Subglacial volcano
A subglacial volcano, also known as a glaciovolcano, is a volcanic form produced by subglacial eruptions or eruptions beneath the surface of a glacier or ice sheet which is then melted into a lake by the rising lava. Today they are most common in Iceland and Antarctica; older formations of this type are found also in British Columbia and Yukon Territory, Canada.
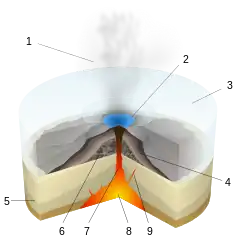







During the eruption, the heat of the lava from the subglacial volcano melts the overlying ice. The water quickly cools the lava, resulting in pillow lava shapes similar to those of underwater volcanoes. When the pillow lavas break off and roll down the volcano slopes, pillow breccia, tuff breccia, and hyaloclastite form. The meltwater may be released from below the ice as happened in Iceland in 1996 when the Grímsvötn caldera erupted, melting 3 km3 of ice and giving rise to a large glacial lake outburst flood.
The shape of subglacial volcanoes tends to be quite characteristic and unusual, with a flattened top and steep sides supported against collapse by the pressure of the surrounding ice and meltwater. If the volcano eventually melts completely through the ice layer, then horizontal lava flows are deposited, and the top of the volcano assumes a nearly level form. However, if significant amounts of lava are later erupted subaerially, then the volcano may assume a more conventional shape. In Canada the volcanos have been known to form both conical and nearly level shapes.[1] The more distinctly flat-topped, steep-sided subglacial volcanoes are called tuyas, named after Tuya Butte in northern British Columbia by Canadian geologist Bill Mathews in 1947. In Iceland, such volcanoes are also known as table mountains.
Jökulhlaups
Subglacial eruptions often cause jökulhlaups or great floods of water. In November 1996 the Grímsvötn Volcano beneath the Vatnajökull ice sheet erupted and caused a Jökulhlaup that affected more than 750 km2 (290 sq mi) and destroyed or severely damaged several bridges.[2] During the ice ages, such floods from Lake Missoula were estimated to have discharges exceeding 17 × 106 m³/s (4.5 × 109 gal/s) and covered a third of eastern Washington state. Sonia Esperanca, program director in the National Science Foundation commented on the danger of subglacial volcanoes: "When an ice-covered volcano erupts, the interplay among molten magma, ice and meltwater can have catastrophic results."[3]
Antarctica eruption
In January, 2008, the British Antarctic Survey (Bas) scientists led by Hugh Corr and David Vaughan, reported (in the journal Nature Geoscience) that 2,200 years ago, a volcano erupted under the Antarctica ice sheet (based on airborne survey with radar images). The biggest eruption in the last 10,000 years, the volcanic ash was found deposited on the ice surface under the Hudson Mountains, close to Pine Island Glacier.[4]
On Mars
Many scientists believe that liquid water exists many kilometers below the surface of Mars, but at this point in time it is impossible to drill to those depths with the rovers in existence. Meredith Payne and Jack Farmer of Arizona State University have studied images from the Viking and Mars Orbiter cameras in search of possible sub-glacial volcanoes that could carry microbes to the surface.[5]
Ice cores
It is possible to track catastrophic subglacial volcano eruptions in time with the analysis of ice cores such as the Vostok core. Subglacial volcanic eruptions are identified by layers of high concentrations of NO−
3 and SO2−
4.[6]
See also
- Subglacial eruption
- Subglacial mound
- Underwater volcano
- Tuya
- Tindur
- Subglacial caldera
- 1996 eruption of Gjálp
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Subglacial volcanoes. |
- Volcanoes of Canada: Types of volcanoes Accessed Jan. 8, 2006
- "Volcanoes of Canada". Geological Survey of Canada. Archived from the original on February 2, 2009. Retrieved January 19, 2009.
- http://www.accessscience.com/content.aspx?searchStr=subglacial+volcano&id=735200
- "Volcanoes Under Glaciers in Iceland, Canada and the United States". Archived from the original on May 4, 2010. Retrieved June 1, 2010.
- Black, Richard (20 January 2008). "Ancient Antarctic eruption noted". BBC News. London: BBC. Archived from the original on 15 January 2009. Retrieved 22 October 2011.
- "Subglacial Volcanoes On Mars". Archived from the original on 2011-06-06.
- "International Glaciological Society" (PDF). International Glaciological Society (IGS). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2018-05-04.
