Kharijite Rebellion (866–896)
The Kharijite Rebellion was a major Kharijite uprising against the Abbasid Caliphate between 866 and 896. Centered in the districts of Mosul and Diyar Rabi'a in the province of al-Jazira (upper Mesopotamia), the rebellion lasted for approximately thirty years, despite numerous attempts by both the central government and provincial authorities to quell it. It was finally defeated in 896 after the caliph al-Mu'tadid (r. 892–902) undertook several campaigns to restore caliphal authority in the region.
| Kharijite Rebellion (866–896) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
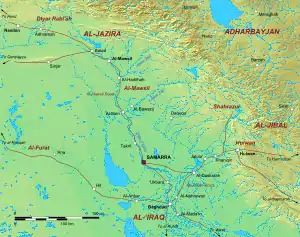 Eastern al-Jazira and northern Iraq in the late ninth century | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Abbasid Caliphate | Kharijite rebels | ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Yarjukh Musa ibn Bugha Muflih Masrur al-Balkhi Al-Mu'tadid Al-Husayn ibn Hamdan |
Musawir ibn 'Abd al-Hamid al-Shari Harun ibn 'Abdallah al-Bajali (POW) Hamdan ibn Hamdun (POW) | ||||||
The uprising was initially led by a local Kharijite named Musawir ibn 'Abd al-Hamid al-Shari. Following Musawir's death in 877, he was eventually succeeded by Harun ibn 'Abdallah al-Bajali, who remained in command until the end of the rebellion.
Background
The Kharijite movement was a prominent religious sect in early Islamic history, known for its members' fanaticism and staunch opposition to the Muslim ruling establishment. The Kharijites' views on the nature of the caliphate caused them to reject the legitimacy of the rule of the Alids, Umayyads and Abbasids alike, and over the course of the seventh through ninth centuries they were responsible for numerous rebellions against the established government. Few of these attempts proved to be successful, but the Kharijites' continual presence in many Muslim-held regions meant that they were a near-constant source of trouble for the caliphs' governors.[1]
In the caliphal province of al-Jazira, Sufri Kharijism had enjoyed a strong following since the late seventh century, particularly among the Arabs of the Rabi'a tribe. Between 750 and 865 more than a dozen Kharijite revolts were launched in this region, although most of them were easily put down by the Abbasid government. The most recent uprising had occurred in 862, approximately four years before Musawir's revolt.[2]
Beginning in 861 the Abbasid Caliphate entered a period of severe weakness, during which the central government in Samarra was paralyzed by a vicious struggle between the caliphs and the military establishment for control. Over the course of the 860s the government was repeatedly beset with financial difficulties, riots in the capital and rebel movements in multiple provinces. These problems were exacerbated in 865, when the rival caliphs al-Musta'in and al-Mu'tazz fought a civil war in central Iraq, which left thousands dead and caused major economic damage to the region. Even after the end of the war in early 866, the instability continued unabated, with troop riots repeatedly occurring in both Samarra and Baghdad.[3]
Outbreak of the rebellion
According to the historian Ibn al-Athir, the immediate cause of the rebellion was the authorities' arrest and detention of a young man in al-Haditha. This individual was a son of Musawir ibn 'Abd al-Hamid, who was a dihqan of the town of al-Bawazij.[4] When he learned of his son's incarceration, he responded angrily to the news and gathered a number of supporters, who pledged allegiance to him. The group marched on al-Haditha and entered it; the chief of police there was forced to go into hiding, and Musawir's son was freed from prison.[5]
Support for Musawir quickly grew, with Bedouin Arabs and Kurds of the region flocking to his side. Following an aborted advance on the district capital of Mosul,[6] the rebels advanced south toward the Khurasan Road between Baghdad and Hulwan in autumn 867. When the governor of Baghdad sent two commanders to protect the road, Musawir engaged one of them in battle, killing him and several hundred of his men, and forced the other one to retreat back to Baghdad. He then followed up on this victory by proceeding to Hulwan, where he fought and killed more than four hundred of its defenders.[7]
Inside the city of Mosul, various governors succeeded one after other: in the begin of the rebellion, the Khuza'i governor Aqaba ibn Muhamed was deposed by the Taghlibi Arab leader Ayyub ibn Ahmad, who put his own son Hasan as governor.[8] In early 868, in response to the growing power of the rebels, the deputy governor of Mosul, the Azdi Allah ibn Sulayman, raised an army and headed for Musawir in the vicinity of the Zab Rivers. The two sides encountered each other in May 868, and engaged in battle in the middle of a valley. After heavy fighting the rebels emerged victorious; the loyalist army suffered heavy casualties and the deputy governor Allah ibn Sulayman fled to Irbil. This victory increased Musawir's authority in the region,[9] and in the following year he undertook an expedition against Mosul itself. Due to the weakness of the defenders he was able to enter the city without opposition. He remained in Mosul for a short time, during which he conducted the Friday prayers, and then withdrew to al-Haditha.[10] After this, the abbasid caliph named the Turkish Azkutigin as governor of Mosul. He sent his son Azkutigin in 874 as deputy, but he was expelled by the citizens of the city, Azkutigin sent two more deputies Hytham ibn Abd Allah and the Taghlibi Ishaq ibn Ayyub, but they were expelled too. Over the course of the next several years, Musawir remained active within a large portion of the district of Mosul, together with part of northern Iraq.[11] Lieutenants were sent to administer the areas under his control; they established garrisons and collected taxes from local residents.[12] Travel through the region became difficult for government agents, who risked being captured and killed by Musawir's partisans. He also received support from nearby Arab and Kurdish tribes, who sympathized with his cause and fought against the government.[13]
Abbasid campaigns against Musawir
Beginning in 867, the Abbasid government in Samarra undertook a series of military campaigns in an effort to suppress the Kharijite rebellion. These operations began under the caliph al-Mu'tazz (r. 866–869), whose forces however had little success against the rebels.[14] He initially sent the officers Satikin[15] and Khutarmish against Musawir; the latter was defeated in the district of Jalula in December.[16] In September 868 Nushara ibn Tajibak, a lieutenant in Salih ibn Wasif's service, managed to inflict a defeat on Musawir and killed a large number of his followers.[17] In the following year, Yarjukh was sent against the rebel, but he was defeated and forced to flee to Samarra.[18]
Following the overthrow and death of al-Mu'tazz, his successor al-Muhtadi (r. 869–870) continued the campaigns. Upon receiving reports in January 870 that Musawir was attacking the town of Balad, the caliph ordered the commanders Musa ibn Bugha, Muflih and Bayakbak to proceed against him; a political crisis in the capital, however, resulted in this expedition's postponement. After a delay of several months, Musa and Bayakbak reassembled their troops and departed for al-Jazira on April 6. The army set up a base at al-Sinn and Muflih proceeded to pursue Musawir, eventually engaging the rebel on a mountain near al-Haditha. The battle proceeded poorly for Musawir, whose forces were weakened from a recent battle against a dissident Kharijite, and he eventually ordered a retreat. Muflih then advanced to various cities in Diyar Rabi'a, in an effort to reestablish order.[19]
The caliphal forces remained at al-Sinn for some time, but in early June Musa and Muflih were made aware of a plot by al-Muhtadi to either have them assassinated or imprisoned; they immediately responded by abandoning al-Jazira and withdrawing toward the Khurasan Road.[20] At Khanaqin Musa encountered Musawir, who had a strong numerical advantage, but in spite of this the Kharijites were routed and suffered severe losses.[21] After al-Muhtadi was killed on June 17 and replaced with al-Mu'tamid (r. 870–892), Muflih resumed his offensive against the Kharijites. He initially succeeded in forcing Musawir to abandon al-Haditha, but he was unsuccessful in his attempts to defeat the rebel and eventually returned to Samarra in August, allowing Musawir to regain his authority in the region.[22]
Muflih again went on campaign in around early 872; he proceeded to Takrit and fought some Arab tribesmen that were reportedly sympathetic to Musawir.[23] Later that year, Masrur al-Balkhi undertook two expeditions against Musawir; in the first, he installed a lieutenant in al-Haditha and captured a number of Kharijites, bringing them back to Samarra; in the second, he advanced to al-Bawazij and defeated Musawir in combat, capturing a number of his followers in the process, before departing for the capital around the end of October.[24] Masrur undertook further campaigns in 874 and 875, both times in response to the killing of government officials by Musawir's followers; on the latter occasion he was assisted by al-Mu'tamid's brother Abu Ahmad (the future al-Muwaffaq).[25]
Musawir's death and succession disputes
Musawir died in ca. 877, shortly after he had set out from al-Bawazij to meet yet another government army. Following his death, the Kharijites sought to find someone to succeed him. They initially called upon Muhammad ibn Khurzad of Shahrazur to assume the leadership, but he turned down their request, so they turned to another man named Ayyub ibn Hayyan al-Wariqi al-Bajali and gave the oath of allegiance to him instead.
Ibn Khurzad subsequently regretted his decision and requested that he be reconsidered as leader, but the Kharijites refused to go back on their choice. In response, Ibn Khurazd gathered a number of men loyal to him and attacked Ayyub ibn Hayyan, killing him. Following this, the Kharijites threw their support behind Muhammad ibn 'Abd Allah ibn Yahya al-Wariqi, but he ended up being killed by Ibn Khurzad as well. The Kharijites finally selected Harun ibn 'Abd Allah al-Bajali, who soon gained a large number of supporters. Ibn Khurzad decided not to fight against Harun, and the latter assumed Musawir's former position within the district of Mosul.[26]
Despite Harun's apparent victory in the succession dispute, however, his relationship with Ibn Khurzad remained poor. In ca. 881 Ibn Khurzad decided to make a move against Harun; he gathered his supporters and advanced against him. Harun assembled his own followers in response, and the two sides encountered each other near Mosul. In the ensuing battle, Harun was defeated and two hundred of his men were killed. He soon regained control of the situation, however, by soliciting the support of the local Taghlib Arabs and writing offers to Ibn Khurzad's followers, urging them to defect to his side. Most of them agreed to do so, and Ibn Khurzad's position quickly deteriorated as a result. He was eventually killed in Shahrazur, and Harun became the undisputed head of the Kharijite rebels.[27]
The Kharijites under Harun
Under Harun's command, the Kharijites continued their activities in the area around Mosul. They subdued numerous villages and rural districts adjacent to the Tigris River, putting deputies over these territories and levying taxes and tithes from the inhabitants.[28] Harun also established an alliance with Hamdan ibn Hamdun, a Taghlibite chieftain and the eponymous founder of the Hamdanid dynasty, and over the course of the next several years the two leaders jointly conducted a number of campaigns within the Mosul district.[29]
In ca. 885 Harun and Hamdan decided to march on Mosul; they entered the city and Harun led the people in the prayers in the Friday Mosque. News of this incident was reported to Baghdad.[30] A short time later, the district began to suffer from raiding activities by the Banu Shayban; in response, Harun and Hamdan assembled their forces in an effort to stop them. The two leaders met and advanced against the Arabs, but the Shaybanis defeated them in battle and forced them to fall back.[31]
Harun undertook another advance against Mosul four years later, after he received word that Ishaq ibn Kundaj, the city's governor, had killed a local Kharijite. He summoned his followers in al-Haditha and marched against the city, intending to attack its people in revenge. The city notables, however, managed to convince Harun to back down after they disassociated themselves from the governor's actions and apologized for the killing.[32]
In ca. 892, Harun and Hamdan entered into an alliance with the inhabitants of Mosul, after the latter had rebelled against their governor, Muhammad ibn Ishaq ibn Kundaj, and expelled his deputy from the city. The deputy turned to the Banu Shayban for assistance, prompting them to enter the district in force. Harun, Hamdan, and a number of Mosuli volunteers banded together to fight the Shaybanis and expel them from the region. The two sides met in the vicinity of the city, and after engaging each other in battle the Mosulis won an initial victory. The Shaybanis, however, regrouped and returned to the battlefield; the Mosulis, who had taken to looting after the engagement, were caught by surprise. Many of them were killed and the Shaybanis won the battle.[33]
In the following year, an internal dispute broke out among the Kharijites, and many of them decided to reject Harun's leadership. The leader of the dissidents was one Muhammad ibn 'Ubaydah, a member of the Banu Zuhayr from the village of Qabratha, who gathered a number of supporters from the tribal Arabs and began collecting taxes for himself. He also built a fortress at Sinjar and put his son in charge of it, leaving a large amount of his plunder there. In response, Harun marched toward the fortress with over a thousand men and laid siege to it. The Banu Zuhayr within the fortress eventually agreed to submit after they were granted a guarantee of safe-conduct; the gates were opened to Harun's men, and Muhammad's son and several of his followers were beheaded. Harun then advanced against Qabratha, where Muhammad himself was stationed. In the ensuing battle Harun's forces were at first forced to fall back, but they subsequently rallied and defeated the dissidents, killing a large number of them. Muhammad fled to Amid, but was captured by its governor Ahmad ibn 'Isa al-Shaybani and sent to Baghdad, where he was flayed on the caliph's orders.[34]
End of the rebellion
In October 892 the caliph al-Mu'tamid died and was succeeded by his nephew al-Mu'tadid. At the time of his ascension, al-Mu'tadid was already an experienced military commander, having previously campaigned against both the Zanj rebels in southern Iraq and the Tulunids in Syria. The new caliph immediately strove to reestablish the central government's control over the core provinces of the Abbasid Caliphate, which under his predecessors had slipped into the hands of autonomous governors and rebel groups. Included among his objectives was the resubjugation of al-Jazira, which was a major source of grain for the capital. Toward this end, he personally undertook several campaigns against the various factions in al-Jazira, in an effort to break their hold over the region and force them to recognize his authority.[35]
Al-Mu'tadid's first campaign in al-Jazira, in 893, was directed against the Banu Shayban in the region of the Zab Rivers.[36] In January 895 he again advanced into the province; this time, his intended target was Hamdan ibn Hamdun, due to the latter's association with Harun and the Kharijites. After first battling against some tribal Arabs and Kurds in the region, al-Mu'tadid proceeded toward Hamdan's fortress at Mardin. Hamdan decided to flee and the defenders quickly surrendered to the caliph.[37] Al-Mu'tadid then returned to Mosul and sent an order to Hamdan to submit to him, but when Hamdan ignored the summons he sent his commanders Wasif Mushgir and Nasr al-Qushuri against him. Hamdan's forces were quickly defeated by Wasif and he himself was compelled to flee; eventually, however, he surrendered to the caliph's forces and was put under guard.[38]
Following Hamdan's surrender, the caliph turned his focus to Harun himself. Nasr al-Qushuri wrote a threatening latter to the Kharijite, in an attempt to convince him to submit; Harun, however, wrote back a defiant response, rejecting Nasr's demands. When al-Mu'tadid was shown the letter, he appointed al-Hasan ibn Ali Kurah over Mosul and charged him with combatting the Kharijites. After crossing the Zab, al-Hasan encountered Harun and the two armies began a grueling engagement. The battle finally ended in defeat for the Kharijites; Harun fled to the desert and some of his followers surrendered to the caliph.[39]
In March 896 al-Mu'tadid again departed for the district of Mosul, in order to campaign against Harun. On this occasion he was joined by Hamdan ibn Hamdun's son al-Husayn, who had peaceably submitted to the caliph during the latter's struggle against his father. Al-Mu'tadid himself advanced to Takrit, while he dispatched al-Husayn and Wasif Mushgir to pursue Harun. Al-Husayn met the rebel near the Tigris and routed his forces; Harun attempted to flee, but al-Husayn pursued him and eventually caught up to him, together with one hundred of his followers. Despite a plea by Harun to refrain from fighting, al-Husayn ordered his men to attack; the Kharijites were again defeated and Harun himself was captured.[40]
Aftermath
Al-Husayn brought Harun to al-Mu'tadid, who sent a dispatch announcing the victory to Baghdad. He then marched back to the capital with Harun in custody, reaching it on May 9. To celebrate the capture of the Kharijite, the streets of Baghdad were decorated and the caliph's army was assembled before the city gate. The caliph himself then entered the city and proceeded to his palace. Al-Husayn and other army commanders were rewarded with robes of honor, after which they rode in triumph through the city. Harun was put on display; mounted on an elephant, he was forced to sit in a woman's litter and wear humiliating clothing.[41]
As a reward for al-Husayn's capture of Harun, al-Mu'tadid agreed to pardon his father Hamdan and release him from custody. Al-Husayn and his brothers were subsequently appointed to various posts, including a number of governorships in al-Jazira. In the following century the Hamdanids succeeded in establishing a de facto independent state in al-Jazira and northern Syria, with al-Husayn's nephews Nasir al-Dawla and Sayf al-Dawla ruling over Mosul and Aleppo respectively.[42]
Following the defeat of the Kharijites, al-Mu'tadid continued his efforts to regain control of al-Jazira. In 899 he captured Amid from Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Shaybani,[43] and by the end of his reign in 902 most of the province was back under the central government's authority.[35] Kharijite rebel activity in the province subsequently tapered off, with only one further revolt in 929 being recorded.[44]
Notes
- Levi Della Vida, pp. 1074-77
- Vaglieri, pp. 39-40; Madelung, pp. 766-67
- Gordon, pp. 90-104; Waines, pp. 299-303
- Al-Tabari, v. 35: p. 147
- Ibn al-Athir, pp. 186-87; Weil, p. 406
- Ibn al-Athir, p. 187; Weil, p. 406
- Al-Tabari, v. 35: pp. 147-49; Ibn al-Athir, p. 190; Weil, p. 406
- C. Edmund Bosworth, p. 413
- Ibn al-Athir, p. 195; Weil, p. 407
- Ibn al-Athir, p. 205; Weil, p. 417; Honigmann and Bosworth, p. 900
- Ibn al-Athir, pp. 195, 219; Weil, p. 465
- Vaglieri, p. 40; al-Tabari, v. 36: p. 24; Ibn al-Athir, 220
- Al-Tabari, v. 36: pp. 136, 158; Ibn al-Athir, pp. 238, 248, 272
- Al-Ya'qubi, p. 614, who states (in summary form) that al-Mu'tazz was prompted to action after Musawir expelled the governor of Mosul, marched in the direction of Surra Man Ra'a (Samarra) and occupied the town of al-Muhammadiyyah, "three farsakhs from the palaces of the caliph"
- Al-Tabari, v. 35: p. 147. Satikin was an officer in the service of Bugha al-Saghir; al-Tabari, v. 35: p. 153
- Al-Tabari, v. 35: p. 151; Ibn al-Athir, p. 192; Weil, p. 406
- Al-Tabari, v. 35: pp. 146, 155; Ibn al-Athir, p. 196
- Al-Tabari, v. 35: p. 161
- Al-Tabari, v. 36: pp. 87, 90-91. Halfway through al-Tabari's account of the fight between the caliphal army and Musawir, he switches the name of the commander from Muflih to Musa. Ibn al-Athir, p. 219, gives sole credit to Muflih as the commander during the battle, but dates the fight to after Mu'tamid's ascension. He also adds the detail that the campaigns against Musawir in this year were prompted after Musawir's seizure of parts of Iraq had hindered the ability of the government to pay the troops' salaries, causing the army to clamor for action against the Kharijites. Al-Mas'udi, v. 8: p. 8, claims that the campaign took place after Musawir had approached Samarra with an army and caused a measure of disorder around the capital.
- Al-Tabari, v. 36: pp. 91-92, 95, 96; Ibn al-Athir, p. 220; Weil, pp. 418-19
- Al-Tabari, v. 36: p. 112; Ibn al-Athir, p. 227. Weil, p. 465, sourcing Ibn Khaldun, claims that Musawir was actually the winner of this battle
- Al-Tabari, v. 36: p. 116; Ibn al-Athir, pp. 219-20, 227
- Al-Tabari, v. 36: p. 136; Ibn al-Athir, p. 238
- Al-Tabari, v. 36: p. 148; Ibn al-Athir, p. 238, who however presents a different order of events; Weil, p. 465
- Al-Tabari, v. 36: pp. 158, 164; Ibn al-Athir, pp. 248, 259; Weil, p. 466
- Ibn al-Athir, pp. 272-73; Weil, p. 466
- Ibn al-Athir, pp. 306-07; Weil, pp. 466-67
- Ibn al-Athir, pp. 306-07
- Canard, "Hamdanids," p. 126
- Al-Tabari, v. 37: p. 150; Ibn al-Athir, p. 345; Weil, p. 467
- Ibn al-Athir, p. 346
- Ibn al-Athir, p. 358; Weil, p. 467
- Ibn al-Athir, p. 369; Weil, pp. 467-68
- Ibn al-Athir, p. 375; Weil, p. 489
- Kennedy, p. 760
- Al-Tabari, v. 38: pp. 7-8; Ibn al-Athir, p. 374; Weil, p. 489
- Al-Tabari, v. 38: pp. 15-17; Ibn al-Athir, pp. 377; Weil, pp. 489-90
- Al-Tabari, v. 38: pp. 20-22; Ibn al-Athir, p. 379; Weil, p. 490
- Ibn al-Athir, pp. 380-81; Weil, p. 490
- Al-Tabari, v. 38: pp. 27-28; Ibn al-Athir, pp. 384-85; al-Mas'udi, v. 8: p. 168; Weil, p. 490
- Al-Tabari, v. 38: p. 29; Ibn al-Athir, p. 385; al-Mas'udi, v. 8: pp. 168-69; Weil, pp. 490-91. Ibn al-Athir claims that Harun was subsequently crucified. Rosenthal, p. 15, however, claims that he survived his capture, and died in prison in ca. 917.
- Canard, "Hamdanids," pp. 126-29
- Canard, "Isa b. al-Shaykh," p. 91
- Vaglieri, p. 40; Madelung, p. 767
References
- Canard, M. (1971). "Hamdanids". In Lewis, B.; Ménage, V. L.; Pellat, Ch. & Schacht, J. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume III: H–Iram. Leiden: E. J. Brill. OCLC 495469525.
- Canard, M. (1978). "Isa b. al-Shaykh". In van Donzel, E.; Lewis, B.; Pellat, Ch. & Bosworth, C. E. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume IV: Iran–Kha. Leiden: E. J. Brill. OCLC 758278456.
- Gordon, Matthew S. (2001). The Breaking of a Thousand Swords: A History of the Turkish Military of Samarra (A.H. 200–275/815–889 C.E.). Albany, New York: State University of New York Press. ISBN 0-7914-4795-2.
- Honigmann, E. & Bosworth, C.E. (1991). "Al-Mawsil". In Bosworth, C. E.; van Donzel, E. & Pellat, Ch. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume VI: Mahk–Mid. Leiden: E. J. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-08112-3.
- Ibn al-Athir, 'Izz al-Din. Al-Kamil fi al-Tarikh, Vol. 6. Beirut: Dar al-‘Ilmiyyah, 1987.
- Kennedy, H. (1993). "Al-Mawsil". In Bosworth, C. E.; van Donzel, E.; Heinrichs, W. P. & Pellat, Ch. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume VII: Mif–Naz. Leiden: E. J. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-09419-2.
- Levi Della Vida, G. (1978). "Kharidjites". In van Donzel, E.; Lewis, B.; Pellat, Ch. & Bosworth, C. E. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume IV: Iran–Kha. Leiden: E. J. Brill. OCLC 758278456.
- Madelung, W. (1997). "Sufriyya". In Bosworth, C. E.; van Donzel, E.; Heinrichs, W. P. & Lecomte, G. (eds.). The Encyclopaedia of Islam, New Edition, Volume IX: San–Sze. Leiden: E. J. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-10422-8.
- Al-Mas'udi, Ali ibn al-Husain. Les Prairies D'Or. Ed. and Trans. Charles Barbier de Meynard and Abel Pavet de Courteille. 9 vols. Paris: Imprimerie Nationale, 1861-1917.
- Yarshater, Ehsan, ed. (1985–2007). The History of al-Ṭabarī (40 vols). SUNY Series in Near Eastern Studies. Albany, New York: State University of New York Press. ISBN 978-0-7914-7249-1.
- Vaglieri, L. Veccia. "Le vicende del kharigismo in epoca abbaside." Rivista degli Studi Orientali, XXIV (1949), pp. 31–44.
- Waines, David. "The Third Century Internal Crisis of the Abbasids." Journal of the Economic and Social History of the Orient, 20.3 (1977), pp. 282–306.
- Weil, Gustav. Geschichte der Chalifen, Vol. 2. Mannheim: Bassermann Verlag, 1848.
- Al-Ya'qubi, Ahmad ibn Abu Ya'qub. Historiae, Vol. 2. Ed. M. Th. Houtsma. Leiden: E. J. Brill, 1883.