List of regions of the United States
This is a list of some of the regions in the United States. Many regions are defined in law or regulations by the federal government; others by shared culture and history; and others by economic factors.
Interstate regions
Census Bureau-designated regions and divisions
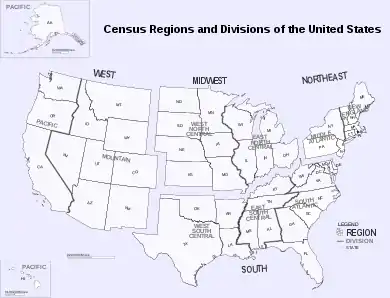
Since 1950, the United States Census Bureau defines four statistical regions, with nine divisions.[1][2] The Census Bureau region definition is "widely used ... for data collection and analysis",[3] and is the most commonly used classification system.[4][5][6][7]
- Region 1: Northeast
- Division 1: New England (Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont)
- Division 2: Mid-Atlantic (New Jersey, New York, and Pennsylvania)
- Region 2: Midwest (Prior to June 1984, the Midwest Region was designated as the North Central Region.)[8]
- Division 3: East North Central (Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio, and Wisconsin)
- Division 4: West North Central (Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, and South Dakota)
- Region 3: South
- Division 5: South Atlantic (Delaware, Florida, Georgia, Maryland, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, District of Columbia, and West Virginia)
- Division 6: East South Central (Alabama, Kentucky, Mississippi, and Tennessee)
- Division 7: West South Central (Arkansas, Louisiana, Oklahoma, and Texas)
- Region 4: West
- Division 8: Mountain (Arizona, Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Nevada, New Mexico, Utah, and Wyoming)
- Division 9: Pacific (Alaska, California, Hawaii, Oregon, and Washington)
Puerto Rico and other US territories are not part of any census region or census division.[9]
Standard Federal Regions
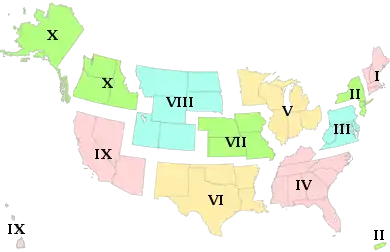
The ten standard federal regions were established by OMB (Office of Management and Budget) Circular A-105, "Standard Federal Regions", in April 1974, and required for all executive agencies. In recent years, some agencies have tailored their field structures to meet program needs and facilitate interaction with local, state, and regional counterparts. However, the OMB must still approve any departures.
- Region I: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, Vermont
- Region II: New Jersey, New York, Puerto Rico, US Virgin Islands
- Region III: Delaware, District of Columbia, Maryland, Pennsylvania, Virginia, West Virginia
- Region IV: Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee
- Region V: Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, Ohio, Wisconsin
- Region VI: Arkansas, Louisiana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas
- Region VII: Iowa, Kansas, Missouri, Nebraska
- Region VIII: Colorado, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, Utah, Wyoming
- Region IX: Arizona, California, Hawaii, Nevada, American Samoa, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands
- Region X: Alaska, Idaho, Oregon, Washington
Note: OMB Circular A-105 was rescinded on June 8, 1995. [10]
Federal Reserve Banks
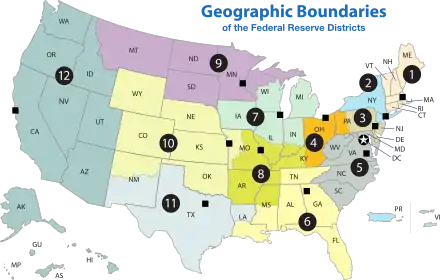
The Federal Reserve Act of 1913 divided the country into twelve districts with a central Federal Reserve Bank in each district. These twelve Federal Reserve Banks together form a major part of the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States. Missouri is the only U.S. state to have two Federal Reserve locations within its borders, as some states are divided into more than one district.
Time zones
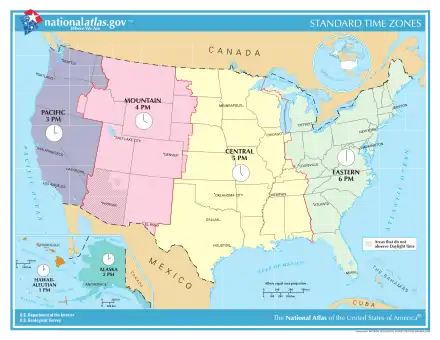
- UTC−12:00 (Baker Island, Howland Island)
- Samoa Time Zone (American Samoa, Jarvis Island, Kingman Reef, Midway Atoll, Palmyra Atoll)
- Hawaii–Aleutian Time Zone (Hawaii, Aleutian Islands (Alaska), Johnston Atoll)
- Alaska Time Zone (Alaska, excluding Aleutian Islands)
- Pacific Time Zone
- Arizona Time Zone (excluding the Navajo Nation)[11]
- Mountain Time Zone (excluding most parts of Arizona)
- Central Time Zone
- Eastern Time Zone
- Atlantic Time Zone (Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands)
- Chamorro Time Zone (Guam, Northern Mariana Islands)
- Wake Island Time Zone (Wake Island)
Courts of Appeals circuits
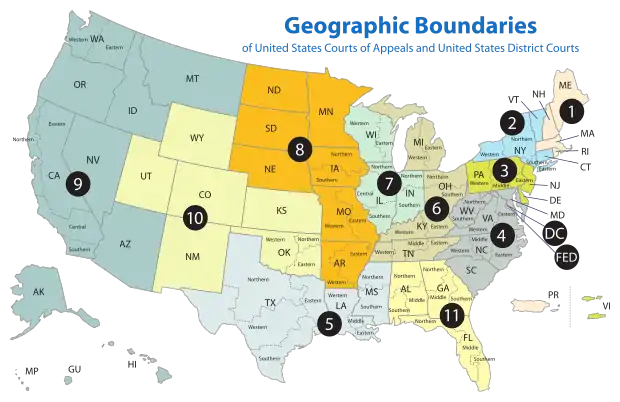
- First Circuit
- Second Circuit
- Third Circuit
- Fourth Circuit
- Fifth Circuit
- Sixth Circuit
- Seventh Circuit
- Eighth Circuit
- Ninth Circuit
- Tenth Circuit
- Eleventh Circuit
- D.C. Circuit
The Federal Circuit is not a regional circuit. Its jurisdiction is nationwide but based on the subject matter.
Bureau of Economic Analysis regions
The Bureau of Economic Analysis defines regions for comparison of economic data.[12]
- New England: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont
- Mideast: Delaware, District of Columbia, Maryland, New Jersey, New York and Pennsylvania
- Great Lakes: Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Ohio and Wisconsin
- Plains: Iowa, Kansas, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota and South Dakota
- Southeast: Alabama, Arkansas, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Virginia and West Virginia
- Southwest: Arizona, New Mexico, Oklahoma and Texas
- Rocky Mountain: Colorado, Idaho, Montana, Utah and Wyoming
- Far West: Alaska, California, Hawaii, Nevada, Oregon and Washington
Energy Information Administration
The Energy Information Administration currently uses the PADD system established by Petroleum Administration for War in World War II.[13] It is used for data collection on refining petroleum and its products. Each PADD is subdivided into refining districts.
- PADD I: East Coast
- East Coast: Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, Connecticut, New Jersey, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Florida; along with counties in New York east of, north of and including Cayuga, Tompkins, and Chemung; and counties in Pennsylvania east of and including Bradford, Sullivan, Columbia, Montour, Northumberland, Dauphin and York.
- Appalachian No. 1: West Virginia along with counties of Pennsylvania and New York State not mentioned above.
- PADD II: Midwest
- Indiana-Illinois-Kentucky: Indiana, Illinois, Kentucky, Tennessee, Michigan, Ohio
- Minnesota-Wisconsin-North and South Dakota: Minnesota, Wisconsin, North Dakota, South Dakota
- Oklahoma-Kansas-Missouri: Oklahoma, Kansas, Missouri, Nebraska, Iowa
- PADD III: Gulf Coast
- Texas Gulf Coast: The Texan counties of Newton, Orange, Jefferson, Jasper, Tyler, Hardin, Liberty, Chambers, Polk, San Jacinto, Montgomery, Harris, Galveston, Waller, Fort Bend, Brazoria, Wharton, Matagorda, Jackson, Victoria, Calhoun, Refugio, Aransas, San Patricio, Nueces, Kleberg, Kenedy, Willacy and Cameron
- Texas Inland: Texan counties not mentioned above.
- Louisiana Gulf Coast: Parishes of Louisiana south of, and including Vernon, Rapides, Avoyelles, Pointe Coupee, West Feliciana, East Feliciana, Saint Helena, Tangipahoa and Washington; along with Pearl River, Stone, George, Hancock, Harrison, and Jackson County of Mississippi; and Alabama's Mobile and Baldwin County.
- North Louisiana-Arkansas: Arkansas and parts of Louisiana, Mississippi and Alabama not mentioned above.
- New Mexico: New Mexico
- PADD IV: Rocky Mountain: Colorado, Montana, Idaho, Wyoming, Utah
- PADD V: West Coast: Washington, Oregon, California, Nevada, Arizona, Alaska, Hawaii[14]
PADD I can also be subdivided into 3 Subdistricts:
- Sub-PAD 1A: New England (Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, Vermont)
- Sub-PAD 1B: Central Atlantic (Delaware, Maryland, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, District of Columbia)
- Sub-PAD 1C: Lower Atlantic (Florida, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Virginia, West Virginia)[15]
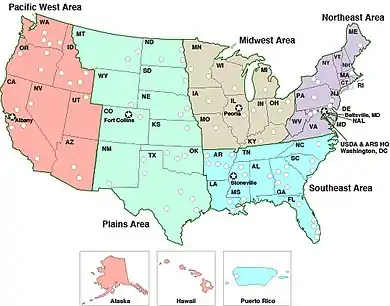
Agricultural Research Service
The Agricultural Research Service (ARS) is the research arm of the USDA. The ARS has sectioned their work into five geographic regions:
- Midwest Area
- Northeast Area
- Pacific West Area
- Plains Area
- Southeast Area
U.S. National Park Service
The U.S. National Park Service divides the U.S. into the following regions for U.S. National Park purposes:[16][17]
- Northeast region (Connecticut, Delaware, most of Maryland, Massachusetts, Maine, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, most of Virginia, most of West Virginia)
- National Capital region (District of Columbia, some of Maryland, some of Virginia, some of West Virginia)
- Southeast region (Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Kentucky, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee, Puerto Rico, U.S. Virgin Islands)
- Midwest region (Arkansas, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Kansas, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, Nebraska, North Dakota, Ohio, South Dakota, Wisconsin)
- Intermountain region (Arizona, Colorado, Montana, New Mexico, Oklahoma, Texas, Utah, Wyoming)
- Pacific region (California, Hawaii, Idaho, Nevada, Oregon, Washington, American Samoa, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands)
- Alaska region (Alaska)
The U.S. Minor Outlying Islands are not part of any U.S. National Park Service region.
Unofficial multi-state and multi-territory regions
- American Frontier
- Appalachia
- Ark-La-Tex
- Black Dirt Region
- Border states:
- Calumet Region
- The Carolinas
- Cascadia
- Central United States
- Coastal states
- Colorado Plateau
- Columbia Basin
- Contiguous United States
- The Dakotas
- Deep South
- Delmarva Peninsula
- Dixie
- Driftless Area
- East Coast
- Eastern United States
- Four Corners
- Great American Desert
- Great Appalachian Valley
- Great Basin
- Great Lakes Region
- Great Plains
- Gulf Coast
- Gulf South
- High Plains
- Interior Plains
- Intermountain States
- Llano Estacado
- Mid-Atlantic states
- Mid-South states
- Midwestern United States
- Mississippi Delta
- Mojave Desert
- Mormon Corridor
- New England
- Northeastern United States
- Northern United States
- Northwestern United States
- Ohio Valley
- Ozarks
- Pacific Northwest
- Pacific States
- Palouse
- Piedmont
- Piney Woods
- Rocky Mountains
- Siouxland
- Southeastern United States
- Southern United States
- Southwestern United States
- Old Southwest
- Tornado Alley
- Trans-Mississippi
- Twin Tiers
- Upland South
- Upper Midwest
- Virginias
- Waxhaws
- West Coast
- Western United States
There are also multi-territory regions:
- Mariana Islands (Guam and the Northern Mariana Islands)
- Samoan Islands (American Samoa, except Swains Island) [note 1]
- Virgin Islands (the Spanish Virgin Islands and the U.S. Virgin Islands) [note 2]
The Belts
Interstate metropolitan areas
- Central Savannah River Area (part of Georgia and South Carolina)
- Baltimore–Washington metropolitan area (District of Columbia and parts of Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania)
- Washington metropolitan area (District of Columbia and parts of Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia)
- Greater Boston (parts of Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and New Hampshire)
- Charlotte metropolitan area (parts of North Carolina and South Carolina)
- Chattanooga Metropolitan Area
- Chicago metropolitan area (parts of Illinois, Indiana, and Wisconsin)
- Cincinnati metropolitan area (parts of Ohio, Indiana, and Kentucky)
- Columbus-Auburn-Opelika (GA-AL) Combined Statistical Area (parts of Georgia and Alabama)
- Delaware Valley (Philadelphia metropolitan area) (parts of Pennsylvania, New Jersey, Delaware, and Maryland)
- Evansville, IN–KY Metropolitan Statistical Area (parts of Indiana and Kentucky)
- Fargo–Moorhead (parts of North Dakota and Minnesota)
- Fort Smith metropolitan area (parts of Arkansas and Oklahoma)
- Front Range Urban Corridor (parts of Colorado and Wyoming)
- Greater Grand Forks (part of Minnesota and North Dakota)
- Hartford-Springfield (parts of Connecticut and Massachusetts)
- Kansas City metropolitan area (parts of Missouri and Kansas)
- Louisville metropolitan area (Kentuckiana) (parts of Kentucky and Indiana)
- Memphis metropolitan area (parts of Tennessee, Arkansas, and Mississippi)
- Michiana (parts of Michigan and Indiana)
- Minneapolis–Saint Paul (the Twin Cities) (parts of Minnesota and Wisconsin)
- New York metropolitan area (parts of New York, New Jersey, Connecticut, and Pennsylvania)
- Omaha–Council Bluffs metropolitan area (parts of Nebraska and Iowa)
- Portland metropolitan area (parts of Oregon and Washington)
- Quad Cities (parts of Iowa and Illinois)
- Sacramento metropolitan area (parts of California and Nevada)
- Greater St. Louis (parts of Missouri and Illinois)
- Texarkana metropolitan area (parts of Texas and Arkansas)
- Tri-Cities (parts of Tennessee and Virginia)
- Twin Ports (Duluth, Minnesota and Superior, Wisconsin)
- Hampton Roads region (parts of Virginia and North Carolina)
- Youngstown–Warren–Boardman metropolitan statistical area (parts of Ohio and Pennsylvania)
Interstate megalopolises
Intrastate and intraterritory regions
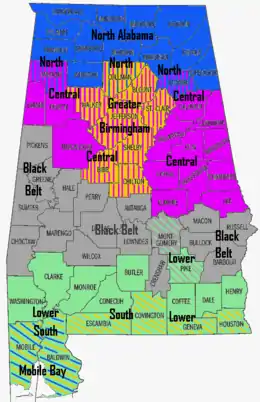
Alabama
Alaska
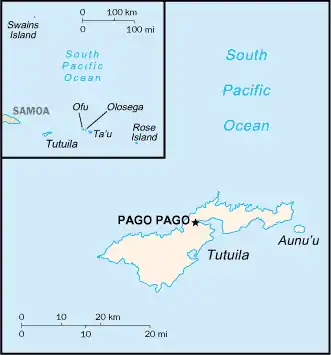
American Samoa
Arizona
Arkansas
California
Colorado
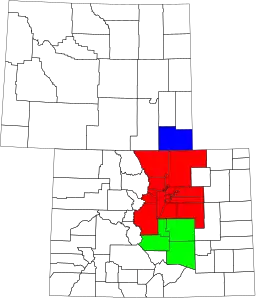
- Central Colorado (part of Southern Rocky Mountains)
- Colorado Eastern Plains (part of High Plains and Great Plains)
- Colorado Front Range (part of Front Range Urban Corridor)
- Colorado Mineral Belt (part of Southern Rocky Mountains)
- Colorado Piedmont (contains parts of the Front Range Urban Corridor and High Plains)
- Colorado Western Slope (part of Southern Rocky Mountains and Colorado Plateau)
- Denver-Aurora Metropolitan Area (part of Front Range Urban Corridor)
- High Rockies (part of Southern Rocky Mountains)
- Northwestern Colorado (part of Southern Rocky Mountains)
- San Luis Valley
- South-Central Colorado (part of Front Range Urban Corridor)
- Southwestern Colorado (part of Southern Rocky Mountains and Colorado Plateau)
Connecticut
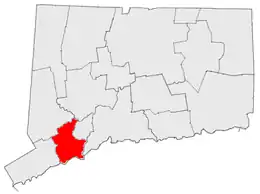
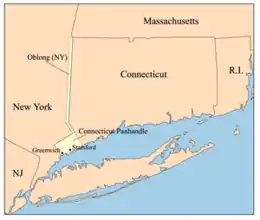
Connecticut has no official regions. After abolishing county governments, all local governing is done by towns and cities, leaving counties as purely geographical and statistical entities. Some unofficial regions of Connecticut include:
- Central Naugatuck Valley
- Coastal Connecticut
- Connecticut panhandle
- Greater Bridgeport
- Greater New Haven
- Greater Hartford
- Housatonic Valley (shared with Massachusetts)
- Litchfield Hills
- Lower Connecticut River Valley
- Naugatuck River Valley
- New York Metropolitan Area/Gold Coast
- Southeastern Connecticut
- Western Connecticut
Delaware
"Upstate" or "Up North"
- Delaware Valley also known as "Above the Canal" (referring to the Chesapeake and Delaware Canal)
"Slower Lower"
- Cape Region
- Central Kent
- Delaware coast
District of Columbia
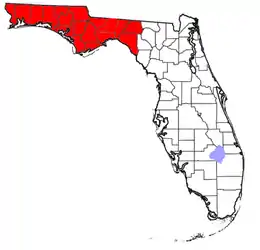
Florida
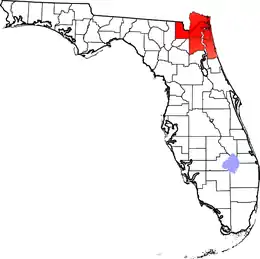
Directional regions
- Central Florida
- North Florida
- Northwest Florida
- North Central Florida
- Northeast Florida
- South Florida
- Southwest Florida
Local vernacular regions
Georgia
Physiographic regions
Hawaiʻi
Idaho
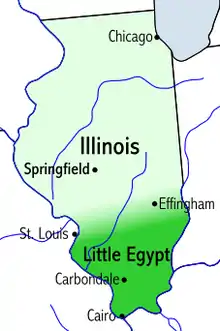
Illinois
- American Bottom
- Central Illinois
- Champaign–Urbana metropolitan area
- Chicago metropolitan area
- Community areas in Chicago
- Driftless Area
- Forgottonia
- Fox Valley
- Metro-East
- Metro Lakeland
- Military Tract of 1812
- Mississippi Alluvial Plain
- North Shore
- Northern Illinois
- Northwestern Illinois
- Peoria, Illinois metropolitan area
- Quad Cities
- River Bend
- Rock River Valley
- Shawnee Hills
- Southern Illinois (sometimes, Little Egypt)
- Streatorland
- Tri-State Area
- Wabash Valley
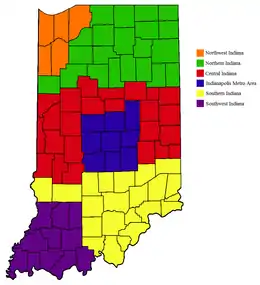
Indiana
Iowa
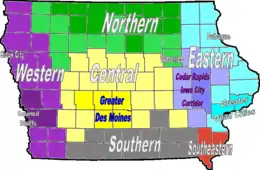
Kansas
Kentucky
Louisiana
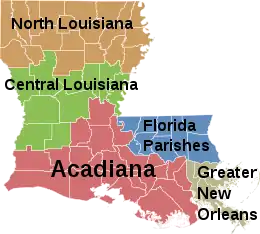
- Cajun Heartland
- River Parishes
- Central Louisiana (Cen-La)
- Florida Parishes
- "French Louisiana" (Acadiana + Greater New Orleans)
- Greater New Orleans
- North Louisiana
- Southwest Louisiana
Maine
Maryland
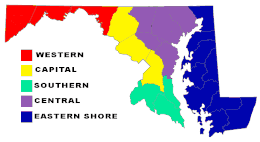
- Baltimore-Washington Metropolitan Area
- Capital region
- Chesapeake Bay
- Eastern Shore of Maryland
- Patapsco Valley
- Southern Maryland
- Western Maryland
Regions shared with other states:
- Allegheny Mountains
- Atlantic coastal plain
- Blue Ridge Mountains
- Cumberland Valley
- Delaware Valley
- Delmarva Peninsula consists of Maryland's and Virginia's Eastern Shore and all of Delaware
- Piedmont (United States)
- Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians
Massachusetts
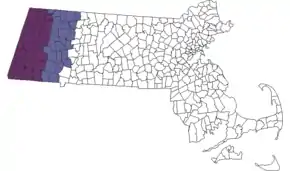
- Western Massachusetts
- The Berkshires (shown in map)
- Housatonic Valley
- Pioneer Valley
- Quabbin-Swift River Valley
- Central Massachusetts
- Northeastern Massachusetts
- Southeastern Massachusetts
Michigan
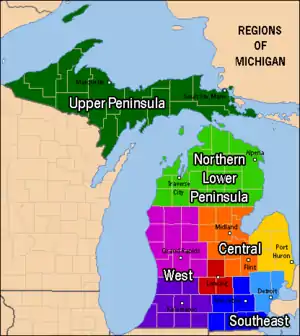
Lower Peninsula
Upper Peninsula
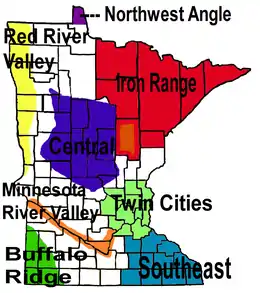
Minnesota
Mississippi
- Mississippi Alluvial Plain
- Mississippi Delta
- Mississippi East Gulf Coast Plain
- Mississippi Gulf Coast
- Natchez Trace
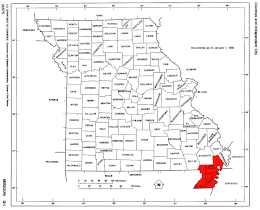
Missouri
Montana
- Big Horn Mountains
- Eastern Montana
- The Flathead
- Glacier Country
- Glacier National Park
- Regional designations of Montana
- South Central Montana
- Southwestern Montana
- Two Medicine
- Western Montana
- Yellowstone National Park
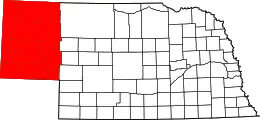
Nebraska
- Nebraska Panhandle
- Northwest Nebraska
- Pine Ridge
- Rainwater Basin
- Sand Hills
- Southeast Nebraska
- South Central Nebraska
- Wildcat Hills
New Hampshire
- Connecticut River Valley
- Dartmouth-Lake Sunapee Region (overlaps with Connecticut River Valley)
- Great North Woods Region
- Lakes Region
- Merrimack Valley
- Monadnock Region (overlaps with Connecticut River Valley)
- Seacoast Region
- White Mountains
New Jersey
- North Jersey
- Skylands
- Amwell Valley
- Black Dirt Region (shared with New York)
- Great Valley
- Sussex County Snow Belt
- Hunterdon Plateau
- Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians
- Highlands
- Somerset Hills
- The Sourlands
- Gateway
- Skylands
- Central Jersey
- South Jersey
- Shore Region
- Northern Headlands
- Pine Barrens
- Delaware Valley
- Southern Shore
- Cape May
- The Glades
- Tri Cities (Bridgeton, Millville, Vineland)
- Tri-County Farm Belt
- Greater Atlantic City
- Pine Barrens
- Central Corridor Piedmont Region
- Shore Region
New York
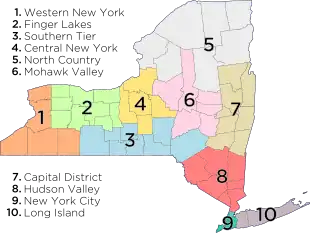
1. Western New York – counties : Niagara, Erie, Chautauqua, Cattaraugus, Allegany
2. Finger Lakes – counties : Orleans, Genesee, Wyoming, Monroe, Livingston, Wayne, Ontario, Yates, Seneca
3. Southern Tier – counties : Steuben, Schuyler, Chemung, Tompkins, Tioga, Chenango, Broome, Delaware
4. Central New York – counties : Cortland, Cayuga, Onondaga, Oswego, Madison
5. North Country – counties : St. Lawrence, Lewis, Jefferson, Hamilton, Essex, Clinton, Franklin
6. Mohawk Valley – counties : Oneida, Herkimer, Fulton, Montgomery, Otsego, Schoharie
7. Capital District – counties : Albany, Columbia, Greene, Warren, Washington, Saratoga, Schenectady, Rensselaer
8. Hudson Valley – counties : Sullivan, Ulster, Dutchess, Orange, Putnam, Rockland, Westchester
9. New York City – counties (boroughs) : New York (Manhattan), Bronx (The Bronx), Queens (Queens), Kings (Brooklyn), Richmond (Staten Island)
10. Long Island – counties : Nassau, Suffolk
- Downstate New York
- Upstate New York
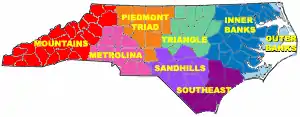
North Carolina
North Dakota
- Badlands
- Missouri Escarpment
- Missouri River Corridor
- Red River Valley
Northern Mariana Islands
Ohio
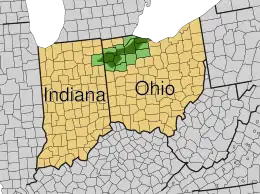
- Allegheny Plateau
- Appalachian Ohio
- Cincinnati-Northern Kentucky metropolitan area
- Columbus, Ohio metropolitan area
- Connecticut Western Reserve (historic, now defunct)
- Great Black Swamp (shared with Indiana)
- The Lake Erie Islands
- Miami Valley
- Northeast Ohio (often used interchangeably with Greater Cleveland, but also includes the counties of Ashtabula, Portage, Summit, Trumbull, Mahoning and Columbiana.)
- Northwest Ohio
Oklahoma
Oregon
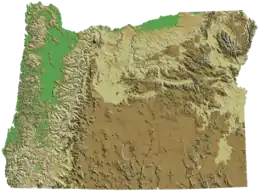
- Cascade Range
- Central Oregon
- Columbia Plateau
- Columbia River
- Columbia River Gorge
- Eastern Oregon
- Goose Lake Valley
- Harney Basin
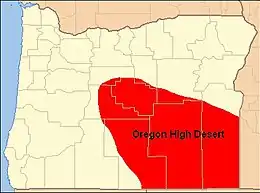
- High Desert
- Hood River Valley
- Mount Hood Corridor
- Northwest Oregon
- Oregon Coast
- Palouse
- Portland metropolitan area
- Rogue Valley
- Southern Oregon
- Treasure Valley
- Tualatin Valley
- Warner Valley
- Western Oregon
- Willamette Valley
Pennsylvania
- Allegheny National Forest
- Coal Region
- Cumberland Valley
- Delaware Valley
- Dutch Country
- Endless Mountains
- Highlands Region
- Laurel Highlands
- Lehigh Valley
- Main Line
- Northern Tier
- Northeastern Pennsylvania
- Northwest Region
- Pittsburgh metropolitan area
- The Poconos
- South Central Pennsylvania
- Susquehanna Valley
- Western Pennsylvania
- Wyoming Valley (Scranton/Wilkes-Barre Metropolitan Area)
Puerto Rico
Rhode Island
South Carolina
- The Lowcountry
- The Midlands
- The Upstate
- Travel/Tourism locations
- Other geographical distinctions
- Blue Ridge Mountains
- Charleston metropolitan area
- Coastal South Carolina
- Columbia metropolitan area
- The Piedmont
- Rock Hill, South Carolina Area
- The Sandhills
- Sea Islands
- West Ashley
South Dakota
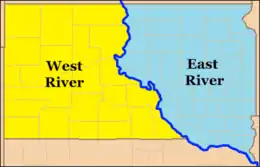
East River and West River
- East River and West River, divided by the Missouri River
- Badlands
- Black Hills
- Coteau des Prairies
Tennessee
- East Tennessee
- Middle Tennessee
- West Tennessee
- Other geographical distinctions:
Texas
- Brazos Valley
- Central Texas
- Gulf Coast
- East Texas
- North Texas
- South Texas
- Mission Country
- Rio Grande Valley
- Southeast Texas
- Texas Midwest/West-Central Texas (includes Abilene, San Angelo, Brownwood, Texas)
- Texas Urban Triangle (Houston to San Antonio to Dallas-Fort Worth)
- West Texas
- Concho Valley
- Edwards Plateau
- Llano Estacado (a portion of northwest Texas)
- Permian Basin
- South Plains (includes 24 counties south of the Texas Panhandle and north of the Permian Basin)
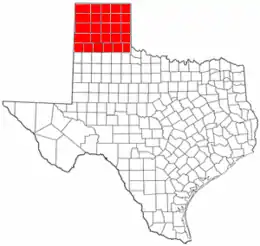
- Texas Panhandle (pictured)
- Trans-Pecos
- Great Plains
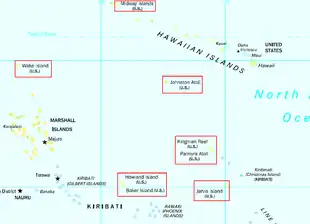
U.S. Minor Outlying Islands
Utah
- Cache Valley
- Colorado Plateau
- Dixie
- Great Salt Lake Desert
- Mojave Desert
- San Rafael Swell
- Southeastern Utah
- Southwestern Utah
- Uinta Mountains
- Wasatch Back
- Wasatch Front
- Wasatch Range
Vermont
Virginia
Washington
West Virginia
- Eastern Panhandle
- North Central West Virginia
- Northern Panhandle
- Potomac Highlands
- Southern West Virginia
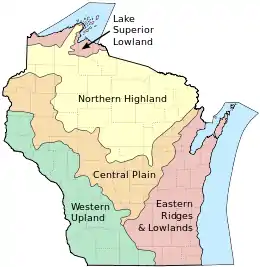
Wisconsin
Wisconsin can be divided into five geographic regions.
Other regional listings
Regions of the Boy Scouts of America
See also
- Geography of the United States
- Historic regions of the United States
- List of metropolitan areas of the United States
- Media market, e.g., Nielsen Designated Market Area
- Political divisions of the United States
- United States territory
- Vernacular geography
Notes
- This region also includes the Independent State of Samoa, which is not a part of the United States
- This region also includes the British Virgin Islands, which is not a part of the United States
- Claimed by Tokelau[18]
- Midway Atoll, part of the Northwest Hawaiian Islands, is not politically part of Hawaii; it is one of the United States Minor Outlying Islands
- Claimed by Haiti
- Claimed by the Marshall Islands
References
- "Statistical Groupings of States and Counties" (PDF). census.gov. United States Census Bureau. Retrieved December 16, 2020.
- United States Census Bureau, Geography Division. "Census Regions and Divisions of the United States" (PDF). Retrieved January 10, 2013.
- "The National Energy Modeling System: An Overview 2003" (Report #:DOE/EIA-0581, October 2009). United States Department of Energy, Energy Information Administration.
- "The most widely used regional definitions follow those of the U.S. Bureau of the Census." Seymour Sudman and Norman M. Bradburn, Asking Questions: A Practical Guide to Questionnaire Design (1982). Jossey-Bass: p. 205.
- "Perhaps the most widely used regional classification system is one developed by the U.S. Census Bureau." Dale M. Lewison, Retailing, Prentice Hall (1997): p. 384. ISBN 978-0-13-461427-4
- "[M]ost demographic and food consumption data are presented in this four-region format." Pamela Goyan Kittler, Kathryn P. Sucher, Food and Culture, Cengage Learning (2008): p.475. ISBN 9780495115410
- "Census Bureau Regions and Divisions with State FIPS Codes" (PDF). US Census Bureau. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 21, 2013. Retrieved June 20, 2010.
- "Census Bureau Regions and Divisions with State FIPS Codes" (PDF). US Census Bureau. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 21, 2013. Retrieved June 20, 2010.
- "Geographic Terms and Concepts - Census Divisions and Census Regions". US Census Bureau. Retrieved August 19, 2015.
- "Rescission of OMB Circulars". Federal Register. March 22, 1995.
- "No DST in Most of Arizona". www.timeanddate.com. Retrieved August 14, 2020.
- "BEA Regions". Bureau of Economic Analysis. February 18, 2004. Retrieved December 27, 2012.
- "Records of Petroleum Administration for War". Retrieved January 3, 2012.
- "Appedix A: District Description and Maps" (PDF). Energy Information Administration. October 2012. Retrieved January 3, 2012.
- "PADD Definitions". Energy Information Administration. Archived from the original on October 16, 2011. Retrieved January 3, 2012.
- https://web.archive.org/web/20190705075545/https://www.nps.gov/orgs/rtca/contactus.htm U.S. National Park Service. Rivers, Trails, and Conservation Assistance Program. Contact Us. (archived) Retrieved July 5, 2019.
- U.S. National Park Service. Partnerships - Contact Us. Retrieved September 1, 2019.
- The World Factbook CIA World Factbook - American Samoa. Retrieved July 5, 2019.
- "United States Regions". National Geographic.
- "US Geography regions". Ducksters.
- "Regions of the US". Flocabulary.
.png.webp)