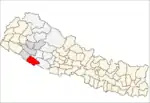
Khajura Rural Municipality
Khajura Rural Municipality also known as Khajura Bajaar is a municipality in Banke District in the Bheri Zone in mid-western Nepal.[1] The municipality was established on 10 March 2017 by merging the existing six Village Development Committees i.e. Radhapur, Sitapur, Bageshwari, Sonpur, Udharapur, Raniyapur. The town is in Nepalganj-Gulariya highway and one of the fastest developing places in Nepal. A neighboring city Nepalgunj is on east(8 km), and further 6 km is the Indian border. In fact it is a growing city in the western region of Nepal.
Khajura Rural Municipality
खजुरा गाउँपालिका Khajura Bajaar | |
|---|---|
| खजुरा गाउँपालिका | |
| Nickname(s): खजुरा बजार | |
| Motto(s): सम्बृद्द खजुरा, हाम्रो चाहना | |
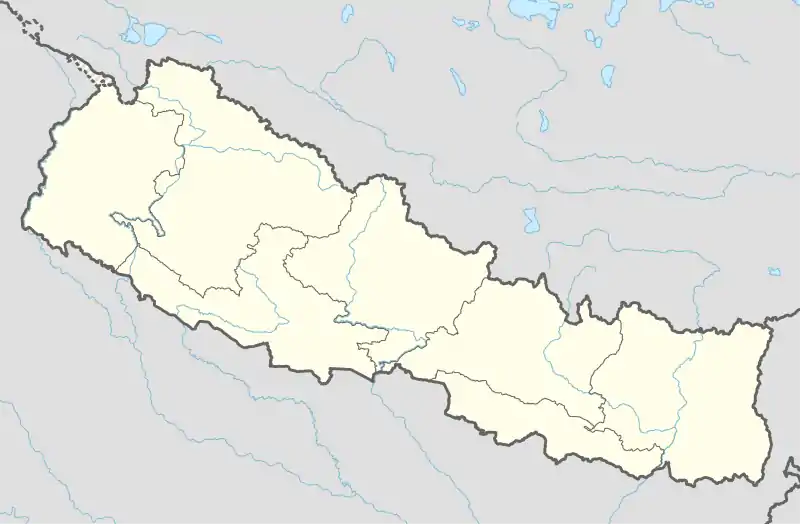 Khajura Rural Municipality Location in Nepal | |
| Coordinates: 28°12′N 81°41′E | |
| Country | |
| Province | Lumbini Province |
| District | Banke District |
| Established | 10 March 2017 |
| Government | |
| • Type | rural council |
| • Chairperson | Kismat Kumar Kakshapati |
| • Deputy-Chairperson | Ekmaya BK |
| Population (2011) | |
| • Total | 50,961 |
| • Rank | 3rd (Nepal) |
| Time zone | UTC+5:45 (Nepal Time) |
| Area code(s) | 081-560XXX |
| Website | http://www.khajuramun.gov.np/ |
It is accessible by air (Nepalgunj Airport) and by road (559 km west of Kathmandu).
Khajura Rural Municipality
Khajura will become the third municipality in the Banke District, with the first being Nepalgunj and second being Kohalpur.
As a municipality, Khajura Bajaar will assume greater local government autonomy and greater financial resources as part of the central governments' effort to promote decentralized power.
The municipality status of Kohalpur has been repeatedly stalled due to the failure to ratify the national constitution. A fourth deadline to ratify the constitution was missed on 27 May 2012.[2]
Geography
Khajura Bajaar is located in the Banke District in the Mid-West Region of Nepal (Therai region), with a total area of 2816.6 hectares. The climate is subtropical and the temperature varies between a maximum of 46 °C and minimum of -2 °C.
Demography
Infrastructure and Basic Services
- Nepal Cancer Hospital[3]
References
- Gaviria, G., Lee, J., Ospina, P., Soloman, S. and Suharyanto I. (2012). 'Kohalpur: strategic transition from VDC to municipality and potentials for sustainable growth along a strategic highway junction', in Urban Management 2012 Applied Research Project: Four Case Studies in Nepal. Berlin: Technische Universitat Berlin.CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Gurubacharya, Binaj. "Nepal Fails to Agree on Constitution". AP. Archived from the original on 29 May 2012. Retrieved 29 May 2012.
- "Nepal Cancer Hospital - Khajura, Banke". Nepal Cancer Hospital. Retrieved 29 August 2018.