Glycerol phenylbutyrate
Glycerol phenylbutyrate (USAN), trade name Ravicti, is a medication used in the treatment of certain inborn urea cycle disorders. The medication works by preventing the harmful buildup of ammonia in the body.[1] It is an FDA-approved prescription drug in the US.[2] It is approved for anyone over 2 months of age. It was developed by Hyperion Therapeutics based on the existing drug Buphenyl, and received approval on February 1, 2013.[3] Hyperion has been criticized for setting a high price for the drug. The price was set at US$250,000–290,000. In 2014, the drug generated $30.8 million in net sales, far behind the older and less expensive Buphenyl ($113.6 million in sales).[4] In March 2015, Horizon Pharma acquired Hyperion Therapeutics and thus Raviciti.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ravicti |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| License data | |
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.228.552 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
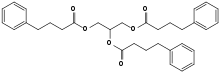
| Formula | C33H38O6 |
| Molar mass | 530.661 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
References
- "FDA approves new drug for the chronic management of some urea cycle disorders". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 1 February 2013. Archived from the original on 2013-03-07. Retrieved 2013-04-01.
- "FDA Approved Drug Products: Ravicti". Drugs@FDA. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- Herder M (April 2016). "Orphan drug incentives in the pharmacogenomic context: policy responses in the USA and Canada". Journal of Law and the Biosciences. 3 (1): 158–166. doi:10.1093/jlb/lsv060. PMC 5033429. PMID 27774236.
- "Horizon Pharma to Acquire Hyperion Therapeutics for $1.1B". Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News. 30 March 2015.
External links
- "Glycerol phenylbutyrate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.