the Gallo-Roman amphitheatre, one of the largest in ancient Gaul.
- The Gothic Limoges Cathedral (Cathédrale Saint-Étienne de Limoges), begun in 1273 and only finished in 1888. It is noted for a fine loft built in 1534 and for the partly octagonal bell tower. The main artistic works are a Renaissance rood screen and the tomb of the bishop Jean de Langeac, with sculpted scenes of the Apocalypse.
- The Chapelle Saint-Aurélien (14th–17th centuries). It includes the relics of St. Aurelian, the second bishop of Limoges, and has medieval statues and Baroque works of art.
- The church of St-Pierre-du-Queyroix, begun in the 12th century
- Church of St-Michel-des-Lions, begun in 1364. It houses the relics of St. Martial and has stained-glass windows from the 15th–16th century. The most striking feature is the 65 m-high tower, with a spire surmounted by a big bronze ball.
- The bridges of Saint Martial (dating from the Roman era) and of St-Etienne (13th century).
- The Limoges Fine Arts Museum (Musée des Beaux-Arts), housed in the 18th-century bishops' palace ('Palais de l'Évêché').[17]
- The railway station, Gare de Limoges Bénédictins, inaugurated in 1929.
- The Château de La Borie (17th century), at 4 km (2.5 mi) from the city. It is home to the Centre Culturel de Rencontre de La Borie et l'Ensemble Baroque de Limoges.
- The remains of the 12th-century Castle of Chalucet, 10 km (6.2 mi) south of the city. During the Hundred Years' War it was a base of the bands of pillagers which ravaged the country.
- The city's botanical gardens include the Jardin botanique de l'Evêché next to the cathedral and the Jardin botanique alpin "Daniella".
- The University of Limoges was founded in 1968.[18]
Art and literature

"Le marché de Limoges" (Limoges market) is the name of a section of Pictures at an Exhibition by Modest Mussorgsky.
In 1768,[7] kaolin, a rock rich in fine, white clay which is used for making porcelain, was discovered at Saint-Yrieix-la-Perche, 30 km south of Limoges. Under the impetus of the progressive economist Anne Robert Jacques Turgot, Baron de Laune, who had been appointed intendant of this impoverished and isolated region, a new ceramics industry was developed, and Limoges porcelain became famous during the 19th century. However, Limoges porcelain is a generic term for porcelain produced in Limoges rather than at a specific factory (there are still several porcelain factories in and around Limoges). More than 50% of all porcelain made in France comes from Limoges[7]
Limoges is mentioned in T.S. Eliot's poem Gerontion (London 1919), lines 23 to 25:
"... Mr. Silvero/ With caressing hands, at Limoges/ Who walked all night in the next room."
Eliot's compatriot and mentor Ezra Pound visited Limoges in 1912 when researching the landscape and the work of the 12th-century troubadours. As he states in his essay Troubadours: Theirs Sorts and Conditions: "... a man may walk the hill roads and river roads from Limoges and Charente to Dordogne and Narbonne and learn a little, or more than a little, of what the country meant to the wandering singers ..."
There is also a reference to Limoges in Jean-Paul Sartre's novel Nausea, near the middle of the book in the Shrove Tuesday section, when the magistrate says: "I had a similar case at the beginning of my career. It was in 1902. I was deputy magistrate at Limoges ..."
Transport
The main railway station of Limoges is the Gare de Limoges-Bénédictins. It offers direct connections with Paris, and Toulouse, and several regional destinations. Limoges was the last major urban centre of Metropolitan France to be connected to the national motorway system; since the early 1990s, the motorway A20 connects Limoges with Chateauroux, Vierzon, Orléans and Paris to the north, and Brive-la-Gaillarde, Cahors, Montauban and Toulouse to the south. The nearest airport is Limoges – Bellegarde Airport.
Urban transport in Limoges and its metropolitan area is operated by Société de transports en commun de Limoges Métropole (STCL). The Limoges urban bus network includes the Limoges trolleybus system, one of only four such systems currently operating in France.
Notable people
- Bernard Gui (1261–1331), Inquisitor of Toulouse, Bishop of Lodève, buried in Limoges.
- Henri François d'Aguesseau (1668–1751), chancellor of France
- Jean Daurat (or Dorat) (1508–1588), poet and scholar, member of the Pléiade
- Mathieu Couloux
- Stephen Grellet (1773–1855), Quaker missionary
- Jean-Baptiste Jourdan (1762–1833), marshal of France
- Thomas Robert Bugeaud de la Piconnerie, Duke of Duchy of Isly (1784–1849), marshal of France
- Fabienne Delsol, a singer active since 1996
- Roger Gonthier (1884–1978), architect
- Jean-Baptiste Joseph Émile Montégut (1825–1895), critic
- René Navarre (1877–1968), actor
- Pierre-Auguste Renoir (1841–1919), painter
- Michel Chevalier (1806–1879), engineer, economist, and statesman
- Marie François Sadi Carnot (1837–1894), President of France
- André Antoine (1858–1943), theater pioneer, actor, director, filmmaker
- Maryse Bastié (1898–1952), aviator
- Raoul Hausmann, artist born in Vienna, in 1886, co-founder of Dada-Berlin, famous for his collages. Moved to Limoges for safety in 1939 and then to Peyrat-le-château where he died in 1971. The Rochechouart Art Museum (west of Limoges) holds several of his works.
- Fred Sirieix (born 1972), maître d' famous for appearing on First Dates.
- Franck Pulcini, 20th-century French trumpeter.
Twin towns - sister cities

Limoges is twinned with:[19]
See also
- Roman Catholic Diocese of Limoges, the Bishopric of Limoges
- Communes of the Haute-Vienne department
- Chapel of St. Aurelianus, Limoges
References
- "Populations légales 2017". INSEE. Retrieved 6 January 2020.
- "Limoges". Collins English Dictionary. HarperCollins. Retrieved 24 September 2014.
- "Limoges". Merriam-Webster Dictionary. Retrieved 1 July 2019.
- "Limoges". The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language (5th ed.). Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. Retrieved 1 July 2019.
- "Louvre museum notice". Louvre.fr. Archived from the original on 15 June 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- Sumption, Jonathan. 2009. The Hundred Years War III: Divided Houses. 82–83
- "Limoges". Facstaff.uindy.edu. Archived from the original on 18 July 2011. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- "F4 History: 1993, A surprise from France".
- "Une liste de 200 personnalités "à abattre" a été découverte lors de perquisitions chez des". 26 September 1992.
- "Climatological Information for Limoges, France". Meteo France. 6 August 2019.
- "LIMOGES–BELLEGARDE (87)" (PDF). Fiche Climatologique: Statistiques 1981–2010 et records (in French). Meteo France. Retrieved 6 August 2019.
- "Normes et records 1961–1990: Limoges-Bellegarde (87) – altitude 402m" (in French). Infoclimat. Archived from the original on 3 March 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2019.
- Comparateur de territoire: Commune de Limoges (87085), Aire urbaine Limoges (035), INSEE
- Haute-Vienne, habitants.fr
- Population en historique depuis 1968, INSEE
- "Catholic Encyclopedia: St. Martial". Newadvent.org. 1 October 1910. Retrieved 14 March 2011.
- "Découvrez le musée des Beaux-Arts de Limoges - Musée des Beaux-Arts de Limoges". www.museebal.fr.
- Université de Limoges website Archived 21 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine (in English)
- "Les villes jumelles : une autre façon d'aborder les relations internationales". limoges.fr (in French). Limoges. Retrieved 14 November 2019.
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Missing or empty
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. Missing or empty |title=(help)- INSEE commune file
Bibliography
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Limoges. |
- City council website
- Adrien Dubouché Museum – ceramics, glassware, porcelain from Limoges
- History and Geography at Academy of Limoges