Lake Tengiz
Tengiz Lake (Kazakh: Теңіз көлі, Teńiz kóli; Russian: Тенгиз[2]) is a saline lake in north-central part of Kazakhstan.[3] Its eastern shore is deeply indented and includes the Tengizi Islands.[4]
| Tengiz Lake | |
|---|---|
 2008 | |
 Tengiz Lake | |
| Location | Kazakhstan |
| Coordinates | 50°26′23″N 68°54′0″E |
| Type | Salt lake |
| Native name | Теңіз көлі |
| Basin countries | Kazakhstan |
| Surface area | 1,382 km2 (534 sq mi) |
| Average depth | 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) |
| Max. depth | 6.7 m (22 ft) |
| Islands | Tengizi Islands |
| Official name | Kourgaldzhin and Tengiz Lakes |
| Designated | 11 October 1976 |
| Reference no. | 107 [1] |
Lake Tengiz is an important wetland site for birds. It is a part of a Ramsar wetland site of international importance, the Tengiz-Korgalzhyn Lake System. 318 species of birds have been recorded at Lake Tengiz, 22 of which are endangered.[5] It is the most northerly nesting site for the Greater flamingo; in the years 2006-2011 around 45,000 members of that species were noted. In 2015, however, the number dropped to less than 15,000. The lake is part of the Korgalzhyn Nature Reserve, for which it was nominated in 2008 together with the Naurzum Nature Reserve as the first natural UNESCO World Heritage site in Kazakhstan (Saryarka — Steppe and Lakes of Northern Kazakhstan).
On 16 October 1976, the Soviet spacecraft Soyuz 23 unintentionally splashed down into the northern part of the lake, which was frozen, crashing through the ice. The crew was saved thanks to a very difficult but successful rescue operation.[6]
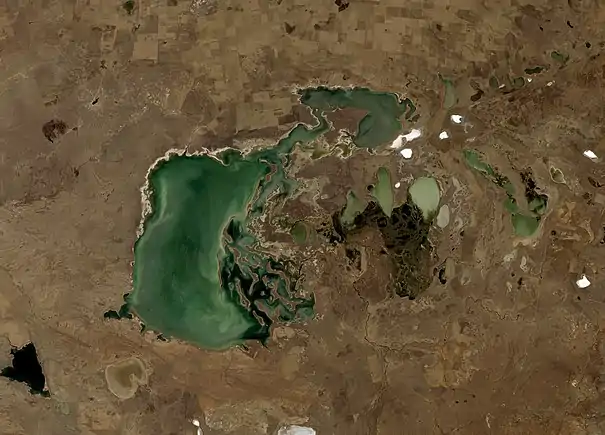
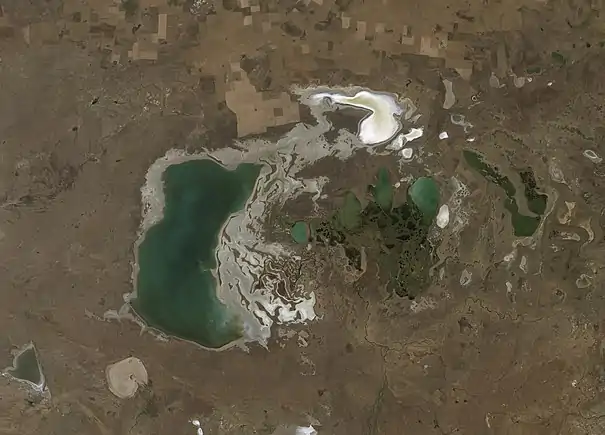
 Tengiz Lake with a relative low level,
Tengiz Lake with a relative low level,
3 September 2011, north-east part and lake margins dried up,
photo taken by Landsat 5 satellite.
References
- "Kourgaldzhin and Tengiz Lakes". Ramsar Convention Sites Information Service. Retrieved 25 April 2018.
- Tengiz, dengiz, deniz, etc. means "sea" in Turkic languages
- "Tengiz", a LakeNet profile
- Lake Tengiz - Britannica.com
- "Tengiz Lake and Korgaljinski Lakes" Archived 30 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- Encyclopedia Astronautica, Soyuz 23