Iron(II) lactate
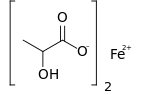
Ferrous lactate, or iron(II) lactate, is a chemical compound consisting of one atom of iron (Fe2+) and two lactate anions. It has the chemical formula Fe(C
3H
5O
3).
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Ferrous 2-hydroxypropanoate | |
| Other names
Iron dilactate Iron(II) lactate E585 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.025.098 |
| E number | E585 (acidity regulators, ...) |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H10FeO6 | |
| Molar mass | 233.9888 g/mol (anhydrous) 288.03464 g/mol (trihydrate) |
| Appearance | greenish-white powder |
| Melting point | 500 °C (932 °F; 773 K) |
| trihydrate: 2.1 g/100ml (10 °C) 8.5 g/100ml (100 °C) dihydrate: 2% (25 °C)[1] | |
| Solubility | soluble in alkali citrates negligible in alcohol insoluble in ether |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Uses
It is used as a food additive with E number E585. It is an acidity regulator and colour retention agent, and is also used to fortify foods with iron.
References
- Iron(II) lactate dihydrate MSDS Archived 2014-05-03 at the Wayback Machine at Jost Chemical
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.