Lake Sonoma
Lake Sonoma is a reservoir west of Cloverdale in northern Sonoma County, California, created by the construction of Warm Springs Dam. Access from U.S. Route 101 is by way of Canyon Road (from the south) from Geyserville, or Dutcher Creek Road (from the north) from Cloverdale.
| Lake Sonoma | |
|---|---|
 The lake, just behind the Warm Springs Dam, which is to the right of this view | |
 Lake Sonoma  Lake Sonoma | |
 | |
| Location | Sonoma County, California |
| Coordinates | 38°43′05″N 123°00′34″W |
| Lake type | reservoir |
| Primary inflows | Dry Creek |
| Primary outflows | Dry Creek[1] |
| Catchment area | 130 sq mi (340 km2)[2] |
| Basin countries | United States |
| Max. length | 5.7 mi (9 km)[1] |
| Surface area | 2,700 acres (1,100 ha)[3] |
| Water volume | 381,000 acre⋅ft (0.470 km3)[2] |
| Shore length1 | 50 miles (80 km)[3] |
| Surface elevation | 200 feet (61 m)[1] |
| 1 Shore length is not a well-defined measure. | |
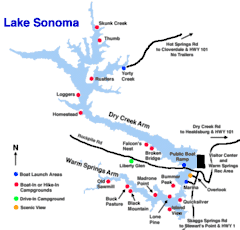
The lake provides water for countywide growth and development, and for recreation. At full capacity, it has 50 miles (80 km) of shoreline, a surface area of more than 2,700 acres (11 km2),[3] and holds 381,000 acre feet (470,000,000 m3) of water.[2] Activities include boating, swimming, fishing, riding, hiking, camping, and hunting.[3] Notable features include the Milt Brandt Visitor Center, the adjacent Congressman Don Clausen Fish Hatchery, and the Warm Springs Recreation Area below the dam.
History
Pomo people had lived in the Dry Creek area since at least the 18th century, and some of them resisted the creation of the lake. Archaeologists at Sonoma State University have written about the prehistory and history of Warm Springs Dam, Lake Sonoma, and the Dry Creek Valley.[4]
Warm Springs Dam
The US Army Corps of Engineers built Warm Springs Dam across Dry Creek. Completed in 1982, this rolled-earth embankment dam is 319 ft (97 m) high, 3,000 ft (900 m) long, and 30 ft (9 m) wide at the top. It contains 30,000,000 cu yd (23,000,000 m3) of earth.[2] The dam aids in flood control, and a hydroelectric plant produces electricity from the water released downstream. A minimum amount of flow must be maintained in Dry Creek to allow fish migration.
Water quality
The California Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA) has developed a safe eating advisory for Lake Sonoma based on levels of mercury or PCBs found in fish caught from this water body.[5]
Campgrounds
Lake Sonoma offers 96 drive-in campsites and two group sites at the Liberty Glen campground. The campground is located on a ridgeline overlooking Lake Sonoma, each campsite includes a firepit, picnic table and tent area, with primitive facilities and no potable water.
There are an additional 15 secluded campsites surrounding the lake: 14 can be reach by boat and 11 can be reached by hiking or horseback. [6]
Panorama

See also
References
- U.S. Geological Survey Geographic Names Information System: Lake Sonoma
- "Dams Owned and Operated by Federal Agencies" (PDF). Retrieved January 4, 2008.
- "Lake Sonoma: Welcome". U.S. Army Corps of Engineers.
- "Before Warm Springs Dam". Sonoma State University Anthropological Studies Center.
- Admin, OEHHA (December 30, 2014). "Lake Sonoma". OEHHA. Retrieved June 13, 2018.
- http://www.lakesonoma.com/camping---directions.html
External links
 Media related to Lake Sonoma at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Lake Sonoma at Wikimedia Commons- news article about annual inspection of Warm Springs Dam