Furoxan
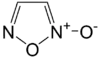
Furoxan or 1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide is a heterocycle of the isoxazole family and an amine oxide derivative of furazan. It is a nitric oxide donor.[1] As such, furoxan and its derivatives are actively researched as potential new drugs and insensitive high density explosives. Ipramidil is an example.
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,5-Oxadiazole 2-oxide | |
| Other names
Furazan N-oxide; Furazan 2-oxide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | C528141 |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H2N2O2 | |
| Molar mass | 86.050 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Furoxanes can be formed by dimerization of nitrile oxides.
References
- Clara Cena; Massimo Bertinaria; Donatella Boschi; Marta Giorgis; Alberto Gasco (2006). "Use of the furoxan (1,2,5-oxadiazole 2-oxide) system in the design of new NO-donor antioxidant hybrids" (PDF). Arkivoc (HL-1787GR): 301–309.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.