Languages of Denmark
The Kingdom of Denmark has only one official language,[3] Danish, the national language of the Danish people, but there are several minority languages spoken, namely Faroese, German, and Greenlandic.
| Languages of the Kingdom of Denmark [1][2] | |
|---|---|
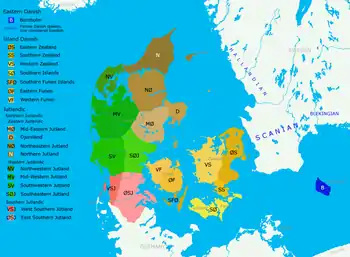 Danish dialects | |
| Official | Danish |
| Regional | (Officially recognised) Faroese Greenlandic |
| Minority | German |
| Foreign | English (about 86%) German (about 47%) Swedish (about 13%) |
| Signed | Danish Sign Language |
| Keyboard layout | |
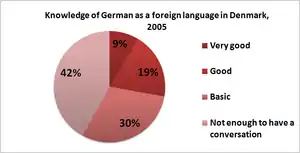
A large majority (about 86%)[1] of Danes also speak English as a second language; it is mandatory for Danish students to learn from the first grade in the public elementary schools (Danish: folkeskole), by far the most popular option in the country. In the 1st (or 3rd, depends on the school) grade of folkeskole, a third language option is given, usually German or French. The vast majority pick German (about 47% of Danes report being able to speak conversational German). The third most widely understood foreign language is Swedish, with about 13% of Danes reporting to be able to speak it.[4]
Officially recognized minority languages
Faroese
Faroese, a North Germanic language like Danish, is the primary language of the Faroe Islands, a self-governing territory of the Kingdom. It is also spoken by some Faroese immigrants to mainland Denmark. Faroese is similar to Icelandic, and also the Old Norse language spoken.
References
- "Europeans and their Languages" (PDF). Ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 6 October 2017.
- "Denmark". Ethnologue.com. Retrieved 28 September 2017.
- "Facts and Statistics". Denmark.dk. Retrieved 16 September 2014.
- "Special Eurobarometer 386: Europeans and their languages" (PDF). European Commission. Archived from the original (PDF) on 6 January 2016. Retrieved 26 February 2014.
