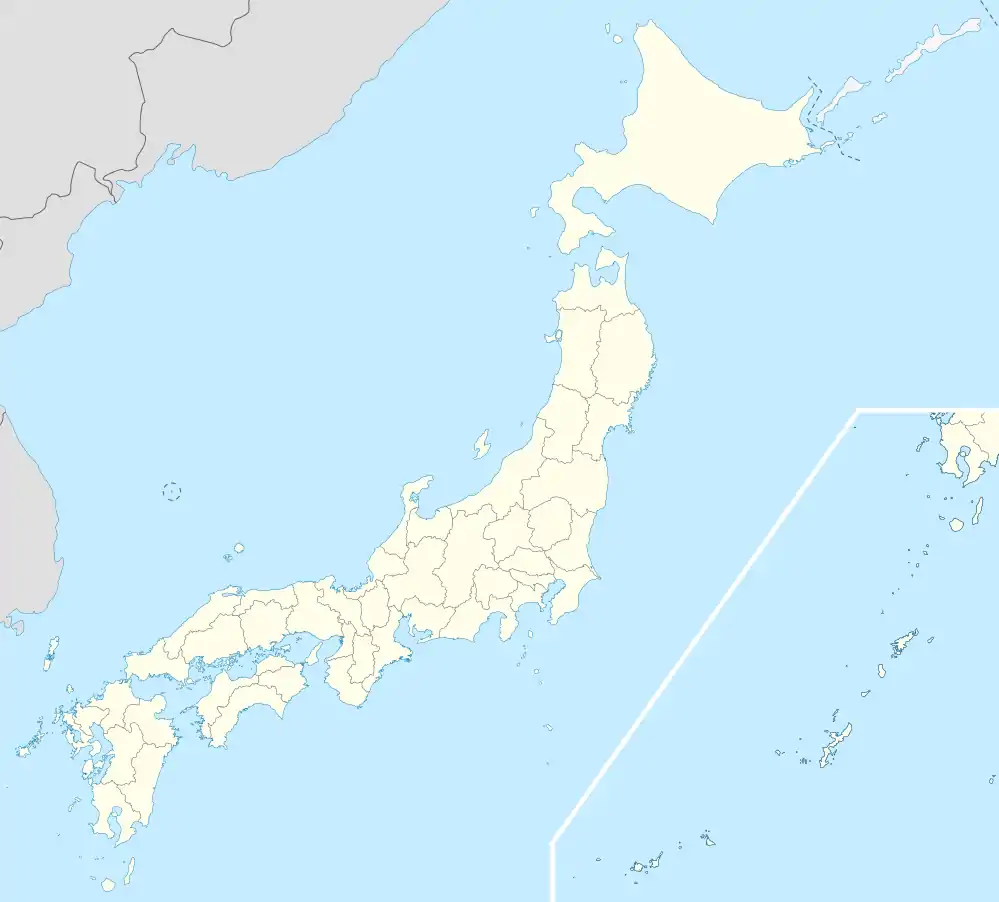
Japan 2023 FIFA Women's World Cup bid
The Japan bid for the 2023 FIFA Women's World Cup was a bid to host the 2023 FIFA Women's World Cup by Japan Football Association (JFA). The single bid was announced on 12 December 2019.[1] The bid entailed 8 venues in 8 host cities, with a final to have been played in Tokyo at the New National Stadium. The bid was withdrawn on 22 June 2020, with the JFA indicating support for the Australia-New Zealand bid.[2]
| Japan bid | |
|---|---|
| for the 2023 FIFA Women's World Cup | |
 Japan 2023 bid logo | |
| Bid Details | |
| Bidding nation | Japan |
| Bidding federation | Japan Football Association |
| Proposed venues | 8 (in 8 cities) |
| Bid result | |
| Withdrawn on 22 June 2020 | |
| Official website | |
| japan2023bid.com | |
Background
Japan have considered bidding on the tournament after declining their initial intention to bid on the 2019 FIFA Women's World Cup. Japan Football Association vice president Kozo Tashima is reported to have said that the facilities will be renovated and ready for the World Cup.[1] On 20 February 2019 The Japan Football Association announced that it will go forward with a long-planned bid to host the 2023 Women's World Cup.[3] On 5 July 2019 Japan unveiled its bid logo along with the slogan "Time to Fly".[4] The bid included eight stadiums, including several venues that are set to play host to the 2020 Summer Olympics football tournament.[5]
Proposed venues
The following host cities, venues and capacities were included in the Bid Book submitted to FIFA:[6]
| Shinjuku, Tokyo | Suita, Osaka | Saitama City | Kobe, Hyōgo |
|---|---|---|---|
| National Stadium | Suita City Football Stadium | Saitama Stadium | Kobe Misaki Stadium |
| Capacity: 80,016 |
Capacity: 40,000 |
Capacity: 62,000 |
Capacity: 30,000 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| Kyoto City | |||
| Kyoto Stadium | |||
| Capacity: 22,000 | |||
 | |||
| Sendai, Miyagi | |||
| Sendai Stadium | |||
| Capacity: 19,694 | |||
 | |||
| Sapporo, Hokkaido | |||
| Sapporo Dome | |||
| Capacity: 42,000 | |||
 | |||
| Toyota, Aichi | |||
| Toyota Stadium | |||
| Capacity: 45,000 | |||
 | |||
Withdrawal
The JFA withdrew their bid to host the tournament on 22 June 2020,[7] citing Brazil's withdrawal as unifying the CONMEBOL vote for Colombia, ASEAN Football Federation's backing of Australia and New Zealand, and the unlikelihood of their bid being successful due to the delayed Tokyo 2020 women's football tournament. The JFA also suggested that without the burden of hosting the tournament, they could provide more resources to their national team in the hope of winning the tournament.[8]
See also
References
- "Japan to bid for 2023 Women's World Cup". The Japan Times. 1 February 2015.
- "OFFICIAL: Japan has withdrawn from consideration for hosting the #WWC2023 and put its support behind @AsOne2023". Dan Orlowitz on Twitter. 22 June 2020.
- "Football: Japan to bid for 2023 Women's World Cup, Nadeshiko enter camp". Kyodo News. 20 February 2019.
- "Japan Reveals Official Logo of Bid to Host 2023 Women's World Cup". Japan Football Association. 5 July 2019.
- Orlowitz, Dan (12 December 2019). "Japan submits bid for 2023 Women's World Cup to FIFA". The Japan Times. Retrieved 12 December 2019.
- "Japan bidding to host the FIFA Women's World Cup 2023™" (PDF). Japan Football Association (JFA). Retrieved 14 December 2019.
- "Football: Japan to withdraw hosting bid for 2023 Women's World Cup". Kyodo News. 22 June 2020.
- "OFFICIAL: Japan has withdrawn from consideration for hosting the #WWC2023 and put its support behind @AsOne2023". Dan Orlowitz on Twitter. 22 June 2020.