Kadavu Island
Kadavu (pronounced [kanˈdaβu]), with an area of 411 square kilometres (159 sq mi), is the fourth largest island in Fiji, and the largest island in the Kadavu Group, a volcanic archipelago consisting of Kadavu, Ono, Galoa and a number of smaller islands in the Great Astrolabe Reef. Its main administrative centre is Vunisea, which has an airport, a high school, a hospital, and a government station, on the Namalata Isthmus where the island is almost cut in two. Suva, Fiji's capital, lies 88 kilometres (55 miles) to the north of Kadavu. The population of the island province was 10,167 at the most recent census in 2007.
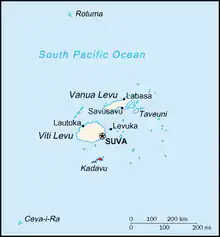
Kadavu Island belongs to Kadavu Province.
Geography
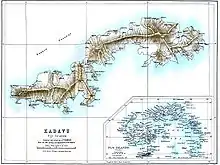 Kadavu on the map of J.P.Thomson, 1889 |
 Vunisea |
The island is 60 kilometres (37 miles) long, with a width varying from 365 metres (1,198 ft) to 8 kilometres (5 miles). The island is almost sliced in two at the narrow Namalata Isthmus, which separates Namalata Bay on the northern coast from Galoa Harbour on the southern coast. Within Galoa Harbour lie Galoa Island and the tiny islet of Tawadromu. Kadavu is characterized by its rugged and mountainous terrain. The tallest mountain is Nabukelevu, also known as Mount Washington, which stands at 805 metres (2,641 feet) high, on the western end of the island.

Flora and fauna
Kadavu still has 75% of its original rainforest cover and a rich bird diversity, including four species endemic to the island, the velvet dove, the crimson shining-parrot, the Kadavu honeyeater and the Kadavu fantail, in addition to several endemic subspecies (such as a subspecies of the island thrush). Offshore, stringing around the south, east and then away to the north, is the Great Astrolabe Reef, a large barrier reef that is one of Fiji's premier scuba diving resorts.
A 7,800 hectares (19,000 acres) area covering the interior of the eastern part of the island is the East Kadavu Important Bird Area. It contains populations of the vulnerable Shy Ground-dove, Crimson Shining-parrot and Collared Petrel.[1]

Economy and culture

Kadavu is one of the least developed areas of Fiji. There are few roads, and the local economy is largely dependent on subsistence farming, supplemented by exports to Viti Levu. The main commercial crop is yaqona (known as Kava around the Pacific islands). There are no banks on Kadavu. Tourism is becoming popular, however, with snorkeling and diving among the major attractions. The chiefly system in Kadavu gives much greater authority to local chiefs than most other areas in Fiji, where local chiefs are more often subservient to a few "paramount chiefs."
On 17 December 2005, Ratu Josateki Nawalowalo, Chairman of the Kadavu Provincial Council, announced major development plans to build roads throughout the island and to upgrade jetties, improving Kadavu's links with the mainland. He revealed that much of the finance would be provided by the government of Taiwan.
History
William Bligh was the first known European to sight Kadavu, which he discovered in 1792 on his second voyage to Fiji on HMS Providence. He was followed in 1799 by the United States vessel Ann & Hope, skippered by C. Bently en route from Australia. In 1827, French commander Dumont d'Urville nearly shipwrecked Astrolabe on the reef that now bears the vessel's name. The island later became home to beche-de-mer traders, as well as whalers from Sydney, Australia, and New England in the United States. Galoa Harbour became a regular port of call for vessels carrying mail between Sydney, San Francisco, and Auckland.
Origin of the Kadavu People
Most Kadavuans are not sure where their ancestors may have originated from. Some say that they never travelled from other places but were always present on the island. While some have various theories. However, a well-known linguist feels that the people of Kadavu may have come from the East, given the similarity of words with the southernmost part of the Lauan group of islands and the core belief that Kadavu's ancestors settled from the East, as opposed to the rest of Fiji where the movement was Westwards. It can also be seen that Kadavuans generally possess Polynesian attributes, which may further add to the belief. Yet, the notion is debatable as Kadavu and Lau never had any affiliation in the past, be it tribal or provincial. It has only been in the last decade or so that the two provinces coined the term "Yanu" (meaning island or islanders), to forge a relationship.
Pride of Kadavu
Kadavu Island is nicknamed "Bird land" and rightly so, as it has a number of rare birds that are endemic to the island. These birds have survived on Kadavu due to the richness and abundance of natural resources as well as the climatic conditions of the island. The most famous bird is the Kadavu crimson shining-parrot, which stands out from other parrots in the country, with its blue-collar at the back of the neck. The Kadavu fantail, the whistling dove and the honeyeater are amongst other rare birds found only in Kadavu.
Additionally, locals say that Kadavu is the most beautiful island, it grows the best and strongest kava, biggest dalo, largest fish, sweetest mangoes, and prettiest girls in all Fiji. So far Kadavu has had the most Hibiscus Queens. Lenora Qereqeretabua, Lynda Tabuya, Mere Nailatikau, Sera Tikotikoivatu, and now Marie Falls whose mother is from Kadavu.
Demographics
The Kadavu archipelago sits on the earthquake belt and the cyclone path of Fiji. Kadavu has weathered many earthquakes and cyclones in the past. Along with the isolation and seclusion from the mainland, the people have struggled more than most provinces in Fiji. History has proven that people that go through difficulties and trying times can develop a resilient attitude towards life. Thus, these challenges have shaped and moulded Kadavuans to be amongst the most intelligent and high achieving people in Fiji. They can be seen at all top-level positions in the country and undeniably have a knack for breaking into new grounds and frontiers. The beautiful "Kadavu House" in the capital city of Suva is a testimony of their achievement. Kadavu is the only province in Fiji that hits the million dollar mark and more, as the people are the most generous givers in the country. The people are fondly called "Me Damu" (rams/goats) by their notorious "Tauvus" particularly the Stallion province of Nadroga and the Rooster province of Ra with whom they share a fierce friendly rivalry. Wherever in the world, they may be, Kadavuans are deeply connected to their island province, and are intensely proud of their identity as a "Kai Kadavu."
Kadavuans
Well-known Kadavu names include former Foreign Minister Kaliopate Tavola, former Forests and Fisheries Minister Konisi Yabaki of Tiliva village, current MP and Opposition Whip Ms Lynda Tabuay also from Tiliva village, Former Minister and PSC Chairman Sakeasi Waqanivavalagi, James Ah-Koy, former Minister for Finance, Senator, and businessman, Apaitia Seru, former Attorney General, Minister for Justice and Chief Magistrate, Akuila Yabaki, former lawyer and Attorney-General the Kelemedi Bulewa of Ravitaki Village, former lawyer, High Court judge and senator Epineri Vula of Tawava Village (Yawe), a Methodist minister and political activist, Jeremaia Naivalurua II and his sons, Senator Mataiasi Waqavesi Naivalurua and Apolosa Laburuburu Naivalurua, and Senator Sela Donumaitoga Nanovo and Josateki Nawalowalo, Chairman of the Kadavu Provincial Council and of the Fiji Kava Council. Yet another noted Kadavuan was Jesoni Vitusagavulu, Fiji's former Ambassador to the United States (appointed in 2005). Also Colonel Matereti Sarasau of Dagai Village, Sitiveni Ratuva of Yale Village, and Inoke Nabulivou of Dravuwalu Village, past President of the Methodist Church of Fiji and Rotuma. Another notable Kadavuan is the immediate past Commander of the Republic of Fiji Military Forces, Mosese Tikoitoga.
Transport
Ferry service by Patterson Brothers Shipping Company LTD connects Kadavu to Viti Levu.
References
- "BirdLife Data Zone". datazone.birdlife.org. Retrieved 29 May 2017.
- Fiji. By Korina Miller, Robyn Jones, Leonardo Pinheiro – 2003– Page 230
- Oceania by Australian National Research Council, University of Sydney, Published 1930, Editors: Apr. 1930-Mar. 1931, A.R. Radcliffe Brown; Sept. 1931-Dec. 1932, R. Firth; Mar. 1933– A.P. Elkin. Pages 145 to 148. Original from the University of Michigan.
- Scottish Geographical Magazine By Royal Scottish Geographical Society, Published 1999, Pages 123 to 126.
- Sofer, Michael (2007) Yaqona and the Peripheral Economy Revisited, Asia Pacific Viewpoint, Vol. 48(2), pp. 234–249. Sofer, Michael (2009) Twenty Years of Change in the Fijian Periphery: The Case of the Kadavu Island, Fiji, Singapore Journal of Tropical Geography, Vol. 30, pp. 343–357. Sofer, M. (2015) Kadavu Island: Adaptation and stagnation in the Fijian periphery, Miscellanea Geographica: Regional Studies on Development, Vol. 19(2), pp. 14–20. DOI: 10.1515/mgrsd-2015-0006
- BirdLife International (2012). "Prosopeia splendens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2013.2. International Union for Conservation of Nature. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Kadavu. |
 Kadavu travel guide from Wikivoyage
Kadavu travel guide from Wikivoyage- Information on Kadavu.
- General Information on Kadavu.