Kistecephalia
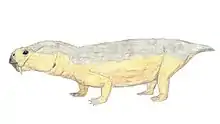
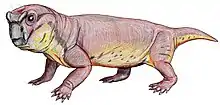
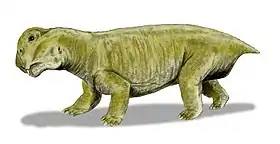
Kistecephalia is a clade of dicynodont therapsids. The group was first named in 1894, and was reinstated as a clade in 2009. Kistecephalia is a stem-based taxon defined as all taxa more closely related to Cistecephalus microrhinus than Emydops arctatus.[1] It includes the families Myosauridae, Kingoriidae, and Cistecephalidae and is part of the larger group Emydopoidea. Kistecephalians were small in comparison to other dicynodonts. One group of kistecephalians, the cistecephalids, are thought to have been burrowers. Below is a cladogram from Kammerer et al. (2011) showing the phylogenetic relationships of kistecephalians:[2]
| Therochelonia |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kistecephalia Temporal range: Late Permian - Middle Triassic | |
|---|---|
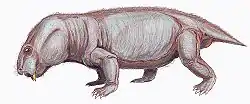 | |
| Restoration of the kistecephalian Dicynodontoides recurvidens | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Clade: | Therapsida |
| Clade: | †Dicynodontia |
| Superfamily: | †Emydopoidea |
| Stem group: | †Kistecephalia Seeley, 1894 |
References
- Kammerer, C.F.; Angielczyk, K.D. (2009). "A proposed higher taxonomy of anomodont therapsids" (PDF). Zootaxa. 2018: 1–24.
- Kammerer, C.F.; Angielczyk, K.D.; Fröbisch, J. (2011). "A comprehensive taxonomic revision of Dicynodon (Therapsida, Anomodontia) and its implications for dicynodont phylogeny, biogeography, and biostratigraphy". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology. 31 (Suppl. 1): 1–158. doi:10.1080/02724634.2011.627074.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.