Hawker Tornado
The Hawker Tornado was a British single-seat fighter aircraft design of World War II for the Royal Air Force as a replacement for the Hawker Hurricane. The planned production of Tornados was cancelled after the engine it was designed to use, the Rolls-Royce Vulture, proved unreliable in service. A parallel airframe that used the Napier Sabre engine continued into production as the Hawker Typhoon.
| Tornado | |
|---|---|
.jpg.webp) | |
| Role | Single-seat fighter |
| Manufacturer | Hawker Aircraft |
| First flight | 6 October 1939 |
| Primary user | Royal Air Force |
| Number built | 4 (3 prototypes and 1 production) |
Design and development
Shortly after the Hawker Hurricane entered service, Hawker began work on its eventual successor. Two alternative projects were undertaken: the Type N (for Napier), with a Napier Sabre engine, and the Type R (for Rolls-Royce), equipped with a Rolls-Royce Vulture powerplant. Hawker presented an early draft of its ideas to the Air Ministry which advised that a specification was in the offing for such a fighter. The specification was released by the ministry as Specification F.18/37 after further prompting from Hawker.[1] The specification called for a single-seat fighter armed with twelve 0.303 in (7.7 mm) machine guns, a maximum speed of 400 mph (644 km/h) at 15,000 ft (4,600 m) and a service ceiling of 35,000 ft (10,700 m) were required. Two prototypes of both the Type N and R were ordered on 3 March 1938.
Technical description
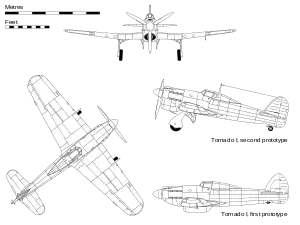
Both prototypes were very similar to the Hurricane in general appearance, and shared some of its construction techniques. The front fuselage used the same swaged and bolted duralumin tube structure, which had been developed by Sydney Camm and Fred Sigrist in 1925. The new design featured automobile-like side-opening doors for entry, and used a large 40 ft (12 m) wing that was much thicker in cross-section than those on aircraft like the Spitfire. The rear fuselage, from behind the cockpit, differed from that of the Hurricane in that it was a duralumin, semi-monocoque, flush-riveted structure. The all-metal wings incorporated the legs and wheel-bays of the wide-track, inward-retracting main undercarriage. The two models were also very similar to each other; the R plane had a rounder nose profile and a ventral radiator, whereas the N had a flatter deck and a chin-mounted radiator. The fuselage of the Tornado ahead of the wings was 12 in (30 cm) longer than that of the Typhoon, the wings were fitted 3 in (76 mm) lower on the fuselage, and the radiator was located beneath the fuselage. The X-24 cylinder configuration of the Vulture required two sets of ejector exhaust stacks on each side of the cowling,[2] and that the engine was mounted further forward than the Sabre in order to clear the front wing spar.[3]
Flight trials
On 6 October 1939, the first prototype (P5219) was flown by P.G. Lucas, having first been moved from Kingston to Langley for completion. Further flight trials revealed airflow problems around the radiator, which was subsequently relocated to a chin position. Later changes included increased rudder area, and the upgrading of the powerplant to the Vulture Mark V engine. Hawker production lines focused on the Hurricane, with the result that completion of the second prototype (P5224) was significantly delayed. It featured the chin radiator, additional window panels in the fairing behind the cockpit, and the 12 .303 in machine guns were replaced by four 20 mm Hispano cannon. It was first flown on 5 December 1940, and was powered by a Vulture II, although as in the case of the first prototype, a Vulture V was later installed.
Production
In order to avoid upsetting the Hurricane lines, production was sub-contracted to Avro (another company in the Hawker group) in Manchester[2] and Cunliffe-Owen Aircraft in Eastleigh, with orders for 1,760 and 200 respectively being placed in 1939. However, only one of these aircraft, from Avro, was ever built and flown, this being R7936. Shortly after its first flight at Woodford, on 29 August 1941, the Vulture programme was abandoned, followed closely by the cancellation of the Tornado order. At that time four aircraft were at various stages of production at the Avro plant at Yeadon, West Yorkshire.
Vulture engine
The Vulture was effectively cancelled by Rolls-Royce in July 1941, partly due to the problems experienced in its use on the Avro Manchester, but mostly to free up resources for Merlin development and production. The Rolls-Royce Merlin was also starting to deliver the same power levels. However, the Vulture engine installation in the Tornado was relatively trouble free[2] and the aircraft itself had fewer problems in flight than its Sabre-engined counterpart. The third prototype (HG641), the only other Tornado to fly, was flown on 23 October 1941, powered by a Bristol Centaurus CE.4S sleeve valve radial engine. This Tornado was built from two incomplete production airframes (R7937 and R7938), was a testbed for a number of Centaurus engine/propeller combinations and was the progenitor of the Hawker Tempest II.
Specifications (Tornado with Vulture II)
Data from The Typhoon and Tempest Story,[2] Hawker Aircraft Since 1920[4]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 32 ft 10 in (10.01 m)
- Wingspan: 41 ft 11 in (12.78 m)
- Height: 14 ft 8 in (4.47 m)
- Wing area: 283 sq ft (26.3 m2)
- Airfoil: root: NACA 2219; tip: NACA 2213[5]
- Empty weight: 8,377 lb (3,800 kg)
- Gross weight: 9,520 lb (4,318 kg)
- Max takeoff weight: 10,668 lb (4,839 kg)
- Fuel capacity: 140 imp gal (168 US gal; 636 l)
- Powerplant: 1 × Rolls-Royce Vulture II X-24 liquid-cooled piston engine, 1,760 hp (1,310 kW)
- or 1x 1,980 hp (1,476 kW) Rolls-Royce Vulture V
- or 1x 2,210 hp (1,648 kW) Bristol Centaurus CE 4S
- Propellers: 3-bladed de Havilland Hydromatic constant-speed propeller, 14 ft 0 in (4.27 m) diameter
Performance
- Maximum speed: 398 mph (641 km/h, 346 kn) at 23,000 ft (7,010 m) (Vulture V)
- Service ceiling: 34,900 ft (10,600 m)
- Time to altitude: 20,000 ft (6,100 m) in 7 minutes 12 seconds
- Wing loading: 37.7 lb/sq ft (184 kg/m2)
- Power/mass: 0.1858 hp/lb (0.3055 kW/kg)
Armament
- Guns: Provision for 12 × .303 in (7.7 mm) Browning machine guns (1st prototype P5219) or 4 × 20 mm Hispano cannon. (2nd and Centaurus prototypes P5224, HG641).
Avionics
TR 9 VHF R/T fitted (P5224)
References
Notes
- Buttler
- Thomas and Shores 1988.
- "Hawker Tornado", Flight: 391, 13 April 1944
- Mason 1991
- Lednicer, David. "The Incomplete Guide to Airfoil Usage". m-selig.ae.illinois.edu. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
Bibliography
- Darling, Kev. Hawker Typhoon, Tempest and Sea Fury. Ramsgate, Marlborough, Wiltshire, UK: The Crowood Press Ltd., 2003. ISBN 1-86126-620-0.
- Hannah, Donald. Hawker FlyPast Reference Library. Stamford, Lincolnshire, UK: Key Publishing Ltd., 1982. ISBN 0-946219-01-X.
- James, Derek N. Hawker, an Aircraft Album No. 5. New York: Arco Publishing Company, 1973. ISBN 0-668-02699-5. (First published in the UK by Ian Allan in 1972)
- Mason, Francis K. Hawker Aircraft Since 1920 (3rd revised edition). London, UK: Putnam, 1991. ISBN 0-85177-839-9.
- Mason, Francis K. The Hawker Typhoon and Tempest. Bourne End, Buckinghamshire, UK: Aston Publications, 1988. ISBN 0-946627-19-3.
- Mondey, David. The Hamyln Concise Guide to British Aircraft of World War II. London: Chancellor Press, 1994. ISBN 1-85152-668-4.
- Myers, Gerald. Mother worked at Avro. Page 27.
- Sharpe, Michael. History of the Royal Airforce. Pages 64–66.
- Thomas, Chris and Shores, Christopher. The Typhoon and Tempest Story. London: Arms and Armour Press, 1988. ISBN 0-85368-878-8.
- Townend, David R. Clipped Wings – World War Two Edition. Markham: Aerofile Publications, 2010. ISBN 978-0-9732020-1-4.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Hawker Tornado. |
- Hawker Tornado – British Aircraft Directory
- Hawker Tornado – British Aircraft of World War II
- A photograph of the Vulture-engined second prototype, P5224
- A photograph of the Centaurus-engined third prototype, HG641
- A later photograph of HG641 with a different nose configuration