Lakki Marwat District
Lakki Marwat (Pashto: لکی مروت, Urdu: لکی مروت) is a district in Bannu Division of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province in Pakistan. It was created as an administrative district on July 1, 1992, prior to which it was a tehsil of Bannu District.
Lakki Marwat
لکی مروت | |
|---|---|
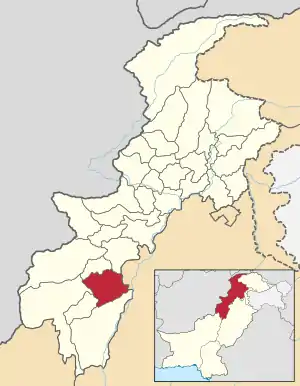 Location of Lakki Marwat District in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province. | |
| Country | Pakistan |
| Province | Khyber Pakhtunkhwa |
| Headquarters | Lakki Marwat |
| Area | |
| • District | 3,164 km2 (1,222 sq mi) |
| Population | |
| • District | 876,182 |
| • Density | 280/km2 (720/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 89,420 |
| • Rural | 786,762 |
| Time zone | UTC+5 (PST) |
| Number of Tehsils | 2 |
| Website | www |
Demographics
According to the census of 1998, the district had a population of 490,025.[2] Out of this only a total of 46,878 people or 9.6% of the population was recorded as urban inhabitants,[2] while 443,147 people or 90.4% of the population was recorded as rural dwellers.
The district covers 3,164 km², with population density of 155 people per km², compared to the population density of 233 people per km² in the North-West Frontier Province as a whole. The population density at the 1981 census was 91 people per km², which indicates a high rate of population growth in the intervening 17 years.
The major first language is Pashto, spoken natively by 99.3% of the population.[3]
Administration
The district has one municipal committee and one town committee.[2] There are 157 mauzas (the smallest revenue unit).[2]
Political representation
At the provincial level, the district is represented by three elected members to the provincial assembly according to the following constituencies:[4]
- PK-74 (Lakki Marwat-1)
- PK-75 (Lakki Marwat-2)
- PK-76 (Lakki Marwat-3)
Climate
The region has all the characteristics of a desert due to its sand dunes, scorching heat and dry weather. Summers are hot, while winters are moderately cool. The summer season begins from early April and continues till late October. June is the hottest month with a maximum temperature range of 42 to 45 Degree Celsius and a minimum temperature range of about 30 to 35 Degree Celsius. Periodic sand storms rage through the area during May and June due to the Prevalent low humidity. The hot wind, locally known as "Lu" blows across the district in these months. The cool wave starts from somewhere in late October. December, January and February are the winter months. Though the daytime temperature in winter is not that low, however there is always a sharp decrease in nights. The mean maximum and minimum temperatures during this period are 20 and 4 Degree Celsius respectively. Rainfall is rare and sporadic and generally occurs in July and August.
Topography

The district is a combination of hills and sandy plains. The hilly areas are along the boundaries of the district especially in the east, southeast, southwest and northwest. In the southeast, the Marwat range separates Lakki Marwat from Dera Ismail Khan District while in the east the Karak Niazi range separates it from Mianwali District. It is surrounded by Baittani range on the west and southwest, which separates it from Tank District and the tribal Area adjoining Tank District and South Waziristan Agency. The Marwat range culminates and Baittani ranges starts near Sheikh Badin. The general elevation of these hills ranges from 500 to 1000 meters above sea level. The land beyond these hills gradually slopes to the central part, which looks like a basin. A large number of streams flow from the surrounding hills, the Kurram river flows through the district from North West to the south east and joins the Indus River south of Isa Khel town. One of its important tributary is Gambila River. The major part of this basin is an alluvial plain. The northern portion of this plain is situated chiefly in the Kurram Gambila Doaba and irrigated by Kurram River. It is a flat sandy area. The southern part is made up of undulating dunes of sand, furrowed at regular intervals by deep torrent beds which carry the drainage of the Marwat and Baittani ranges to the Gambila. It is good for cultivation, water table is quite deep below the soil surface. In the western portion of the district, the soil is fairly stiff clay covered by a layer of stones at the foot of the hills. The whole district is intersected by numerous hill torrents and deep ravines. The general elevation of the plain area is about 200 to 300 meters above sea level.
Transport
Lakki Marwat was connected with Mari Indus through a narrow gauge railway line during the Raj. The city, a tehsil of Bannu then, was a railway junction. One line went to Bannu, its district, and the other to Tank. The extent of railways network has ever since defined the limits of the settled area bordering the tribal area to its west. The railway track has since been uprooted and the area now is connected through a network of roads. A detailed account of the rise and fall of this particular railway junction was published in the Daily Dawn .
Neighboring areas
See also
References
- "DISTRICT WISE CENSUS RESULTS CENSUS 2017" (PDF). www.pbscensus.gov.pk. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2017-08-29. Retrieved 2017-09-01.
- 1998 District Census Report of Lakki Marwat, Population Census Organisation, Statistics Division, Government of Pakistan, Islamabad, 2000 Pg 23
- 1998 District Census report of Lakki Marwat. Census publication. 109. Islamabad: Population Census Organization, Statistics Division, Government of Pakistan. 2000. p. 28.
- "Constituencies and MPAs – Website of the Provincial Assembly of the NWFP". Archived from the original on 2008-04-28. Retrieved 2007-12-01.