Fastback
A fastback is an automotive styling feature which is defined by the rear of the car having a single slope from the roof to the rear bumper and depending on how the feature is incorporated into the individual styling is very similar to kammback styling.[2][3][4]


.jpg.webp)


.jpg.webp)
.jpg.webp)


Some models (such as the Ford Mustang) have been specifically marketed as a fastback, often to differentiate the model from other body styles (e.g. coupe models) in the same model range. The 4-door coupe is a common branding tool used today to describe fastback sedans.
Definition
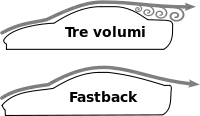
A fastback is often defined as having a single slope from the roof to the rear of the vehicle.[5]
.jpg.webp)

The term "fastback" is not interchangeable with "liftback". "Fastback" mainly describes the shape of the car and may be applied to fastback sedans (with a fixed rear window) as well as to liftbacks, with an opening rear gate that includes the window.
More specifically, Road & Track have defined the fastback as
A closed body style, usually a coupe but sometimes a sedan, with a roof sloped gradually in an unbroken line from the windshield to the rear edge of the car. A fastback naturally lends itself to a hatchback configuration and many have it, but not all hatchbacks are fastbacks and vice versa.[6]
In the case of the Ford Mustang, the term fastback is used to differentiate against the coupé notchback body style,[7][8] which has a steeper rear window, followed by a horizontal bootlid.
History
Automobile designers in the 1930s began using elements of aircraft aerodynamics to smooth out the boxy-looking vehicles of their day.[9] Some designs that were ahead of their time when exhibited during the early 1930s included "teardrop" streamlining of the car's rear; a configuration similar to what would become known as "fastback" 25 years later."[10] Merriam-Webster first recognized the term "Fastback" in 1954, many years before the popularization of the term "hatchback", which entered the dictionary in 1970.[11] Opinions vary as to whether the terms are mutually exclusive.
Early examples of fastback cars include the 1929 Auburn Cabin Speedster, 1933 Cadillac V-16 Aerodynamic Coupe, 1935 Stout Scarab,[12] the 1933 Packard 1106 Twelve Aero Sport Coupe,[13] Bugatti Type 57 Atlantic, Tatra T87, Porsche 356, Saab 92/96, Standard Vanguard, GAZ-M20 Pobeda, and Bentley Continental R-Type.
In North America the numerous marketing terms for the fastback body-style included "aerosedan", "club coupe", "sedanette" and "torpedo back".[14] Cars included Cadillac's Series 61 and 62 Club Coupes, as well as various other models from General Motors, Ford, and Chrysler. By the early 1940s until 1950 nearly every domestic manufacturer offered at least one fastback body-style within their model lineups. In the mid-1960s the appearance was revived on many GM and Ford products until the mid-1970s.
In Europe, there was a sloping rear on streamlined cars as early as 1945, from which, among other things, the shapes of the VW Beetle and Porsche 356 are derived. In the upper middle and upper class, fastbacks were exotic for a long time. The few exceptions included streamlined bodies from the 1940s and Tatra and Citroën cars.
In Australia fastback cars became known as the "sloper" and began to be introduced in 1935 - first designed by General Motors' Holden as one of the available bodies on Oldsmobile, Chevrolet, and Pontiac chassis. The sloper design was added by Richards Body Builders in Australia to Dodge and Plymouth models in 1937, by Ford Australia in 1939 and 1940, as well as a sloper style made on Nash chassis.[15] According to automotive historian G.N. Georgano, "the Slopers were advanced cars for their day".[16]
In Japan, the Toyota AA passenger car first adopted the fastback style in 1936. Toyota AA was strongly influenced by the 1933 DeSoto Airflow. After World War II, the 1965 Mitsubishi Colt 800 was the first Japanese car to adopt the fastback style.[17] The Prince Skyline 1900 Sprint was developed by Prince Motor Company in 1963, but was never marketed.[18] In the Japanese Kei car, the 1958 Subaru 360 adopted the fastback style. After that, all Japanese car makers completed the adoption of the fastback style with the 1967 Honda N360 (Kei car), the 1968 Nissan Sunny Coupe,[19] and the 1968 Mazda Familia Rotary Coupe,[20] 1970 Suzuki Fronte "stingray look", 1971 Daihatsu Fellow MAX.[21] From the late 1960s to the 1970s, the American Coke bottle styling became popular in Japan, and Toyota Motor Corporation proposed a new style called "Liftback" with the 1973 Toyota Celica.[22][23][24]
The 4-door coupe re-branding in 2004
A decisive change of course took place in 2004 , when the first generation of the Mercedes-Benz CLS, was launched on the market. It was called a 4-door coupé, a purely marketing term describing the fastback sedan. It had fastback coupé-profiled bodywork, but two doors on each side. The CLS is considered as the forerunner of this market segment, but in reality it can be said that it has dusted off and reinterpreted the concept. It was briefly used on the 1992-1997 Infiniti J30/Nissan Leopard J Férié
It was certainly the first of the new course, and was followed by other competing models, such as the Audi A7 or the BMW 6 Series Gran Coupé, but also models of different segments, such as the Audi A5 Sportback, the BMW 4 Series Gran Coupé, the Volkswagen CC, Mercedes-Benz CLA-Class, Aston Martin Rapide, and Porsche Panamera. Cars with a 4-door coupe- type body are often classified as crossover cars due to the fact that they combine the characteristics of two different body types in one car.
Aerodynamic advantages
Fastbacks provide an advantage in developing aerodynamic vehicles with a low drag coefficient.[25] For example, although lacking a wind tunnel, Hudson designed its post-World War II cars to look aerodynamic and "tests conducted by Nash later found that the Hudson had almost 20% less drag than contemporary notchback sedans".[26]
List of fastback cars
References
- McCourt, Mark J. (July 2013). "1967 AMC Marlin". Hemmings Motor News. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- Flammang, James M. (1990). Standard Catalog of American Cars, 1976-1986. Krause Publications. p. viii. ISBN 9780873411332. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- "fastback". Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- "fastback". The Oxford Pocket Dictionary of Current English. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- "fastback". Random House Kernerman Webster’s College Dictionary. 2010. Retrieved 1 March 2016.
- Dinkel, John (2000). Road & Track Illustrated Automotive Dictionary. Bentley. ISBN 0-8376-0143-6.
- "1965 Ford Mustang Fastback Guide". www.autotrader.com. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- "1967 Mustang Specifications". www.mustangspecs.com. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- Walker, Clinton (2009). Golden Miles: Sex, Speed and the Australian Muscle Car. Wakefield Press. p. 16. ISBN 9781862548541. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- Georgano, Nick N., ed. (2000). The Beaulieu encyclopedia of the automobile. Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers. p. 960. ISBN 978-1-57958-293-7. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- "hatchback". Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- Clements, Rob. "EyesOn Design 2007 Report". Ultimatecarpage.com. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- Adler, Dennis (2004). Packard. MotorBooks/MBI. p. 960. ISBN 978-0-7603-1928-4. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- "The Forty-Niners". Time. 24 January 1949. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- "The Sloper Page". Hand Publishing. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- Walker, p. 18.
- サイドガラスは上ヒンジ! 日本初のファストバックスタイルは三菱の水島製作所が作ったこの車|1968年式 三菱 コルト1000F 2ドアDX Vol.1 - Nosweb.jp
- プリンス自動車のインサイドストーリ―第5回│プリンスが自作した1900スプリント - octane.jp
- 【旧車】初代サニークーペ「名機A型エンジンを搭載した小さな傑作車」 - Webモーターマガジン
- 【昭和の名車 18】マツダ ファミリア ロータリークーペ(昭和43年:1968年) - Webモーターマガジン
- 昔はスタイルを優先していた!? 秀逸なデザインの個性派軽自動車5選 - くるまのニュース
- Sobran, Alex (15 May 2017). "This Toyota Celica Liftback GT Beautifully Couples Japanese And American Design". Petrolicious (U.S.). Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- Koch, Jeff (1 January 2016). "1971-'77 Toyota Celica". Hemmings Motor News (U.S.). Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- Fets, Jim (3 December 2010). "Collectible Classic: 1976-1977 Toyota Celica GT Liftback". Automobile Magazine (U.S.). Retrieved 7 September 2020.
- Noffsinger, Ken R. (June 2012). "The G-Series Wind Tunnel Test Report". Retrieved 24 December 2015.
- Severson, Aaron (6 September 2009). "Step-Down: The 1948-1954 Hudsons". Ate Up With Motor. Retrieved 24 December 2015.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Fastbacks. |
