List of exoplanet search projects
The following is a list of exoplanet search projects.
Ground-based search projects
Space missions
Past and current
| Name | Launch date | End date | Number of exoplanets found | Current candidates | Telescope use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MOST | June 20, 2003 | Ongoing | 1+ | 0 | First spacecraft dedicated to the study of asteroseismology |
| EPOXI | July 21, 2005 | August 8, 2013 | 0 | 0 | Characterized planets and fly-by of comet |
| SWEEPS | 2006 | 2006 | 16 | 0 | Based from the HST, a short 7 day mission looking for exoplanets |
| COROT | December 27, 2006 | November 2, 2012 | 34 | 600 | Mission to look for exoplanets using the transit method |
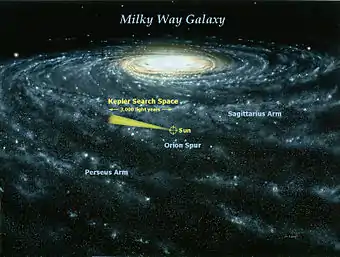
| Kepler | March 7, 2009 | August 15, 2013 | 2,347 | 2,420 | Mission to look for large numbers of exoplanets using the transit method |
| K2 | November 18, 2013 | October 30, 2018 | 427 | 891 (+627 microlensing events) | After the reaction wheels failed on Kepler, this mission was created |
| Gaia | December 19, 2013 | Ongoing | 0 | 0 | Map 1 billion astronomical objects in the Milky Way (First data Release November 2, 2016) |
| ASTERIA | November 2017 | Ongoing | 0 | 0 | CubeSat, technology demonstrator |
| TESS | April 18, 2018 | Ongoing | 82 | 2,413 | To search for new exoplanets; rotating so by the end of its two-year mission it will have observed stars from all over the sky. It is expected to find at least 3,000 new exoplanets. |
| CHEOPS | 2019[37] | Ongoing | 0 | 0 | To learn more about how exoplanets form, probe atmospheres, and characterize super-Earths. 20% of time will be open to community use.[38] Duration: 3.5 (+ 1.5 goal) years |
| 2,757 (3,940 Total)[39] | 3,914 |
Planned
| Name | Launch date | Mission objectives | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| JWST | October 2021 | To study atmospheres of known exoplanets and find some Jupiter-sized exoplanets | 5 (+ 5 goal) years |
| PLATO | 2026 (Soyuz-ST) | To search for and characterize rocky planets around stars like our own. | 4 (+4 goal) years |
| ARIEL | 2028 (Ariane 6-2) | Observe exoplanets using the transit method, study and characterise the planets' chemical composition and thermal structures | 4 years |
| RST | 2025 | To search for and study exoplanets while studying dark matter. It is expected to find about 2,500 planets. | 6 years |
References
- "Mt. Hamilton Telescopes: Carnegie Double Astrograph". www.ucolick.org. Retrieved 2016-07-08.
- "carmenes". carmenes. Retrieved 2018-06-08.
- Reiners, A.; et al. (2018). "The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 609: L5. arXiv:1712.05797. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201732165. S2CID 55661984.
- Trifonov, T.; et al. (2018). "The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 609: A117. arXiv:1710.01595. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201731442. S2CID 119340839.
- Luque, R.; et al. (2018). "The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 620: A171. arXiv:1810.07572. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833423. S2CID 119356918.
- "E-ELT". www.eelt.org.uk. Retrieved 2016-07-08.
- webteam@eso.org. "ESO - The European ELT". www.eso.org. Retrieved 2016-07-08.
- webteam@eso.org. "ESO - Espresso". www.eso.org. Retrieved 2016-07-08.
- F., Pepe; P., Molaro; S., Cristiani; R., Rebolo; C., Santos, N.; H., Dekker; D., Mégevand; M., Zerbi, F.; A., Cabral (2014-01-23). "ESPRESSO: The next European exoplanet hunter". arXiv:1401.5918 [astro-ph.IM].
- Jurgenson, C.; Fischer, D.; McCracken, T.; Sawyer, D.; Szymkowiak, A.; Davis, A.; Muller, G.; Santoro, F. (2016). "EXPRES: A next generation RV spectrograph in the search for earth-like worlds". In Evans, Christopher J; Simard, Luc; Takami, Hideki (eds.). Ground-based and Airborne Instrumentation for Astronomy VI. 9908. pp. 99086T. arXiv:1606.04413. doi:10.1117/12.2233002. S2CID 119210955.
- "FINDS Exo-Earths". www.planetary.org. Retrieved 2016-07-08.
- "Planet Imager » About". planetimager.org. Retrieved 2016-07-08.
- webteam@eso.org. "ESO - HARPS". www.eso.org. Retrieved 2016-07-08.
- "Confirmed Planets". Exoplanet Archive. Caltech. Retrieved 1 February 2020.
- "HATNet / Planets". hatnet.org. The HATNet Exoplanet Survey. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
- "HATSouth / Planets". hatsouth.org. The HATSouth Exoplanet Survey. Retrieved 8 June 2018.
- Butler, R. Paul; Marcy, Geoffrey W.; Vogt, Steven S.; Fischer, Debra A.; Henry, Gregory W.; Laughlin, Gregory; Wright, Jason T. (2003). "Seven New Keck Planets Orbiting G and K Dwarfs". The Astrophysical Journal. 582 (1): 455–466. Bibcode:2003ApJ...582..455B. doi:10.1086/344570.
- "KELT Transit Search to conclude after 17 years of work". keltsurvey.org. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- "KELT Transit Search to conclude after 17 years of work". keltsurvey.org. Retrieved 14 April 2020.
- Ma(馬波), Bo; et al. (2016). "Very Low-Mass Stellar and Substellar Companions to Solar-Like Stars from Marvels. Vi. A Giant Planet and a Brown Dwarf Candidate in a Close Binary System Hd 87646". The Astronomical Journal. 152 (5): 112. arXiv:1608.03597. Bibcode:2016AJ....152..112M. doi:10.3847/0004-6256/152/5/112. S2CID 118506921.
- Dorval, P.; et al. (2020). "MASCARA-4 b/B Ring-1 b: A retrograde hot Jupiter around a bright A-type star". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 635: A60. arXiv:1904.02733. Bibcode:2020A&A...635A..60D. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935611. S2CID 102351446.
- "The MEarth Project: Discoveries". Harvard–Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics. Retrieved 2020-05-23.
- Next Generation Transit Survey Finds its First Planet, NGTS-1b. Sci Tech Daily. October 31, 2017
- Günther, Maximilian N.; et al. (2018). "Unmasking the hidden NGTS-3Ab: A hot Jupiter in an unresolved binary system". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 478 (4): 4720–4737. arXiv:1805.01378. Bibcode:2018MNRAS.478.4720G. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty1193. S2CID 119072135.
- Raynard, Liam; et al. (2018). "NGTS-2b: An inflated hot-Jupiter transiting a bright F-dwarf". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 481 (4): 4960–4970. arXiv:1805.10449. Bibcode:2018MNRAS.481.4960R. doi:10.1093/mnras/sty2581. S2CID 54591252.
- "Discovery of a Sub-Saturn Exoplanet around a Sun-like star - ISRO". www.isro.gov.in. Retrieved 2019-11-25.
- "Home - (QES)". qatarexoplanet.org. Retrieved 2019-05-04.
- "SOPHIE |". exoplanets.ch. Retrieved 2016-07-08.
- "ESO's SPHERE Unveils its First Exoplanet". eso.org. 2017-07-06.
- Delrez, Laetitia; et al. (2018). Spyromilio, Jason; Marshall, Heather K; Gilmozzi, Roberto (eds.). "SPECULOOS: A network of robotic telescopes to hunt for terrestrial planets around the nearest ultracool dwarfs". Ground-Based and Airborne Telescopes Vii. 10700: 107001I. arXiv:1806.11205. Bibcode:2018SPIE10700E..1ID. doi:10.1117/12.2312475. ISBN 9781510619531. S2CID 119012966.
- Thalmann, Christian; Carson, Joseph; Janson, Markus; Goto, Miwa; McElwain, Michael; Egner, Sebastian; Feldt, Markus; Hashimoto, Jun; Hayano, Yutaka (2009-12-20). "Discovery of the Coldest Imaged Companion of a Sun-Like Star". The Astrophysical Journal. 707 (2): L123–L127. arXiv:0911.1127. Bibcode:2009ApJ...707L.123T. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/707/2/L123. ISSN 0004-637X. S2CID 116823073.
- "WASP Planets". WASP Planets. 5 December 2013. Retrieved 2020-05-23.
- "WASP Planets". WASP Planets. Retrieved 2018-07-19.
- Scott, Phillip; et al. (2020-07-14). "GJ 3470 c: A Saturn-like Exoplanet Candidate in the Habitable Zone of GJ 3470". arXiv:2007.07373 [astro-ph.EP].
- "The Extrasolar Planet Encyclopaedia — GJ 3470 c". exoplanet.eu. Retrieved 2020-07-16.
- Schmid, H. M.; et al. (2005-12-01). "ZIMPOL/CHEOPS: a Polarimetric Imager for the Direct Detection of Extra-solar Planets". Astronomical Polarimetry: Current Status and Future Directions. 343: 89. Bibcode:2005ASPC..343...89S.
- "ESA Science & Technology - CHEOPS exoplanet mission meets key milestones en route to 2017 launch".
- "Objectives". sci.esa.int. Retrieved 2016-06-12.
- "Exoplanet Archive Planet Counts". exoplanetarchive.ipac.caltech.edu. Retrieved 2019-04-14.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.