Hopkinton, Rhode Island
Hopkinton is a town in Washington County, Rhode Island. The population was 8,188 at the 2010 census.
Hopkinton, Rhode Island | |
|---|---|
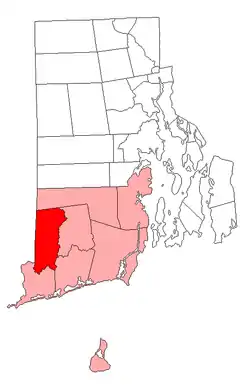 Location of Hopkinton within Washington County, Rhode Island | |
| Government | |
| • Town Council | Barbara A. Capalbo Frank T. Landolfi Sylvia K. Thompson Scott Bill Hirst Sharon Davis |
| • Town Clerk | Elizabeth J. Cook-Martin |
| Area | |
| • Total | 44.1 sq mi (114.0 km2) |
| • Land | 43.0 sq mi (111.0 km2) |
| • Water | 1.1 sq mi (2.8 km2) |
| Population (2010) | |
| • Total | 8,188 |
| • Density | 185.67/sq mi (71.82/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC-5 (Eastern (EST)) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC-4 (EDT) |
| ZIP codes | |
| Area code(s) | 401 |
| Website | http://www.hopkintonri.org |
History

Hopkinton is named after Stephen Hopkins, a signer of the Declaration of Independence who was governor of the Colony of Rhode Island and Providence Plantations when the town was partitioned from Westerly and incorporated in 1757.[1][2] Hopkinton once featured a number of industrial villages, such as Locustville, Moscow, Centerville, and Wood River Iron Works, each being named after the mill which they surrounded. Today only Hope Valley, Rockville, Ashaway, and Bradford are recognized with a post office. The town hall is located in the village of Hopkinton City, which was once a stagecoach hub..
Geography
Hopkinton is found at 41.461 N latitude and 71.778 W longitude and borders Richmond and Charlestown. It is on the Pawcatuck River on the Connecticut border.
According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 44.1 square miles (114 km2), of which 43.0 square miles (111 km2) is land and 1.1 square miles (2.8 km2) (2.58%) is water.
Hopkinton is the southernmost town along Rhode Island's portion of Interstate 95 and is the first Rhode Island town that northbound travelers encounter.
Villages
Hope Valley in the north and Ashaway in the south are the two primary villages in Hopkinton. Two of the four elementary schools in the Chariho Regional School District are located in Hopkinton, one in Hope Valley and one in Ashaway. Other villages that are located in Hopkinton include Barberville, Bethel, Bradford, Burdickville, Canonchet, Centerville, Hopkinton City, Locustville, Moscow, Rockville, South Hopkinton, Woodville, and Yawgoog. Almost all were formed from mills on rivers. Hope Valley and Ashaway have extended their borders as census-designated places into other less-known villages.
Adjacent Towns
Demographics
| Historical population | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Census | Pop. | %± | |
| 1790 | 2,462 | — | |
| 1800 | 2,276 | −7.6% | |
| 1810 | 1,774 | −22.1% | |
| 1820 | 1,821 | 2.6% | |
| 1830 | 1,777 | −2.4% | |
| 1840 | 1,726 | −2.9% | |
| 1850 | 2,477 | 43.5% | |
| 1860 | 2,738 | 10.5% | |
| 1870 | 2,682 | −2.0% | |
| 1880 | 2,952 | 10.1% | |
| 1890 | 2,864 | −3.0% | |
| 1900 | 2,602 | −9.1% | |
| 1910 | 2,324 | −10.7% | |
| 1920 | 2,316 | −0.3% | |
| 1930 | 2,823 | 21.9% | |
| 1940 | 3,230 | 14.4% | |
| 1950 | 3,676 | 13.8% | |
| 1960 | 4,174 | 13.5% | |
| 1970 | 5,392 | 29.2% | |
| 1980 | 6,406 | 18.8% | |
| 1990 | 6,873 | 7.3% | |
| 2000 | 7,836 | 14.0% | |
| 2010 | 8,188 | 4.5% | |
| 2015 (est.) | 8,109 | [3] | −1.0% |
| U.S. Decennial Census[4][5] | |||
As of the census[6] of 2000, there were 7,836 people, 2,965 households, and 2,182 families residing in the town. There were 3,112 housing units at an average density of 72.4 per square mile (27.9/km2). The racial makeup of the town was 96.82% White, 0.61% African American, 0.89% American Indian, 0.43% Asian, 0.27% from other races, and 0.97% from two or more races. Hispanic or Latino of any race were 1.06% of the population.
There were 2,965 households, out of which 35.2% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 61.9% were married couples living together, 7.7% had a female householder with no husband present, and 26.4% were non-families. 21.0% of all households were made up of individuals, and 9.4% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.64 and the average family size was 3.07.
In the town, the population was spread out, with 25.7% under the age of 18, 6.4% from 18 to 24, 31.6% from 25 to 44, 25.4% from 45 to 64, and 11.1% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38 years. For every 100 females, there were 99.7 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 96.9 males.
The median income for a household in the town was $52,181, and the median income for a family was $59,143. Males had a median income of $39,804 versus $29,189 for females. The per capita income for the town was $23,835. About 3.3% of families and 4.8% of the population were below the poverty line, including 5.5% of those under age 18 and 7.2% of those age 65 or over. As of 2017,the largest self-identified ancestry groups or ethnic groups in Hopkinton were:[7]
| Largest ancestries (2017) | Percent |
|---|---|
| English | 24.8% |
| Irish | 22.8% |
| Italian | 18.6% |
| German | 10.5% |
| French (except Basque) | 10.2% |
| Polish | 6.5% |
| Portuguese | 4.5% |
| American | 3.6% |
| Scottish | 3.6% |
| Swedish | 3.3% |
Politics
In the state legislature Hopkinton is located in the 34th Senate District, represented by Republican Elaine J. Morgan,[9] and in the 38th District in the Rhode Island House of Representatives by Democrat Brian Patrick Kennedy.[10] At the Federal level, Hopkinton is located in Rhode Island's 2nd Congressional District, which is currently represented by James Langevin (D). In the United States Senate, Hopkinton is represented by U.S. Senator John F. Reed (D) and U.S. Senator Sheldon Whitehouse (D).
Notable people
The Aldrich and the Rockefeller families each built a small mansion in the Hope Valley region of Hopkinton before the families merged. The Rockefeller house now serves as the rectory for St. Joseph's Parish.
- Prudence Crandall taught the first desegregated classroom in the United States; born in Hopkinton
- Edward Lee Greene, botanist; born in Hopkinton
- Benjamin Randall, Wisconsin State Assemblyman; born in Hopkinton
- John Wilbur, Quaker minister; born in Hopkinton
National Historic Places

See also
References
- Snow, Edwin. Report upon the Census of Rhode Island. Providence Press Company, 1865, p. xxx.
- Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. pp. 160.
- "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for Incorporated Places: April 1, 2010 to July 1, 2015". Archived from the original on June 2, 2016. Retrieved July 2, 2016.
- "Census of Population and Housing". Census.gov. Retrieved June 4, 2016.
- Snow, Edwin M. (1867). Report upon the Census of Rhode Island 1865. Providence, RI: Providence Press Company.
- "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2019-05-26.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2020-02-13. Retrieved 2019-05-26.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Senator Elaine J. Morgan".
- "Representative Brian Patrick Kennedy". Rhode Island General Assembly. Archived from the original on May 7, 2010. Retrieved November 14, 2009.
External links
 Hopkinton, Rhode Island travel guide from Wikivoyage
Hopkinton, Rhode Island travel guide from Wikivoyage- Town of Hopkinton official website