Katla (volcano)
Katla (Icelandic pronunciation: [ˈkʰaʰtla] (![]() listen)) is a large volcano in southern Iceland. It is very active; twenty eruptions have been documented between 930 and 1918, at intervals of 20–90 years. It has not erupted violently for 103 years, although there may have been small eruptions that did not break the ice cover, including ones in 1955,[1] 1999,[2] and 2011.[3]
listen)) is a large volcano in southern Iceland. It is very active; twenty eruptions have been documented between 930 and 1918, at intervals of 20–90 years. It has not erupted violently for 103 years, although there may have been small eruptions that did not break the ice cover, including ones in 1955,[1] 1999,[2] and 2011.[3]
| Katla | |
|---|---|
 Katla eruption, 1918 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 1,512 m (4,961 ft) [1] |
| Listing | List of volcanoes in Iceland |
| Coordinates | 63°38′N 19°03′W |
| Geography | |
 Katla Iceland | |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Subglacial volcano |
| Last eruption | October to November 1918 |
Prior eruptions have had a Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of between 4 and 6 on a scale of 0 to 8. In comparison, the Eyjafjallajökull 2010 eruption had a VEI of 4. Bigger VEI-5 eruptions are comparable to Mount Pinatubo's 1991 eruption, while significantly rarer VEI-6 eruptions would be comparable to Krakatoa's 1883 eruption.
Katla is one of the largest volcanic sources of carbon dioxide (CO2) on Earth, accounting for up to 4% of total global volcanic carbon dioxide emissions.[4]
Geography and physical appearances
Katla is one of the largest volcanoes in Iceland.[5] It is situated to the north of Vík í Mýrdal and to the east of the smaller glacier Eyjafjallajökull. Its peak reaches 1,512 metres (4,961 ft) and is partially covered by the Mýrdalsjökull glacier. The system has an area of 595 km2 (230 sq mi). The Eldgjá canyon is part of the same volcanic system.[6][7]
The caldera of the Katla volcano has a diameter of 10 km (6.2 mi) and is covered with 200–700 metres (660–2,300 ft) of ice. The volcano normally erupts every 40–80 years.[8] The flood discharge at the peak of an eruption in 1755 has been estimated at 200,000–400,000 m3/s (7.1–14.1 million cu ft/sec), comparable to the combined average discharge of the Amazon, Mississippi, Nile, and Yangtze rivers (about 266,000 m3/s (9.4 million cu ft/sec)).
Etymology
The name Katla derives from the word ketill ("kettle"), referring to the form of the volcano. Katla is also used as a female first name.[9]
Prehistoric activity
It is thought that Katla is the source of Vedde Ash,[10] more than 6 to 7 cubic kilometers (1.4 to 1.7 cu mi) of tephra dated to 10,600 years BP[1][11][12][13] found at a number of sites including Vedde in Norway, Denmark, Scotland and North Atlantic cores.
Historic activity
Sixteen eruptions have been recorded for Katla since 930. The last major eruption started on 12 October 1918 and lasted for 24 days.[14] It was likely a VEI-5 level eruption. The 1918 eruption resulted in extending the southern coast by 5 km due to laharic flood deposits. Its present dormancy is among the longest in known history.[15]
Minor (VEI-1?) eruptions occurred in:
Major eruptions occurred in:
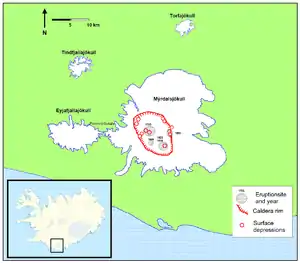 Locations of caldera rim and previous eruptions Most of these eruptions resulted in glacial floods. The severe fissure eruption in 934 was one of the largest lava eruptions in the past 10,000 years.[16] Before the Hringvegur (Iceland's Ring Road) was constructed in 1974, people feared traversing the plains in front of the volcano because of the frequent jökulhlaup (or glacier bursts) and the deep river crossings. Especially dangerous was the glacier outburst that followed the eruption of 1918. Present day activity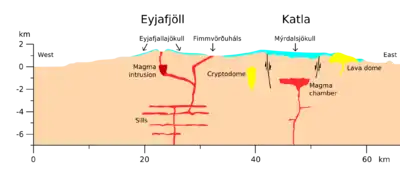 Schematic cross-section from west to east across the Eyjafjallajökull and Katla volcanoes. Magmatic intrusions are drawn in red, rhyolitic domes and the cryptodome in yellow; glaciers are shown in light blue. Katla has been showing signs of unrest since 1999, and geologists have concerns that it might erupt in the near future.[17] Particularly, monitoring has been intensified following the March 2010 eruptions of a smaller neighbouring volcano, the Eyjafjallajökull glacier.[18] The eruption of this nearby long-dormant volcano in March and April 2010 prompted fears among some geophysicists that it might trigger an eruption at the larger and more dangerous Katla.[19][20][21] In the past 1,000 years, all three known eruptions of Eyjafjallajökull have triggered subsequent Katla eruptions.[20] Following the 2010 Eyjafjallajökull eruptions, on 20 April 2010 Icelandic President Ólafur Grímsson said "the time for Katla to erupt is coming close ... we [Iceland] have prepared ... it is high time for European governments and airline authorities all over Europe and the world to start planning for the eventual Katla eruption".[22] Increased earthquake activity has been noticed on Katla since the eruption at Eyjafjallajökull, but no other signs of an imminent eruption have been observed. These quakes are located mainly on the northwestern rim of the caldera. On 9 October 2010, a sudden rise in harmonic tremor was observed in the stations around Katla, a sign of a possible impending eruption.[23] As of 2010, volcanologists are continuing to monitor Katla, aware that any eruption from Katla following an eruption from Eyjafjallajökull has historically occurred within months of the latter. The Icelandic Meteorological Office updates its website with reports of quakes both at Eyjafjallajökull and Katla.[24] 2011 activityIn 2011, geologic activity led many to speculate that a very small subglacial eruption had taken place.[3] In June 2011, harmonic tremor was again detected at Katla volcano. A few days later, an earthquake swarm took place in the caldera, indicating magma movement inside the volcano, leading to increased fears of an eruption in the near future.[25] On 8 and 9 July, another spike in harmonic tremors occurred, as a small eruption of Katla took place. Cracks formed on the glacier, as well as a cauldron.[26] Icelandic media reported a small subglacial eruption might have started.[27] On the morning of 9 July, a glacier flood was reported in the river Múlakvísl, and also later in the river Skálm. The bridge across Múlakvísl was destroyed as well as other parts of the road, Route 1, on the Icelandic ring road. Helicopter pilots flying over the glacier also reported cracks in the glacier.[28] Scientists monitoring the activity said speculation that it was caused by a "very small" subglacial eruption lacked confirmation by visual or seismic evidence.[3] 2016 and 2017 activityTremors were detected under Katla in late August 2016.[29][30] A "Specialist Description" describing the activity on 29 August 2016 noted that there was:An update written at 11 Sep 16:38 GMT reported:
In February 2017, seismic activity at the volcano continued.[33] Images
See alsoReferences
External links
|

