List of equipment of the Polish Land Forces
 |
| Polish Armed Forces |
|---|
| Branches |
|
|
| History |
|
Timeline Wars |
| Personnel |
|
Senior officers Rank insignia Awards Oaths |
| Equipment |
|
Land Forces Navy |
List of equipment of the Polish Land forces.
Individual equipment
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helmets | ||||||
| Hełm wz. 2005 |  | Combat helmet | Hełm wz. 2005 | New standard combat helmet of Polish Land Forces. | ||
| Hełm wz. 2000 | .jpg.webp) | Combat helmet | Hełm wz. 2000 | Upgraded version of Hełm wz. 93, Replaced by Hełm wz. 2005. | ||
| Hełm wz. 93 |  | Combat helmet | Hełm wz. 93 | Replaced by Hełm wz. 2005. | ||
| Hełm wz. 67 |  | Combat helmet | Hełm wz. 67 | Used for training. | ||
| HA-03 | Combat helmet | HA-03 | Used in Polish airborne. | |||
| HC-98 | _03.jpg.webp) | Combat helmet | HC-98 | Headphone used by tank crews. | ||
| Camouflage and uniforms | ||||||
| wz. 93 "Pantera" |  | Camouflage | Standard camouflage for Polish Armed Forces, except Polish Special Forces. | |||
| Umundurowanie polowe wz. 93 |  | Military uniform | wz. 127
wz. 127A wz. 124Z |
Put into operation in 1993. Replaced by wz. 2010. | ||
| Umundurowanie polowe wz. 2010 |  | Military uniform | wz. 123UL
wz. 123UP |
Put into operation in 2010. Standard issue uniform of the Polish Armed Forces. | ||
| Polski mundur pustynny |  | Military uniform | wz. 124
wz. 124Pl wz. 123UT |
Polish desert uniforms. | ||
| Bulletproof vests | ||||||
| Kamizelka KLV | Bulletproof vest | In use by drivers of armored cars. | ||||
| Kamizelka przeciwodłamkowa DMV-98 | .jpg.webp) | Bulletproof vest | DMV-98 | In use by airborne troops. | ||
| Kamizelka przeciwodłamkowa OLV |  | Bulletproof vest | ||||
| Kamizelka UKO | [2] | Bulletproof vest | UKO
UKO-M |
UKO is a modern bulletproof vest. Used by Polish troops in Afghanistan. | ||
| Boots | ||||||
 | Boots | wz.928 | ||||
| Desert Boots | wz.920/P | |||||
| Protection against chemical contamination | ||||||
| Maska przeciwgazowa MP-5 | .jpg.webp) | Gas mask | MP-5 | |||
| Maska przeciwgazowa MP-6 | .jpg.webp) | Gas mask | MP-6 | 28 400 | ||
| FOO-1 | .jpg.webp) | FOO-1 | Improved suit for protection against chemical contamination. | |||
| Special equipment | ||||||
| AD-2000 | .jpg.webp) |
Parachute | ||||
Infantry weapons
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Knives and bayonets | ||||||
| 6H4 Bayonet |  | Bayonet | 6H4 | ~100,000 | ||
| Military knife wz. 92 | Combat knife | wz. 92 | ~3000 | |||
| Military knife wz. 98 |  | Combat knife | wz. 98
wz. 98A wz. 98Z |
~500 | ||
| Pistols | ||||||
| P-83 Wanad |  | 9 mm Makarov semi-auto pistol | P-83 | ~5000 | Being slowly supplemented in military service by WIST-94. Still in heavy use in Polish police services.[1] To be replaced with 21,000 new pistols.[2] P-83 and WIST-94 are to be replaced by new handgun in near future.[3] | |
| WIST-94 |  | 9 mm Para semi-auto pistol | WIST-94 WIST-94L | 20,210[4] | P-83 and WIST-94 are to be replaced by new Handgun in near future.[3] | |
| P99 |  | 9 mm Para semi-auto pistol | P99 QA | ~500 | Limited usage in Polish Land Forces, mostly used by generals and officers.[5] | |
| PR-15 Ragun |  |
9 mm Para semi-auto pistol | PR-15 | ~6,500, 20000 ordered, designated Vis 100 [6] | To replace the WIST-94 and its variants. Began testing in April 2017, and was promptly ordered. Initial batch of units received by the Military in early 2018. | |
| Flare gun | ||||||
| Wz. 78 |  | 26 mm flare gun | ||||
| Submachine gun | ||||||
| PM-84 Glauberyt |  | 9 mm Para submachine gun | PM-84P
PM-98 PM-06 |
~15,000 | Around 30,000 are in storage | |
| Shotguns | ||||||
| Mossberg 500 |  | 12 gauge shotgun | M590 | ~150[7] | ||
| Assault rifles | ||||||
| AKM | 7.62×39mm assault rifle | AKM
AKMŁ AKMS |
~10,000 | Around 300,000 are in storage. Replaced by Beryl and Grot. Used for training. | ||
| FB Mini-Beryl |  | 5.56mm NATO carbine | 1996B
1996C |
~3,000
~17,000[8] |
||
| FB Beryl | 5.56mm NATO assault rifle | 1996A
1996B 1996C |
~45,000
~10,000 ~39,000 |
Standard service rifle | ||
| MSBS Grot |  | 5.56mm NATO modular rifle | MSBS-R
MSBS C16 FB-M1 MSBS C16 FB-M2 |
640
1,412 |
Future standard service rifle. Almost 37,000 delivered. A total of 63,000 rifles on order.[9] | |
| Sniper rifles | ||||||
| SVD |  | 7.62×54 mmR sniper rifle | SWD
SWD-M |
1,100
158 |
SWD-M is a Polish limited modernization including new optics and bipod. | |
| Bor |  | 7.62mm NATO sniper rifle | 196 | 196 delivered of 853 ordered. | ||
| Sako TRG | .jpg.webp) | 7.62mm NATO sniper rifle | TRG-21 TRG-22 | 40 206 | ||
| Sako TRG M10 SWS | .jpg.webp) | 338 Lapua Magnum sniper rifle | 150 | |||
| WKW Wilk |  | .50 BMG anti-materiel rifle | 76 | |||
| General-purpose machine guns | ||||||
| PK | .jpg.webp) .jpg.webp) | 7.62×54mmR general purpose machine gun | PK
PKB PKL PKS PKT PKM PKMS PKMSN PKMSN-1 |
~10,000
? ~100 ? ~2,000 |
Around 10,000 are in storage | |
| UKM-2000 | .jpg.webp) | 7.62mm NATO general purpose machine gun | UKM-2000P
UKM-2000P zmod.[10] UKM-2000C UKM-2000D |
894
290 337 8 |
[11] | |
| Rheinmetall MG3 | .jpg.webp) | 7.62mm NATO general purpose machine gun | MG3A1 | ~600 | Used on ex-German vehicles | |
| Heavy machine guns | ||||||
| DShK |  | 12.7 mm Russian heavy machine gun | DSzKM | ~160 | Only used on WZT-2 ARV and 152mm SpGH DANA[12] | |
| NSW |  | 12.7 mm Russian heavy machine gun | NSW
NSWT |
~1,500 | NSW – Polish designation for NSV. To be replaced by WKM-B.[13] | |
| WKM-B |  | .50 BMG heavy machine gun | WKM-B
WKM-Bz |
~450
8 |
NSW adapted to the .50 BMG NATO round.[13] | |
| Grenades | ||||||
| Rifle Grenades |  | HEAP grenade Incendiary grenade Smoke grenade Illuminating grenade | GNPO
NGZ-93 NGD-93 NGOS |
They can be fired from Kbs wz. 1996 Beryl and Kbk wz. 1996 Mini-Beryl. | ||
| RGD-2 | .jpg.webp) | Smoke grenade | RGD-2B
RGD-2CZ |
Only white and black smoke. | ||
| UGD-200 | UGD-200 | Smoke grenade | Color or white smoke. | |||
| RGO-88 | Fragmentation grenade | |||||
| RGZ-89 |  | Anti-personnel grenade | ||||
| F-1 |  | Anti-personnel grenade | Being replaced by RGZ-89 and RGO-88. | |||
| RG-42 | 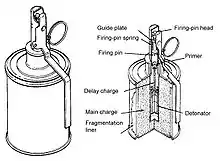 | Anti-personnel grenade | Being replaced by RGZ-89. | |||
| Recoilless rifles and grenade launchers | ||||||
| SPG-9 |  | 73 mm recoilless rifle | SPG-9
SPG-9D SPG-9N |
Limited use by airborne forces. | ||
| Carl Gustav |  | 84 mm multi-role recoilless rifle | 34[14] | Used only by paratroopers and special forces. | ||
| AT4 | .jpg.webp) | 84-mm portable single-shot recoilless smoothbore weapon | Used only by paratroopers and special forces. | |||
| Kbkg wz. 1960 | 7.62×39mm carbine-grenade launcher | wz. 1960
wz. 1960/72 |
Unknown number in use at now. Most are replaced by wz. 83 Pallad-D. | |||
| wz. 74 Pallad wz. 83 Pallad-D |  | 40 mm grenade launcher | wz. 74 Pallad wz. 83 Pallad-D | ~6500 ~450 | wz. 74 Pallad can be attached to AKM, AKMS, kbk wz. 88 Tantal and kbs wz. 96 Beryl. To be replaced by GPBO-40. Pallad-D is also known as Wz. 1983 grenade launcher. To be replaced by GSBO-40. | |
| GPBO-40 GSBO-40 |   | 40 mm grenade launcher | GPBO-40 GSBO-40 | 746[15][16] 160[17] | GPBO-40 is an underbarrel grenade launcher, can be attached to kbs wz. 1996 Beryl. GSBO-40 is a stand-alone version with stock and pistol grip. | |
| Mk.19 |  | 40 mm automatic grenade launcher | 190 | |||
| RPG-7 |  | 40 mm rocket-propelled grenade launcher | RPG-7
RPG-7D RPG-7DN1 RPG-7W |
~2,000 | Some of them (RPG-7DN1) are equipped with Polish NV sight PCS-5. | |
| RPG-76 Komar | 40 mm rocket-propelled grenade launcher | ~90,000* | *in storage. Some used by Polish troops in Iraq and in Afghanistan. | |||
| Land mines | ||||||
| M18 Claymore |  | Anti-personnel mine | ||||
| TM-62M |  | Anti-tank mine | ||||
| MPP-B Wierzba | Anti-tank mine | |||||
| Mortars | ||||||
| LM-60 Pluton |  | 60 mm mortar | LM-60D
LM-60K |
376[18]
20[18] |
||
| M-98 |  | 98 mm mortar | 93[19] | |||
| LRM vz. 99 ANTOS | 60,7 mm mortar | LRM vz. 99 ANTOS | 200+ | [20][21] | ||
| Wz. 38/43 |  | 120 mm mortar | 131[19] | To be replaced by RAK mortar. | ||
| 2B11 |  | 120 mm mortar | 14[19] | To be replaced by RAK mortar. | ||
| Anti-aircraft and anti-tank missile systems | ||||||
| PPZR Grom | .jpg.webp) | 72 mm man-portable surface-to-air missile launcher | Grom | 480 launchers[22] | 2000 missiles delivered. | |
| PPZR Piorun | 72 mm man-portable surface-to-air missile launcher | Piorun | 140 | 420 launchers and 1300 missiles ordered.[23] 140 launchers and 265 delivered.[24] | ||
| Spike |  | Anti-tank guided missile system | Spike-LR | 264 launchers[18] | Deal with Israeli manufacturer included production of components and assembly in Poland; include 264 launchers; total of 2675 Spike-LR version delivery 2004-2013.[18] | |
Military vehicles
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tanks | |||||||
| Leopard 2 | .jpg.webp) .jpg.webp) .jpg.webp) |
Main battle tank | Leopard 2A4
Leopard 2A5 Leopard-NJ Leopard 2PL |
130[14][18][25][26]
105[27][28][29][30] 2[31] 12[24] |
All Leopard 2A4s from the first (128) and the second (14) batches are going to be upgraded to Leopard 2PL standard.[32] | ||
| PT-91 "Twardy" |  | Main battle tank | PT-91
PT-91MA PT-91MA1 |
92[25]
27[25] 113[18][25][26] |
PT-91 - originally produced PT-91. PT-91MA - T-72M upgraded to PT-91 standard.[33] PT-91MA1 - T-72M1 upgraded to PT-91 standard. There are some ambitious plans for the modernization of all of PT-91s to PT-91M2 standard. | ||
| T-72 |  | Main battle tank | T-72
T-72A T-72M1 T-72M1R T-72M1D SJ-09 |
382[19] | 318 to be refurbished and modified to T-72M1R standard.[34] Currently 54 T-72M1 are modified to T-72M1R.[35][36] | ||
| Infantry fighting vehicle | |||||||
| BWP-1 | .jpg.webp) .jpg.webp) | Amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle | BWP-1
BWP-1D |
1,131[18]
33[18] |
BWP-1 - Polish designation for BMP-1. BWP-1D - Polish designation for BMP-1K (MP-31 in Polish service is sometimes also called BWP-1D[18]). ~800 BWP-1s are operational. To be replaced by new tracked infantry vehicle. | ||
| M1 IFV Rosomak ("Wolverine") |  | Amphibious wheeled infantry fighting vehicle | Rosomak | 836 | Rosomak M1 (KBWP) - wheeled infantry fighting vehicle equipped with HITFIST-30P turret. Also some up-armoured M1M variants for use in Afghanistan − no longer amphibious due to extra weight.[37] Licensed variant of the Patria AMV manufactured in Poland.[38] | ||
| Armoured personnel carrier | |||||||
| M2/M3 Rosomak ("Wolverine") | .jpg.webp)  | Amphibious wheeled armoured personnel carrier. Licensed variants of the Patria AMV manufactured in Poland. |
Rosomak-M2 Rosomak-M3 Rosomak-S Rosomak-NJ |
? Base model
31 27 4[38] |
M2 Rosomak - (unarmed or with .50 BMG) amphibious armoured personnel carrier. M3 Rosomak - up-armoured to (M1 IFV standard armour) personnel carrier, armed with .50 BMG WKM-B or Mk 19 + PKM or UKM-2000 as secondary weapon. Rosomak-S - armoured personnel carrier carries full squad with two Spike-LR ATGM. Rosomak-NJ - vehicle for driver training. | ||
| MT-LB | .jpg.webp) | Multi-purpose amphibious tracked armoured personnel carrier | MT-LB L
MT-LB Z MT-LB R WD krel |
41
6 6 2 |
The MT-LB L vehicles are used for driver training. MT-LB Z, MT-LB R and WD krel are a part of the Przebiśnieg electronic warfare system. | ||
| Armored reconnaissance vehicles | |||||||
| BRDM-2 |   | Amphibious armoured scout car | BRDM-2
BRDM-2M-96 BRDM-2M-96i BRDM-2M-97 BRDM-2M-98 BRDM-2M-96ik BRDM-2RS |
115[18]
~50 ~60 37 ~1[18] 54[39][40] 12[39] |
BRDM-2RS - Polish designation for BRDM-2RKhb. 8 are in service with the Polish Navy.[18] 10 BRDM-2M-96ik were used by Polish forces of ISAF.[40] However they are now together with 12 vehicles used in Iraq, back in Poland. | ||
| WSRiD Rosomak ("Wolverine") |  | Amphibious wheeled armoured reconnaissance vehicle |
|
2[38] |
Rosomak WSRiD - Multi-sensor reconnaissance and supervision vehicle. Licensed variant of the Patria AMV manufactured in Poland. | ||
| BWP-1 |  | Amphibious tracked reconnaissance vehicle |
BWR-1D BWR-1S |
22[18] 16[18] |
BWR-1D - Polish designation for BRM-1K. BWR-1S - Polish designation for BPzV "Svatava". Some number of BWR-1S are going to be modernized with new thermal sights and other minor changes. | ||
| TRI |  | Engineering reconnaissance | TRI Hors TRI-D Durian | 77 13 | Opal-I landing | ||
| Light armored vehicle | |||||||
| Humvee | .jpg.webp) | Four-wheel drive multi-purpose vehicle | Tumak-2[41]
Tumak-3[41] M1043A2[41] |
96[41]
60[41] 1[41] |
M1043A2 with Kobuz RWS, sometimes referred as Tumak-4. | ||
| Skorpion-3 |  | Four-wheel multi-purpose drive vehicle | Skorpion-3 | 90 | Armored heavier Honker version. | ||
| Armoured recovery vehicle | |||||||
| WZT-2 | .jpg.webp) | Armoured recovery vehicle | 40[18] | Based on T-55 chassis. Used for lighter vehicles, like APC's. | |||
| WZT-3M |  | Armoured recovery vehicle | 29 | Based on PT-91 Twardy chassis. | |||
| WPT Mors |  | Armoured recovery vehicle | 74 | ||||
| Bergepanzer 2 | .jpg.webp) | Armoured recovery vehicle | Bergepanzer 2A2 | 28[42] | All 28 vehicles to be modernised to the Bergepanzer 2PL standard.[43] | ||
| WRT Rosomak ("Wolverine") |  |
Technical reconnaissance vehicle | WRT | 34 | Rosomak-WRT - technical reconnaissance vehicle to assist with technical problems in the field. Armed with UKM-2000C 7.62mm MG in ZSMU-1276A remote controlled armament module.[44][45] Licensed variant of the Patria AMV manufactured in Poland. | ||
| CKPEiRT Hardun | Heavy evacuation and technical rescue vehicle | Hardun | 27 | Based on Scania CB 8x8[46][47] | |||
| Military engineering vehicle | |||||||
| MID Bizon-S |  | Engineering-roading machine | MID MID-M | 8 | |||
| PTS | .jpg.webp) | Tracked amphibious medium transporter | PTS-M | A small number are used by the Land Forces. 50 are in service with the Polish Navy.[18] | |||
| ISM Kroton |  | Minelayer | 6 | Opal-II landing. | |||
| Keiler |  | Armoured mine clearing vehicle | 4[48] | ||||
| Bożena |  | Remote-controlled self-propelled mine roller | 14[18][26] | ||||
| UMI |  | Excavator-loader | |||||
| SŁ-34C |  | Bulldozer-loader | |||||
| K-407C |  | Excavator | |||||
| Armoured vehicle-launched bridge | |||||||
| BLG-67 | .jpg.webp) | Armoured bridge layer | BLG-67M2 | 126[49] | Used by tank and mechanized subunits. To be replaced by MG-20 Daglezja-G. | ||
| Leopard Biber |  | Armoured vehicle-launched bridge | 6[48] | To be replaced by MG-20 Daglezja-G. | |||
| MS-20 Daglezja |  | Armoured vehicle-launched bridge | MS-20 Daglezja MG-20 Daglezja-G MS-40 Daglezja | 12 2 1 | [50] 2 prototypes of Daglezja-G were delivered to Polish Army to test, also, 1 prototype of MS-40 Daglezja was also delivered, awaiting tests. | ||
| PP-64 Wstęga |  | Pontoon bridge | 60[18] | Transported by 70 Star 266 AP-64 and Star 266 BP-64 trucks. | |||
| Bomb disposal | |||||||
| Robot Expert |  | Unmanned de-mining vehicle | |||||
| Robot Inspektor |  | Unmanned de-mining vehicle | |||||
| Robot Talon IV |  | Unmanned de-mining vehicle | |||||
| Forester minex 4530 |  | Metal detector | Forester minex 4530 | ||||
| EOD-9 Bomb suit |  | Protective bomb suit | Latest model heavy high protection suit. | ||||
| Trucks | |||||||
| Tumak-4 | .jpg.webp) | Truck | Tumak-4 | 31 | |||
| Star |      | Truck | Star 200 Star 244 Star 266 Star 266M Star 660M2-D[51] Star 660M3[51] Star 944K Star 944KD Star 1466ML Star 1444 Star 15.225 Star 14.220DK Star 14.225DK R-140M GD-2 (Typ 528) Typ 514 CD-5 (Typ 520) WUS-3 IRS ADK-11 Star 266-based excavator Star-266 AP-64 Star-266 BP-64 | 4,708 (Star 266)[51][52] 292 (Star 266M)[52] a few thousands of specialist Star 266-based vehicles[51] 456 (Star 944K)[52] 185 (Star 944KD)[52] 63 (Star 1466ML)[52] 1 (Star 1444)[52] 1 (Star 15.225)[52] 9 (Star 14.220DK)[52] 16 (Star 14.225DK)[52] | Star 266 - basic medium-capacity transport vehicle of the Polish Armed Forces. Star 266M - modernized Star 266. Star 944 is used as a cargo carrier in logistic subunits on the tactical level. It also serves as a basis for a command vehicle. Star 1466 can be converted into a gun truck by applying STZ armour package for the truck's cabin. Typ 514 - Mobile fuel tank based on Star 1466 | ||
| Jelcz |  |
Truck | 442.32 | 1039
203[53] |
Boxed variant Configured for special purposes | ||
| Jelcz |     | Truck | P/S662D.43 P662D.43 P662D.35 P662D.34 P642D C642D.35 C642D.34 C662D.35 P/S862D.43 P/S842D.43 P/S842D.35 P662.D35 AWRU P882D.53 WA P662D.35 WRUiE |
178[52] 7[52] 15[52] 101[52] 1[52] 36[52] 15[52] 1[52] 70[52] 1[52] 3[52] 8/10[54] 12/30[54] 2/5[54] |
P/S662D.43, P662D.43, P662D.35 and P662D.34 are different variants of JELCZ-662, P642D, C642D.35 and C642D.34 are different variants of JELCZ-642, P/S862D.43 is a variant of JELCZ-862, P/S842D.43 and P/S842D.35 are different variants of JELCZ-842. AWRU armament repair shop part of KMO Rak. WA ammunition vehicles, WRUiE armament and electronics repair shop, part of Regina DMO | ||
| SLT 50 Elefant | Heavy equipment transporter | SLT 50-2 | 6[52][55] | ||||
| Daimler Benz Unimog |  | Truck | 1300L | 69[56] | |||
| Mercedes-Benz |  | Truck | Mercedes-Benz 1017A | 211[56] | |||
| Iveco | .jpg.webp) | Truck | Stralis AT260S35Y/P Eurotrakker MP720E47WT MP720E48WT6x6 MP720T50WT Eurocargo M40.12WM | 460 | Stralis AT260S35Y/P is used by Polish Ground Forces along with high capacity trailers. Eurotrakker MP 720E 47 WT are used along with ZREMB NS 600W trailers for transport of tracked vehicles and containers. It can also be used to evacuate damaged equipment in a similar fashion to ARVs. M40.12WM is used as a biological reconnaissance vehicle. | ||
| Tatra |  | Truck | Tatra 815 | Only specialized variants are in service. | |||
| KrAZ |  | Truck | KrAZ-255B | Only specialized variants are in service. | |||
| Ural |  | Truck | Ural-375D Ural-4320 | Only specialized variants are in service. | |||
| Kamaz |  | Truck | Only specialized variants are in service. | ||||
| GAZ |  | Truck | GAZ-66 | Only specialized variants are in service. | |||
| ZiL |  | Truck | ZIL-131 ZIL-157 | Only specialized variants are in service. | |||
| All-terrain utility vehicle | |||||||
| Honda |  | Quad | TRX-300 FW | ||||
| Polaris | .jpg.webp) | Quad | Sportsan X2 800EFI | ||||
| Arctic Cat |  | Quad | Arctic Cat 400 4x4 | ||||
| Bombardier Outlander |  | Quad | Bombardier Outlander 650 | ||||
| UAZ-469B |  | Four-wheel drive multi-purpose vehicle | UAZ-469B WD-43 RD-115ZT UAZ-469B-rs | 38[57][58] | Only specialized variants are in service.[58] | ||
| Tarpan Honker |  .jpg.webp) | Four-wheel multi-purpose drive vehicle | Tarpan Honker Daewoo Honker Honker-2000 Skorpion-3 Rys[59] ZWD-3 WD-2001 REA "Perkun" Honker Saper | 286[52][60] 348[52][60] 647[52][60] 90[52][60] ? 172[61][62] ? 14 >2[63][64] | To be replaced. | ||
| PWA Aero |  |
Four-wheel all-terrain vehicle of the airmobile troops | PWA Aero | 33/80 | Adapted to be transported by a helicopter (attached below deck) and to be dropped on a 12 ft "V" 108 "PDS landing platform from C-130 or C-295M airplanes. 55 vehicles and 105 special trailers were ordered.[65][66][67] In 2020, the Ministry of National Defense used the option right, thus the number of vehicles purchased increased to 80 and 160 trailers.[68] | ||
| Mercedes-Benz G-Class |  | Four-wheel multi-purpose drive vehicle | GD 290 MB290GD WD MB 250 | 96[52] 25[52] 40[56] | Polish Armed forces currently operate a total number of 140 G-class vehicles.[69] The military police uses 13 GD 290s.[52] | ||
| Land Rover Defender |  | Four-wheel multi-purpose drive vehicle | 10 | ||||
| Ford Ranger | .jpg.webp) |
Four-wheel multi-purpose drive vehicle | XTL | 648[70] | The vehicles received 16-inch steel rims with run-flat inserts and AT BFGoodrich tires. The vehicles are also equipped with a hardtop body and a steel engine housing. Inspektorat Uzbrojenia ordered 648 cars (485 cars for a guaranteed order and 163 in option)[71][70][72] | ||
| Toyota Land Cruiser |  | Four-wheel drive vehicle | Land Cruiser[52][60] | 13[52][60] | |||
| Mitsubishi Pajero |  | Sport utility vehicle | Pajero[52][60] | 4[52][60] | |||
| Daewoo Musso |  | Sport utility vehicle | Musso[52][60] | 6[52][60] | |||
| Ford |  | Van | Transit | Used as a low-capacity transport vehicle which can carry up to 4 tonnes of cargo.[73] | |||
| Fiat Ducato |  | Wheeled vehicle | Fiat Ducato Seicento Van "W"[74] | Both are used as low-capacity transport vehicles which can carry up to 4 tonnes of cargo.[73] | |||
| Volkswagen Transporter |  |
Wheeled vehicle, van | 267[75] | ||||
| Volkswagen Crafter |  |
Wheeled vehicle, van | [75] | ||||
| MAN TGE | .jpg.webp) |
Wheeled vehicle, van | 134[76] | 128 in option | |||
| Command vehicles | |||||||
| ZWDSz |  | Tracked command vehicle | ZWDSz-1 ZWDSz-2 | 13 6 | |||
| SKOT | .jpg.webp) | Armoured wheeled command vehicle | R-2AM R-3M | ||||
| LPG |  | Tracked command vehicle | WD WDSz | 4/10
18/45[54] |
More on order due to Regina program. | ||
| WD Rosomak ("Wolverine") |  |
Armoured wheeled command vehicle | WD | 9/17[77] | 7 for the Multinational Division North East.[78] 2 more ordered for the 18th Division during the MSPO 2019 exhibition.[79] Licensed variant of the Patria AMV manufactured in Poland. On December 21, 2020, an agreement was signed under which in the years 2021-2022 another 8 cars will be delivered to the 16th Mechanized Division.[77] | ||
| AWD Rosomak ("Wolverine") |  |
Armoured wheeled command vehicle (artillery) | AWD | 32/60 | Command vehicle for Rak module mounted on KTO Rosomak chassis.[80][81][82] Licensed variant of the Patria AMV manufactured in Poland. | ||
| MT-LBu |   | Tracked command vehicle | 1W13 1W14 1W15 1W16 MP-21 MP-22 MP-23 MP-24 MP-25 R-330P Piramida-I Beta-3M | 20 (1W13/14/15/16) 24 (MP-21/22/23/24/25)[18] 9 (R-330P)[18] 2 (Beta-3M) | |||
| M113 |  | Tracked command vehicle | M113 M557 | 13 6 | |||
| ZWD-1 | .jpg.webp) | Tracked command vehicle | ZWD-1 | 94 | |||
| ZWD-2 | Tracked command vehicle | ZWD-2 | 5 | ||||
| ZWD-3 |  | Wheeled all-terrain command vehicle | ZWD-3 | ~250 | |||
| Tumak-6 |  | Wheeled all-terrain command vehicle | Tumak-6 | 9 | |||
| ZWD-10R Łowcza | .jpg.webp) | Tracked command vehicle | ZWD-10R | 4 | |||
| ZWD-10R/K Łowcza-3K |  | Wheeled command truck | ZWD-10R/K | 8 | |||
| RWŁC-10/T |  |
Moving node of digital communication | RWŁC-10/T | 23 | [83] | ||
| PKK |  |
Field cryptographic chancellery vehicle | PKK-S | 50 | [84] | ||
| WWK-10/C | .jpg.webp) |
Cable vehicle | WWK-10/C | 17 | [85] | ||
| WD-2001 |  | Wheeled all-terrain command vehicle | WD-2001 | ||||
| Mercedes Benz G-Wagen |  | Wheeled all-terrain command vehicle | Mercedes Benz 461.4 Wolf | ||||
| ADK-11 |  | Wheeled command truck | ADK-11 | ||||
| BRDM-2 |  | Wheeled amphibious command vehicle | R-1A R-5 | 98 | |||
| Ambulance | |||||||
| M113 |  | Multi-purpose tracked armoured personnel carrier | M113G2 Krkw Gep | 16 | |||
| Lotos |  | Armoured ambulance | TS Lotos | 1 | MT-LB landing. | ||
| KTO Ryś |  | Amphibious wheeled armoured personnel carrier | Ryś-Med | 5[18] | |||
| WEM Rosomak ("Wolverine") |  | Armoured ambulance Vehicle | Rosomak-WEM | 33[38] | Licensed variant of the Patria AMV manufactured in Poland. | ||
| Iveco |  | Truck | M40.12WM | 134 | Iveco 40E13WM is used as a 4x4 ambulance | ||
| SCAM |  | Truck | SCAM SM-50[58] SCAM SM-55[58] | 16[52] 46[52][58] | Used as a 4x4 ambulance. | ||
| M1035A2 |  | Four-wheel drive multi-purpose vehicle | Tumak-7 | 3 | M1035A2 version modified in Poland to ambulance vehicle. | ||
| Tarpan S |  | Four-wheel drive multi-purpose vehicle | Tarpan S | Used as 4x4 ambulance | |||
| Radiolocation | |||||||
| NUR-21 | NUR-21 | Radiolocation station | 20[18] | Used for locating aircraft flying at low altitudes. | |||
| NUR-22 |  | Radiolocation station | 10[18] | Based on Tatra 815. Used for locating aircraft flying at low altitudes. | |||
| NUR-31 |  |
Radiolocation station | NUR-31 "Justyna" | ||||
| NUR-41 |  |
Radiolocation station | NUR-41 "Bożena" | ||||
| Liwiec |  | Artillery support radar | 10 | [86] | |||
| Soła | .JPG.webp) |
Radiolocation station | 8 | Sola radar station mounted on Żubr-P.[87] To support Poprad and Pilica VSHORAD.[88][89] | |||
| Breń-2 |  |
Radiolocation station support | [90] | ||||
| Przebiśnieg |  |
Jamming station | 2 | [91] | |||
| Artillery | |||||||
| M120 Rak |  | 120 mm self-propelled mortar | SMK | 64/122 | The M120 Rak 120mm heavy mortar system can be mounted on a variety of vehicles. Pictured here is the: SMK 120 - RAK mortar mounted on KTO Rosomak ("Wolverine") chassis.[80][81][82] | ||
| 2S1 Goździk | .jpg.webp) | 122 mm self-propelled howitzer | 2S1 Goździk 2S1M Goździk 2S1T Goździk | 362[19] | 198 used, rest in storage. 2S1 will be replaced with AHS Krab. | ||
| Wz. 1977 Dana |  | 152 mm self-propelled howitzer | Dana-T | 111[19] | |||
| Krab |  | 155 mm self-propelled howitzer | 56/122[54][92][93] | Squadron-level Fire Module (DMO) REGINA consist of 24 howitzers, 2 command and control vehicle (WDSz), 9 command vehicles (WD), 6 ammunition vehicles (WA), 1 armament and electronics repair shop (WRUiE), 1 liaison officer vehicle [94]2 Regina DMO Squadron Fire Modules delivered. 5 DMOs were ordered, 24 each. In December 2020, an annex to the 2016 contract was signed, in which an additional 2 cannon howitzers were purchased for CSAiU (in total, 122 Krab cannon howitzers will be delivered to the army).[93] | |||
| BM-21 Grad |  | 122 mm self-propelled multiple-launcher rocket system | 93[19] | To be replaced by M142 HIMARS. | |||
| RM-70 |  | 122 mm self-propelled multiple-launcher rocket system | RM-70/85 | 29[19] | |||
| WR-40 Langusta | .jpg.webp) | 122 mm self-propelled multiple-launcher rocket system | 75[19] | ||||
| M142 HIMARS |  | 227 mm self-propelled multiple-launcher rocket system | 0/20[95] | In 2018, an agreement was signed for the supply of 20 launchers and accompanying equipment and vechicles.[95][96] Locally called WR-300 "Homar". | |||
| Tank destroyers | |||||||
| 9P133 "Malyutka" |  | Tank destroyer | 27[18] | ||||
| Tumak-5 | .jpg.webp) | Tank destroyer | 18 | M1045A2 with Spike LR mounted on top. | |||
| Air defence artillery | |||||||
| ZU-23-2 |  | Twin 23 mm anti-aircraft autocannon | ZU-23-2 ZUR-23-2S Jod ZUR-23-2 kg Jodek-G | ~250[18] 136 143[97][55] | |||
| ZSU-23-4 | .jpg.webp) | Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun | ZSU-23-4 ZSU-23-4MP "Biala" | 7[18] 21[18][98] | More ZSU-23-4 are to be modernized to ZSU-23-4MP Biała standard.[18] | ||
| Hibneryt |  | Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun | Hibneryt Hibneryt-KG Hibneryt-P Hibneryt-3 | ~50 ? ~20 | ZU-23-2, ZUR-23-2S Jod or ZUR-23-2 kg Jodek-G (Hibneryt-KG) mounted on a Star 266 truck. Some Hibneryts are going to be modernized to newer versions like Hibneryt-P or Hibneryt-3. | ||
| Anti-aircraft missiles | |||||||
| Poprad | .jpg.webp) | Self-propelled surface-to-air missile system | Żubr P | 60/77[99][100][101] | 77 serial and 2 pre-series (total 79) POPRAD ordered,[102] 2 pre-series implementation vehicles, which are located at the Air Force Training Center.[103] | ||
| 2K12 Kub | .jpg.webp) | Self-propelled surface-to-air missile system | 2K12M Kub-M | 30[18] | 30 is a number of TELs. | ||
| 9K33 Osa |  | Self-propelled surface-to-air missile system | 9K33M2 Osa-AK
9K33M2 Osa-AKM 9K33M2 Osa-P |
64[18] | 64 transporter erector launcher and radars form 16 batteries.[97][55][104] | ||
Aircraft
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Helicopters | ||||||
| Mil Mi-24 |  | Attack helicopter | Mi-24W Mi-24D |
28[19] | Two attack squadrons with 12 helicopters, 4 Mi-24W used by SOS. Some are equipped with the Terma A/S MASE (Modular Aircraft Survivability Equipment).[105] 4 Mi-24W lost in Afghanistan. | |
| Mil Mi-8 | .jpg.webp) | Tactical transport helicopter | Mi-8T | ~10[106] | ||
| Mil Mi-17 |  | Tactical transport helicopter | Mi-17 Mi-17-1V Mi-17AE |
4[106] 12[106] 2[106] |
One squadron with 16 helicopters. Some with the Terma A/S MASE.[105] One medical evacuation squadron with 4 helicopters (2 W-3PL and 2 Mi-17AE). | |
| PZL W-3 |  .jpg.webp) .jpg.webp) | Tactical transport helicopter | W-3W Sokół W-3WA Sokół W-3PL Głuszec W-3WA AE Sokół W-3RR Procjon W-3PSOT |
10 13 7 2 3 1 Total: 36[107] |
||
| PZL Mi-2 | .jpg.webp) | Training helicopter | Mi-2 | 41[108] | ||
| Unmanned aerial vehicles | ||||||
| Aeronautics Defense Orbiter |  |
Small unmanned aerial vehicle | 11[109] | Also operated by Polish Special Forces.[110] | ||
| WB Electronics FlyEye |  | Small unmanned aerial vehicle | 12 | |||
| Boeing Insitu ScanEagle |  | Small unmanned aerial vehicle | 10[111] | |||
Possible/future/ordered equipment
| Model | Image | Origin | Type | Variant | Number | Details |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Designated Marksman Rifle | 7.62mm NATO DMR | 250 | It is planned to buy in near future around 250 examples of designated marksman rifle, to replace old SWD.[112] | |||
| Light portable Anti-Tank missile System. Program "Corsair" |  | 107mm anti-tank guided missile system | Prototype testing scheduled for mid-2015. Serial production to begin in 2017-2018. The system will have three types of warheads weighing about 2.5 kg each: Cumulative, Thermobaric and Explosive. System equipped a thermal sight and guidance module. Cooperation between Bumar Holding and Ukrainian "Luch".[113] | |||
| Light armoured long-range reconnaissance vehicle |  | Light armoured reconnaissance vehicles | 118 | The vehicles will be used by Polish Armed Forces reconnaissance regiments with capable to transport on C130 Hercules. With a maximum payload of 900 kg. In August 2017, MoD selected Polish vehicle named Wirus IV.[114] Deliveries are to be made in 2021-2022.[115] | ||
| New Infantry fighting vehicle BWP Borsuk |  | Developed to replace BWP-1 in land forces. In 2018, he was an importer of a vehicle. In 2020, preliminary studies began, followed by qualification-military studies. During this time, the Technical Documentation of the Product will be prepared, which is a stage preceding the opening of the road to serial production of the vehicle. In the 2020 assessment, Polska Grupa Zbrojeniowa checked that in September 2020, Borsuk BWP begins its first tests at the military training ground in Drawsko Pomorskie, where it underwent a series of tests and fire tests. Serial production of the Borsuk IFV is expected to start at the turn of 2023/24.[116][117] | ||||
| New Amphibious Armoured Scout Car Bóbr-3 |  | 244 | Replacement for BRDM-2. In December 2013, the National Center for Research and Development concluded with a consortium consisting of: AMZ-Kutno (leader), the Military Institute of Chemistry and Radiometry, the Military Institute of Telecommunications and the Military Institute of Armament Technology, signed a contract for the development of a replacement for the currently used vehicles worth PLN 25 million . In August 2020, the state reconnaissance tests of the Bóbr-3 began, which are to last 12 months. After a positive assessment of the vehicle after the state tests have been completed, the army may receive up to 244 copies of the Bóbr-3 vehicle (in accordance with the demand included in the Technical Modernization Plan for 2013-2022).[118][119] | |||
| KMO Rak | .JPG.webp) | 120mm self-propelled mortar | SMG SMK AWD AWRU AWA AWR WZT |
0 122 60 10 24 0 0 |
SMG 120 - Rak mortar mounted on tracked chassis.(modernized Opal-I, in future it would be chassis of Polish IFV) SMK 120 - RAK mortar mounted on KTO Rosomak chassis. Built by Huta Stalowa Wola. Company-level Fire Module (KMO) consists of 8 fire units (SMK), 4 command vehicles (AWD), 2 artillery reconnaissance vehicle (AWR), 3 ammunition vehicles (AWA), 1 armament repair shop (AWRU),1 recovery vehicle (WZT).[120] 8 KMO are delivered. 7 more KMO ordered and additional 2 SMK for Artillery Training Center in Torun.[80][81][82] | |
| DMO Regina | .jpg.webp) | 155mm self-propelled howitzer | Krab
WDSZz WD WA WRUiE |
120
10 45 30 5 |
Squadron-level Fire Module (DMO) REGINA consist of 24 howitzers, 2 command and control vehicle (WDSz), 9 command vehicles (WD), 6 ammunition vehicles (WA), 1 armament and electronics repair shop (WRUiE), 1 liaison officer vehicle [94] | |
| AHS Kryl |  | 155mm self-propelled auto-loading gun | 168 | New self-propelled auto-loading gun for land forces, built by Huta Stalowa Wola, System uses a license built ATMOS 2000 howitzer. The vehicle platform is a special version Jelcz heavy truck. Prototype completion scheduled for 2015. In future the Kryl will replace 152mm SpGH DANA. | ||
| Baobab-K | Minelayer | New minelayer system built by Huta Stalowa Wola. | ||||
| New Self-Propelled Anti-Aircraft Gun Program "Noteć" | Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun | 20 | [121] | |||
| New low range Surface-to-air missile Program, "Narew" | Surface-to-air missile system | 11 batteries | Cooperation between Polski Holding Obronny, Warsaw University of Technology and Military University of Technology in Warsaw Missile is in advanced phase of development. | |||
| M142 HIMARS |  | Multiple rocket launcher | 20 launchers and support vehicles on order.[122] | |||
| Bystra |  |
Active electronically scanned array radar | 16 | Bystra is to support SHORAD and VSHORAD air defence elements.[123] 16 radars ordered during the MSPO 2019 exhibition. Deliveries 2019 - 2025.[124] | ||
| New Attack helicopters Program, "Kruk" | Attack helicopter | 32 | 32 are to be bought as replacement for Mi-24. 4 companies are interested in participation in the tender: Bell Helicopters with AH-1Z, Boeing Defense, Space & Security with AH-64E, AgustaWestland with AW-129 Mangusta and Airbus Helicopters with EC-665 Tiger.[125][126] | |||
| New Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun Program "Sona" | Self-propelled anti-aircraft gun | Planned to replace ZSU-23-4[127] | ||||
| New MBT Program "Wilk" | Main battle tank | Planned to replace old T-72 and PT-91[128][129] | ||||
| New Grenade Launcher Program "Grot" | Grenade launcher | [130] | ||||
| New Tank Destroyer Program "Ottokar-Brzoza" | Tank destroyer | Planned to replace 9M14 Malyutka [131] | ||||
| New Medium Range UAV Program "Gryf" | Tactical class medium range unmanned aerial vehicle | [132][133] | ||||
| Mini-UAV "Wizjer" | Low range unmanned aerial vehicle | NeoX 2 | [134] | |||
| New Low Range UAV Program "Orlik" | Tactical class low range unmanned aerial vehicle | PGZ-19R | [135] | |||
| New Anti-Tank Guided Missile System "Moskit" | Anti-tank guided missile system | Moskit-LR
Moskit-SR |
Probably is a clone of Spike missile system with similar technical specifications and construction things. [136] |
References
- "Pistolet wz. 1964, znany również pod nazwą CZAK" (in Polish). mon.gov.pl. Archived from the original on 15 March 2012. Retrieved 7 July 2020.
- "Nowe pistolety dla WP – Altair Agencja Lotnicza". Altair.com.pl. 8 September 2008. Archived from the original on 10 October 2011. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- "Pistolet dopiero za 2 lata – Altair Agencja Lotnicza". Altair.com.pl. Archived from the original on 8 January 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- Archived 29 April 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- "Nowy pistolet i karabin dla WP – Altair Agencja Lotnicza". Altair.com.pl. Archived from the original on 19 October 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- http://www.milmag.pl/news/view?news_id=1652
- "Polski import i eksport broni strzeleckiej w 2006" (in Polish). altair.com.pl. Archived from the original on 6 August 2016. Retrieved 13 October 2007.
- "Wojsko kupiło prawie 8 tys. karabinów Beryl | DEFENCE24". Defence24.pl. Archived from the original on 7 August 2015. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- "18 tysięcy Grotów dla SZRP". www.milmag.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 8 July 2020.
- "PD2016: Nowe UKM-2000P w WP" (in Polish). altair.com.pl. Archived from the original on 7 June 2016. Retrieved 4 June 2016.
- "Tysiąc UKM-2000 w WP – Altair Agencja Lotnicza". Altair.com.pl. Archived from the original on 17 October 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Wyposażenie Wojsk Lądowych RP". Gdzie zaczyna się wojsko... 7 May 2011. Archived from the original on 19 October 2013. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Bro strzelecka w WP na pocztku XXI wieku". Militech.sownet.pl. Archived from the original on 9 May 2015. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- https://www.webcitation.org/5rOgpOaWZ?url=http://disarmament.un.org/UN_REGISTER.nsf/5cb8afbbb6536a298525647d00612b14/f828bbeb1ff68e068525749d007ef3ba?OpenDocument. Archived from the original on 21 July 2010. Retrieved 26 December 2009. Missing or empty
|title=(help) - "Granatniki unieważnione" (in Polish). milmag.pl. Archived from the original on 27 June 2017. Retrieved 21 June 2017.
- "MON negocjuje zakupy karabinów wyborowych, granatników i moździerzy | DEFENCE24". Defence24.pl. Archived from the original on 28 March 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- "Broń do zadań specjalnych". Polska-zbrojna.pl. Archived from the original on 23 March 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- Archived 9 September 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "UNROCA (United Nations Register of Conventional Arms)". www.unroca.org. Retrieved 3 June 2020.
- "ANTOS mortars for Poland". milmag.pl. Archived from the original on 23 February 2018.
- "ANTOS for Teritorial forces". milmag.pl. Archived from the original on 29 July 2018.
- Archived 18 November 2009 at the Wayback Machine
- "Umowa na "Pioruny" podpisana. 1300 rakiet polskiej produkcji trafi w ręce żołnierzy" (in Polish). wprost.pl. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 20 December 2016.
- Dmitruk, Tomasz (27 December 2020). "Ocena stanu realizacji Planu Modernizacji Technicznej Sił Zbrojnych RP na lata 2013-2022, 2017-2026 i 2021-2035 W zestawieniu uwzględniono także wybrane zadania zawarte w Planie Zakupu Środków Materiałowych. wg. stanu na dzień 27 grudnia 2020 roku".
- "Odpowied na interpelacj w sprawie sytuacji wojsk pancernych". Orka2.sejm.gov.pl. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- Archived 18 February 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- "Historyczny transport Leopardów". 34bkpanc.wp.mil.pl. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 29 November 2015.
- "Kolejne Leopardy dotarły do Polski". Polska-zbrojna.pl. Archived from the original on 22 October 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Druga kompania Leopardów w Żaganiu". Dziennikzbrojny.pl. Archived from the original on 31 May 2014. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- Stern. "PolskaKolej.TV – PKP CARGO dostarczyło 49 Leopardów dla Wojska Polskiego". Polskakolej.tv. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "KWM dostarczy WP dwa Leopardy-NJ – Altair Agencja Lotnicza". Altair.com/pl. Archived from the original on 16 October 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Pierwsze Leopardy 2PL już w Polsce". Polska-zbrojna.pl. Archived from the original on 24 June 2019. Retrieved 17 January 2020.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 19 August 2016. Retrieved 21 July 2016.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Modyfikacja T-72, sukces czy porażka?". DziennikZbrojny.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- "T-72M1 Mod". milmag.pl.
- "T-72M1R".
- "KTO Rosomak". tanks-encyclopedia.com. Tanks Encyclopedia. Retrieved 28 October 2020.
- "Po epoce Rosomaka czas na Borsuka?". DziennikZbrojny.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 6 June 2020.
- Archived 10 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- "Raport WTO – 03/2007 – Kołowa aberracja – Altair Agencja Lotnicza". Altair.com.pl. Archived from the original on 17 February 2012. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- Archived 12 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- "18 Bergepanzerów to protect Leopards". Dziennikzbrojny.pl. Archived from the original on 2 December 2013. Retrieved 4 September 2015.
- "We modernize our Bergepanzery". Dziennikzbrojny.pl. Archived from the original on 14 December 2013. Retrieved 4 September 2015.
- "Rosomak WRT". Defence24.
- "First Rosomak WRT Vehicle Received by the Land Forces". Defense24. 13 December 2016. Retrieved 29 October 2020.
- "Hardun". DziennikZbrojny.pl.
- "Ocena stanu realizacji PMT-25.06.2020p.pdf". Google Docs. Retrieved 29 June 2020.
- "Trade Registers". Armstrade.sipri.org. Archived from the original on 5 August 2009. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- Archived 6 February 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 28 August 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Archived 12 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine
- "Erubaystores.com - Twoje ulubione sklepy internetowe". Militarypedia.corran.pl. Archived from the original on 22 August 2011. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "888 Jelcz 442.32 Trucks for the Polish Military - Defence24.com". www.defence24.com. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- "Kolejne Kraby i Raki w 12 Dywizji Zmechanizowanej". www.polska-zbrojna.pl. Retrieved 31 October 2019.
- Archived 17 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine
- "Resort obrony kupił nie tylko Leopardy". Polska-zbrojna.pl. Archived from the original on 20 December 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Honker". Tomasz Szczerbicki. Archived from the original on 20 December 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- Nowa Technika Wojskowa magazine, issue 03/09
- Archived 15 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- "Armia" magazine, issue 3/08
- Nowa Technika Wojskowa magazine issue 9/07
- Nowa Technika Wojskowa magazine issue 4/08
- Raport WTO magazine issue Raport WTO 9/03
- Raport WTO magazine issue Raport WTO 10/04
- "6. BPD odbiera kolejne pojazdy aeromobilne". www.milmag.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- "AERO spada z nieba". Wydawnictwo militarne ZBIAM (in Polish). 11 June 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- "Samochód do desantowania". polska-zbrojna.pl. Retrieved 13 November 2020.
- "Kolejne wozy Aero trafiły do spadochroniarzy". www.polska-zbrojna.pl. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- Nowa Technika Wojskowa magazine, issue 03/09 96
- "Ford Ranger zamiast Honkera. Oto NOWE samochody dla polskiego wojska". auto.dziennik.pl (in Polish). 15 December 2020. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- "Kielecka premiera Mustanga - Defence24". www.defence24.pl. Retrieved 23 September 2020.
- "Polish Army 4x4 Vehicle Procurement: Ford Vehicles replace Nissans - Defence24.com". www.defence24.com. Retrieved 16 December 2020.
- Nowa Technika Wojskowa magazine, issue 05/09
- "Seicento gotowy do służby w polskim wojsku". New-arch.rp.pl. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- Zbiam (15 May 2019). "Volkswageny dla wojska". Wydawnictwo militarne ZBIAM (in Polish). Retrieved 23 September 2020.
- Bus, MAN Truck &. "MAN TGE dla Wojska Polskiego | MAN Polska Pojazdy ciężarowe". www.truck.man.eu (in Polish). Retrieved 23 September 2020.
- Wiadomości (21 December 2020). "Kolejne zamówienie na wozy dowodzenia Rosomak WD". Frag Out! Magazine (in Polish). Retrieved 3 January 2021.
- "Rosomaki WD przekazane". www.milmag.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 23 September 2019.
- "MSPO 2019: Dwa Rosomaki dowodzenia dla Żelaznej Dywizji". mspo.defence24.pl. Retrieved 23 September 2019.
- "Rak Mortars Headed to Szczecin - Defence24.com". www.defence24.com (in Polish). Retrieved 25 October 2019.
- "More Rak Mortars for the Polish Army - Defence24.com". www.defence24.com (in Polish). Retrieved 25 October 2019.
- "Umowa na Raki dla 18 Dywizji Zmechanizowanej". DziennikZbrojny.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 22 May 2020.
- "RWLC-10/T". Defence24.
- "PKK". Defence24.
- "WWK-10/C". Zbiam.pl.
- "MON kupi radary Liwiec". Polska-zbrojna.pl. Archived from the original on 6 February 2013. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- "Od Loary do baterii przeciwlotniczej 35 mm. PIT-RADWAR w programie "Noteć" - Defence24". www.defence24.pl. Retrieved 19 August 2019.
- Archived 20 April 2013 at the Wayback Machine
- "Soła dla Popradów - Altair Agencja Lotnicza". Altair.com.pl. Archived from the original on 20 December 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Bren-2". Defence24.
- "Przebisneg". WZE.com.
- "More Krab's". Defence24.pl.
- "Dodatkowe Kraby dla Wojska Polskiego". www.milmag.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 3 January 2021.
- "First of the "Regina" Squadron Level Fire Modules to Receive All of Its Inventory in July - Defence24.com". www.defence24.com. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- "Szef MON Mariusz Błaszczak podpisał umowę na dostawę Homara". www.rp.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 3 January 2021.
- "Pierwszy dywizjon HIMARS za 414 mln dolarów. Umowa w środę - Defence24". www.defence24.pl. Retrieved 3 January 2021.
- "Serwis-militarny.net :: Wojsko Polskie - uzbrojenie". Serwis-militarny.net. Archived from the original on 23 February 2015. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Technical support anti-ZSU-23-4MP BIAŁA". Dziennikzbrojny.pl. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 4 September 2015.
- Dmitruk, Tomasz (25 June 2020). "Ocena stanu realizacji Planu Modernizacji Technicznej Sił Zbrojnych RP na lata 2013-2022, 2017-2026 i 2021-2035".
- "More Poprad's". defence24.pl.
- "Już 60 zestawów Poprad trafiło do Sił Zbrojnych RP". DziennikZbrojny.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 28 November 2020.
- "Poprady idą do wojska - Defence24". www.defence24.pl. Retrieved 7 July 2020.
- "Rozbudowa Centrum Szkolenia Sił Powietrznych". www.milmag.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 29 November 2020.
- "DMUs SA will modernize Wasps". Dziennikzbrojny.pl. Archived from the original on 3 February 2014. Retrieved 4 September 2015.
- Testy MASE dla PKW-A (wreszcie) rozpoczete (in Polish), 26 July 2011, archived from the original on 3 February 2012, retrieved 23 May 2012
- Mil Mi-8 i Mi-17 w Wojsku Polskim. Archived 14 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine (in Polish)
- "PZL W-3 Sokół w Wojsku Polskim". Gdzie zaczyna się wojsko… (in Polish). 9 October 2010. Retrieved 12 December 2019.
- "Następca Mi-2 poszukiwany". DziennikZbrojny.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 8 May 2020.
- http://www.samolotypolskie.pl/samoloty/226/126/Aeronautics-Defense-Orbiter2
- Reed Business Information Limited. "Aviation News - Aviation Industry & Airline Statistics". Flightglobal.com. Archived from the original on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- Seffers, George (24 September 2010). "Insitu to Provide ScanEagle Unmanned Planes to Poland". AFCEA Signal. Archived from the original on 9 February 2018. Retrieved 9 February 2018.
- "Następca SWD w WP - Altair Agencja Lotnicza". Altair.com.pl. Archived from the original on 12 January 2016. Retrieved 17 August 2015.
- "Driven pirate with plants Mesko". Dziennikzbrojny.pl. Archived from the original on 14 August 2014. Retrieved 4 September 2015.
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 28 August 2017. Retrieved 28 August 2017.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- "Pierwsze Żmije dopiero w styczniu 2021". Defence 24.
- października 2020, Zbigniew Lentowicz-20 (20 October 2020). "Pancerny Borsuk daje ognia na Drawsku". Radar (in Polish). Retrieved 4 January 2021.
- Pawłowski, Andrzej (23 October 2020). "Borsuk na poligonie w Drawsku Pomorskim". Konflikty.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 4 January 2021.
- "Ruszyły próby LOTR". www.altair.com.pl. Retrieved 4 January 2021.
- "Kleszcze zamiast BRDM-ów". www.polska-zbrojna.pl. Retrieved 4 January 2021.
- "Artyleryjskie Wozy Amunicyjne zamówione". DziennikZbrojny.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 14 August 2019.
- "Changes to the financing of technical modernization of the Polish Armed Forces". Dziennikzbrojny.pl. Archived from the original on 14 August 2014. Retrieved 4 September 2015.
- "Poland announces purchase of HIMARS rocket systems from US". www.thenews.pl. 10 February 2019.
- "Polish Company to supply the Army with AESA Radars - Defence24.com". www.defence24.com. Retrieved 11 August 2019.
- "MSPO 2019: polskie radary AESA dla wojska. Jest umowa - Defence24". www.defence24.pl. Retrieved 24 September 2019.
- "Następca śmigłowca Mi-24 na horyzoncie. Program Kruk rozpoczęty". Defence24.pl. Archived from the original on 4 November 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Czterech kandydatów na następcę Mi-24. Przetarg ruszy we wrześniu 2015 roku". Archived from the original on 8 November 2014. Retrieved 19 December 2014.
- "Program "Sona"".
- "Wilk Program". radar.rp.pl.
- "Korean Industry interested in the Polish MBT Programme". Defence24.
- "Grot grenade launcher".
- "Ottokar-Brzoza".
- "Male UAV "Gryf"".
- "Gryf Programme". dziennikzbrojny.pl.
- "Mini-UAV "Wizjer"". defence24.pl.
- "Orlik Programme". defence24.pl.
- "Anti-Tank "Moskit" System". dziennikzbrojny.pl.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.