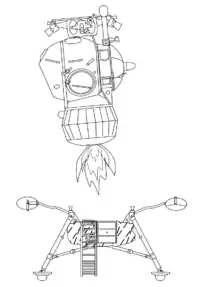
Kosmos 379
Kosmos 379 (Russian: Космос 379 meaning "Cosmos 379") was an unmanned test of the LK (the Soviet counterpart of the Apollo Lunar Module) in Earth orbit.
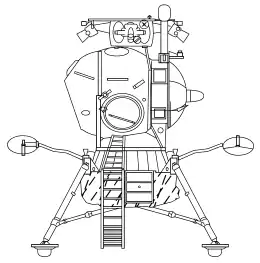 A standard LK | |
| Operator | Soviet Union |
|---|---|
| COSPAR ID | 1970-099A |
| SATCAT no. | 04760 |
| Spacecraft properties | |
| Spacecraft type | T2K |
| Launch mass | 7,495 kilograms (16,524 lb) |
| Start of mission | |
| Launch date | 24 November 1970, 11:00:00 UTC |
| Rocket | Soyuz-L |
| Launch site | Baikonur 31/6 |
| Orbital parameters | |
| Reference system | Geocentric |
| Regime | Low Earth |
| Eccentricity | 0.004161 |
| Perigee altitude | 198 kilometres (123 mi) |
| Apogee altitude | 253 kilometres (157 mi) |
| Inclination | 51.6 degrees |
| Period | 88.7 m |
Mission
Earth orbit simulated propulsion system operations of a nominal lunar landing mission. Kosmos 379 entered a 192 to 232 km low Earth orbit. After three days it fired its motor to simulate hover and touchdown on the moon, in imitation of a descent to the lunar surface after separation of the Blok D lunar crasher propulsion module. The engine firing changed its orbit from 192 km X 233 km to 196 km X 1206 km (delta-V = 263 m/s).
After a simulated stay on the Moon, it increased its speed by 1.518 km/s, simulating ascent to lunar orbit making the final apogee 14,035 km. These main maneuvers were followed by a series of small adjustments simulating rendezvous and docking with the Soyuz 7K-L3. The LK lander tested out without major problems and decayed from orbit on September 21, 1983.[1]
Parameters
- Spacecraft: T2K
- Mass: 5500 kg
- Crew: None
- Launched: November 24, 1970
- Landed: Reentered September 21, 1983
- Orbit: 192 km
External links
- Mir Hardware Heritage