Liechtenstein passport
Liechtenstein passports are issued to nationals of Liechtenstein for the purpose of international travel. Beside serving as proof of Liechtenstein citizenship, they facilitate the process of securing assistance from Liechtenstein consular officials abroad (or missions of Switzerland in case a Liechtenstein representation is not available).[3]
| Liechtenstein passport | |
|---|---|
 The front cover of a contemporary Liechtenstein biometric passport | |
 The data page of a contemporary Liechtenstein biometric passport | |
| Type | Passport |
| Issued by | |
| First issued | 26 October 2006[1] |
| Purpose | Identification |
| Eligibility | Liechtenstein citizenship |
| Expiration | 10 years adults over 15, 3 years minors under 15 |
| Cost | CHF 250 (adults), CHF 50 (minors)[2] |
The passport, along with the Liechtenstein identity card allows for the freedom of movement in any of the states of EFTA[4] and the EEA. This is because Liechtenstein is a member state of EFTA, and by virtue of it also being a member of the European Economic Area (EEA) and part of the Schengen Area.
Physical appearance
Liechtenstein passports are blue with the coat of arms of Liechtenstein emblazoned in the centre. The words "FÜRSTENTUM LIECHTENSTEIN" are inscribed above the coat of arms, with "REISEPASS" and the international biometric passport symbol below.
Effect of Liechtenstein citizenship
Citizens of Liechtenstein are allowed to reside in Switzerland. Additionally, as a member of the European Economic Area (EEA), citizens of Liechtenstein are permitted to take up residence in any EEA member state.
Citizens of EEA member states, which consist of the European Union and three of the four European Free Trade Association states (Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway) enjoy the freedom to travel and work in any EEA country without a visa, although transitory dispositions may restrict the rights of citizens of new member states to work in other countries.
Visa requirements
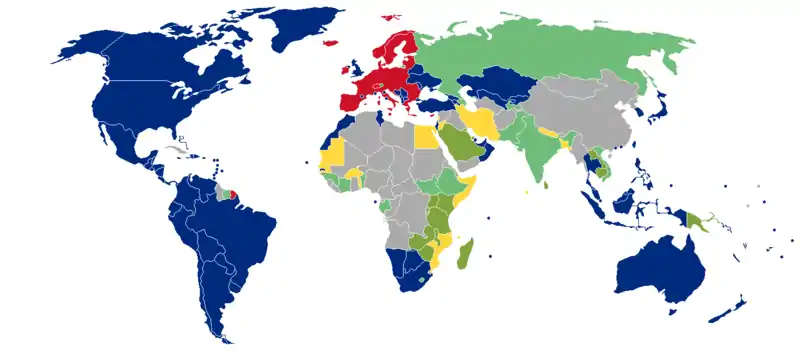
As of March 2020, Liechtenstein citizens had visa-free or visa on arrival access to 178 countries and territories, ranking the Liechtenstein passport 13th in terms of travel freedom overall, and the lowest of the EFTA member states, according to the Henley Passport Index.[5]
In 2017, The Liechtenstein nationality is ranked fourteenth in Nationality Index (QNI). This index differs from the Visa Restrictions Index, which focuses on external factors including travel freedom. The QNI considers, in addition, to travel freedom on internal factors such as peace & stability, economic strength, and human development as well. [6]
As a member state of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), Liechtenstein citizens enjoy freedom of movement to live and work in other EFTA countries in accordance with the EFTA convention.[7] Moreover, by virtue of Liechtenstein's membership of the European Economic Area (EEA), Liechtenstein citizens also enjoy freedom of movement within all EEA member states. The Citizens’ Rights Directive[8] defines the right of free movement for citizens of the EEA,[9] and all EFTA and EU citizens are not only visa-exempt but are legally entitled to enter and reside in each other's countries.
See also
References
- "Council of the European Union - PRADO - LIE-AO-02001". www.consilium.europa.eu.
- Preis und Gültigkeit Archived 2013-12-24 at the Wayback Machine
- "Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Justice and Culture". www.regierung.li. Retrieved 2020-10-25.
- "Short Overview of the EFTA Convention". Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- "Global Ranking - Passport Index 2019" (PDF). Henley & Partners. Retrieved 8 January 2019.
- "The 41 nationalities with the best quality of life". www.businessinsider.de. 2016-02-06. Retrieved 2018-09-10.
- "Short Overview of the EFTA Convention". Retrieved 29 November 2017.
- "EUR-Lex - 32004L0038R(01) - EN - EUR-Lex". Eur-lex.europa.eu. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- Decision of the EEA Joint Committee No 158/2007 of 7 December 2007 amending Annex V (Free movement of workers) and Annex VIII (Right of establishment) to the EEA Agreement, 2008-05-08, retrieved 2021-01-01
Sources
- Immigration and Passport Office
- Council Regulation (EC) No 539/2001 of 15 March 2001 listing the third countries whose nationals must be in possession of visas when crossing the external borders and those whose nationals are exempt from that requirement. For the most up-to-date state see the last consolidated version.