Isotoxal figure
In geometry, a polytope (for example, a polygon or a polyhedron), or a tiling, is isotoxal or edge-transitive if its symmetries act transitively on its edges. Informally, this means that there is only one type of edge to the object: given two edges, there is a translation, rotation and/or reflection that will move one edge to the other, while leaving the region occupied by the object unchanged.
The term isotoxal is derived from the Greek τοξον meaning arc.
Isotoxal polygons
An isotoxal polygon is an even-sided equilateral polygon, but not all equilateral polygons are isotoxal. The duals of isotoxal polygons are isogonal polygons. 4n-gonal are centrally symmetric so are also zonogons.
In general, an isotoxal 2n-gon will have Dn (*nn) dihedral symmetry. A rhombus is an isotoxal polygon with D2 (*22) symmetry. All regular polygons (equilateral triangle, square, etc.) are isotoxal, having double the minimum symmetry order: a regular n-gon has Dn (*nn) dihedral symmetry.
An isotoxal 2n-gon can be labeled as {nα} with outer most internal angle α. The second internal angle β may be greater or less than 180 degrees, making convex or concave polygons. Star polygons can also be isotoxal, labeled as {(n/q)α}, with q<n-1 and gcd(n,q)=1, with q as the turning number or density.[1] Concave inner vertices can be defined for q<n/2. If there is a largest common divisor, like a, {(na/qa)α} can be reduced as a compound a{(n/q)α}, with a copied rotated.
A set of uniform tilings can be defined with isotoxal polygons as a lower type of regular faces.
| Sides (2n) | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| {nα} Convex β<180 Concave β>180 |
{2α} |
 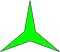 {3α} |
  {4α} |
  {5α} |
  {6α} |
  {7α} |
  {8α} |
| 2-turn {(n/2)α} |
-- | 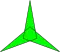 {(3/2)α} |
 2{2α} |
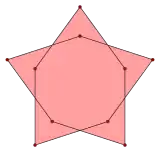  {(5/2)α} |
  2{3α} |
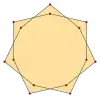  {(7/2)α} |
  2{4α} |
| 3-turn {(n/3)α} |
-- | -- |  {(4/3)α} |
 {(5/3)α} |
 3{2α} |
  {(7/3)α} |
  {(8/3)α} |
| 4-turn {(n/4)α} |
-- | -- | -- |  {(5/4)α} |
 2{(3/2)α} |
 {(7/4)α} |
 4{2α} |
| 5-turn {(n/5)α} |
-- | -- | -- | -- | 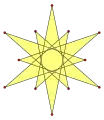 {(6/5)α} |
 {(7/5)α} |
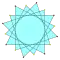 {(8/5)α} |
| 6-turn {(n/6)α} |
-- | -- | -- | -- | -- | 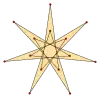 {(7/6)α} |
 2{(4/3)α} |
| 7-turn {(n/7)α} |
-- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- |  {(8/7)α} |
Isotoxal polyhedra and tilings
Regular polyhedra are isohedral (face-transitive), isogonal (vertex-transitive), and isotoxal (edge-transitive).
Quasiregular polyhedra, like the cuboctahedron and the icosidodecahedron, are isogonal and isotoxal, but not isohedral. Their duals, including the rhombic dodecahedron and the rhombic triacontahedron, are isohedral and isotoxal, but not isogonal.
| Quasiregular polyhedron |
Quasiregular dual polyhedron |
Quasiregular star polyhedron |
Quasiregular dual star polyhedron |
Quasiregular tiling |
Quasiregular dual tiling |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 A cuboctahedron is an isogonal and isotoxal polyhedron |
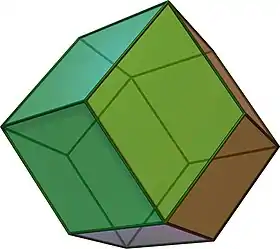 A rhombic dodecahedron is an isohedral and isotoxal polyhedron |
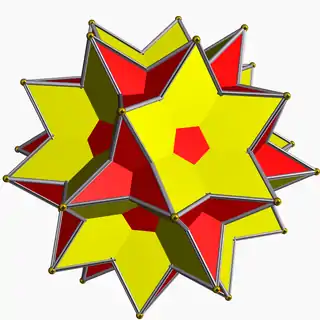 A great icosidodecahedron is an isogonal and isotoxal star polyhedron |
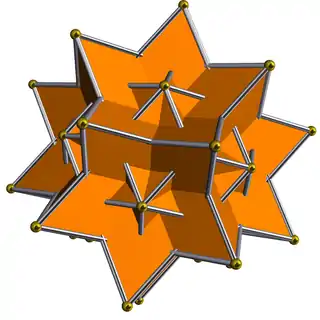 A great rhombic triacontahedron is an isohedral and isotoxal star polyhedron |
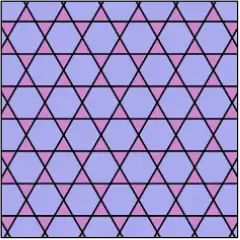 The trihexagonal tiling is an isogonal and isotoxal tiling |
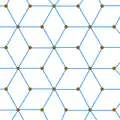 The rhombille tiling is an isohedral and isotoxal tiling with p6m (*632) symmetry. |
Not every polyhedron or 2-dimensional tessellation constructed from regular polygons is isotoxal. For instance, the truncated icosahedron (the familiar soccerball) is not isotoxal, as it has two edge types: hexagon-hexagon and hexagon-pentagon, and it is not possible for a symmetry of the solid to move a hexagon-hexagon edge onto a hexagon-pentagon edge.
An isotoxal polyhedron has the same dihedral angle for all edges.
The dual of a convex polyhedron is also a convex polyhedron.[2]
The dual of a non-convex polyhedron is also a non-convex polyhedron.[2] (By contraposition.)
The dual of an isotoxal polyhedron is also an isotoxal polyhedron. (See the Dual polyhedron article.)
There are nine convex isotoxal polyhedra: the five (regular) Platonic solids, the two (quasiregular) common cores of dual Platonic solids, and their two duals.
There are fourteen non-convex isotoxal polyhedra: the four (regular) Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra, the two (quasiregular) common cores of dual Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra, and their two duals, plus the three quasiregular ditrigonal (3 | p q) star polyhedra, and their three duals.
There are at least five isotoxal polyhedral compounds: the five regular polyhedral compounds; their five duals are also the five regular polyhedral compounds (or one chiral twin).
There are at least five isotoxal polygonal tilings of the Euclidean plane, and infinitely many isotoxal polygonal tilings of the hyperbolic plane, including the Wythoff constructions from the regular hyperbolic tilings {p,q}, and non-right (p q r) groups.
References
- Tilings and Patterns Branko Gruenbaum, G.C. Shephard, 1987. 2.5 Tilings using star polygons, pp.82-85.
- "duality". maths.ac-noumea.nc. Retrieved 2020-09-30.
- Peter R. Cromwell, Polyhedra, Cambridge University Press 1997, ISBN 0-521-55432-2, p. 371 Transitivity
- Grünbaum, Branko; Shephard, G. C. (1987). Tilings and Patterns. New York: W. H. Freeman. ISBN 0-7167-1193-1. (6.4 Isotoxal tilings, 309-321)
- Coxeter, Harold Scott MacDonald; Longuet-Higgins, M. S.; Miller, J. C. P. (1954), "Uniform polyhedra", Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 246 (916): 401–450, Bibcode:1954RSPTA.246..401C, doi:10.1098/rsta.1954.0003, ISSN 0080-4614, JSTOR 91532, MR 0062446, S2CID 202575183