Métro léger de Tunis
The Métro léger de Tunis (Tunis light metro, also Tunis Métro, Tunisian Arabic: المترو الخفيف لمدينة تونس, el-metrū el-khfīf li-mdīnat tūnis) is an expanding public transportation network for the Tunis metropolitan area that was started in 1985. It represents not a typical subterranean heavy rail service, but a light rail system.
 | |||
| Overview | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Locale | Tunis, Tunisia | ||
| Transit type | Light rail | ||
| Number of lines | 6 | ||
| Number of stations | 66 (2009) | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 1985 | ||
| Operator(s) | Société des transports de Tunis | ||
| Number of vehicles | 173 (134 Siemens and 39 Citadis) | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 45.2 km (28.1 mi) | ||
| Track gauge | 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) standard gauge | ||
| Electrification | Overhead lines, 750 V DC | ||
| |||
Metro leger's light rail system has its track at surface level generally with its own rail bed, but at key intersections, the system goes underground to avoid congestion or has the right of way. Together with the TGM commuter rail line it is managed by the parastatal transport authority Société des transports de Tunis (Transtu).
While once a number of African cities had traditional electric tram systems, all but the Alexandria Tram were discontinued. The Metro leger's modern light rail system was originally unique for Africa, but there are now modern trams in Algeria and Morocco, as well.
History
Tunis had an older electric tram system that, like in many cities, eventually was dismantled. With the postwar growth of the metropolitan area and the traffic congestion that followed, the need for a commuter transportation system became evident. The city eventually reached the decision to link the suburbs to the city center with a modern network of light rail. The system was delivered as a turnkey operation by a consortium led by Siemens.[1] The Société du métro léger de Tunis (SMLT) was founded in 1981 to manage the operation.
Construction on Line 1 started the same year, and passenger services commenced in 1985. In 1989, Line 2 was placed into operation, with Line 3 and 4 following the next year. Line 5 became operative in 1992, while in the same year Line 3 was extended to its current length. In 1997, the extension of Line 4 was inaugurated, and further construction for an extension to La Manouba was started in 2007. The Société des transports de Tunis took over management in 2003; it was formed by joining the SMLT and the Société nationale de transports (SNT, founded in 1963) that was responsible for the TGM railway. A new Line 6 was planned to link Tunis with El Mourouj and its construction began in 2005. The completion of this new line finished in 2009. New Alstom Citadis trains to supplement the earlier Siemens trains were introduced in 2007.
Network
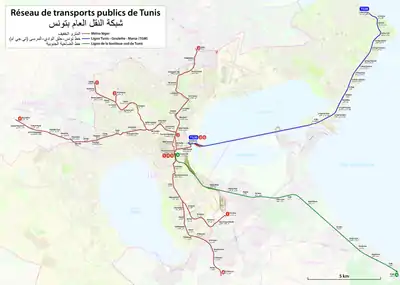
As of 2009, the Metro leger comprised a network of 45.2 kilometers (28.1 mi) with 66 stations. It has a capacity to carry 600,000 passengers per day.[2] There is an intersection with the Tunisian Railways' Tunis Gare Centrale at Place de Barcelone and with TGM at Tunis Marine. The lines are (2009):
- Line 1 : Tunis Marine – Ben Arous (South)
- Length : 9.2 kilometers
- Number of daily trains : 125
- Hours of operation : 03h25 / 23h05
- Running time : 27 minutes
- Line 2 : Place de Barcelone – Ariana (North) [NB. Temporarily starting at République - 1.1.2012]
- Length : 8.9 kilometers
- Number of daily trains : 133
- Hours of operation : 04h20 / 22h50
- Running time: 28 minutes
- Line 3 : Place de Barcelone – Ibn Khaldoun (North-West)
- Length : 8.4 kilometers
- Number of daily trains : 51
- Hours of operation : 05h55 / 19h30
- Running time : 28 minutes
- Line 4 : Tunis Marine – Kheireddine (West)
- Length : 15.1 kilometers
- Numbers of daily trains : 105
- Hours of operation : 04h36 / 22h35
- Running time : 32–35 minutes
- Line 5 : Place de Barcelone – Intilaka (North-West)
- Length : 9.8 kilometers
- Number of daily trains : 103
- Hours of operation : 04h09 / 22h35
- Running time : 34–35 minutes
- Line 6 : Tunis Marine – El Mourouj 4 (South)
- Diametrical Line 12 : 10 décembre – El Ouardia VI (only during rush hours 6h00 – 8h30 and 17h00 – 19h30)
- Length : 12.03 kilometers
- Running time : 39 minutes
- Diametrical line 14 : Den Den – El Ouardia VI (only during rush hours 6h00 – 8h30 and 17h00 – 19h30)
- Length : 14 kilometers
- Running time : 47 minutes
On October 2, 2007, a 2-year project started to extend Line 4 by 5.2 km to reach the Université de la Manouba. Further extensions are planned.
Tram vehicles
.jpg.webp)
By 2006, 136 articulated passenger trams were in operation. They were built by Siemens, and delivered between 1984 and 1997. These trains were derived from the TW 6000 originally developed for Hanover Stadtbahn. The bi-directional trains are powered via a 750 V dc overhead wire and run on a 1,435 mm (4 ft 8 1⁄2 in) track. The trams have a green livery with white and blue lines. A train consists of two wagons each of which has:
- bogies typ Bo-2-2-Bo
- electric motors 2 x 240 kW
- weight of 40.3 tonnes
- length of 30 meters
- width of 2.47 meters
- access from low and high platforms
In 2004, an agreement between the French and Tunisian governments led to the order of 30 new Alstom Citadis trams. Each train consists of two trams of 64 metre length to hold 208 people standing and 58 sitting. The first such trains started to operate on September 17, 2007.[3] 16 more trams were ordered from Alstom in July 2010.[4]
See also
References
- Urbanrail.net information page
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2016-03-11. Retrieved 2016-03-09.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)
- Hella Lahbib (2007-09-18). "Un tramway nommé plaisir" (in French). La Presse de Tunisie.
- "Tunis orders more trams". Railway Gazette International. 22 July 2010. Retrieved 2010-07-23.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tunis Metro. |