Mustafa II
Mustafa II (/ˈmʊstəfə/; Ottoman Turkish: مصطفى ثانى Muṣṭafā-yi sānī; 6 February 1664 – 29 December 1703) was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1695 to 1703.
| Mustafa II مصطفى ثانى | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kayser-i Rûm Amir al-Mu'minin Custodian of the Two Holy Mosques Ottoman Caliph | |||||
 | |||||
| 22nd Sultan of the Ottoman Empire (Padishah) | |||||
| Reign | 6 February 1695 – 22 August 1703 | ||||
| Predecessor | Ahmed II | ||||
| Successor | Ahmed III | ||||
| Born | 6 February 1664 Edirne Palace, Edirne, Ottoman Empire | ||||
| Died | 29 December 1703 (aged 39) Topkapı Palace, Istanbul, Ottoman Empire | ||||
| Burial | Tomb of Turhan Sultan, New Mosque, Istanbul | ||||
| Consorts | Saliha Sultan Şehsuvar Sultan Alicenab Kadın Afife Kadın Ivaz Kadın Bahtiyar Kadın Şahin Kadın | ||||
| Issue | see below | ||||
| |||||
| Dynasty | Ottoman | ||||
| Father | Mehmed IV | ||||
| Mother | Gülnuş Sultan | ||||
| Religion | Sunni Islam | ||||
| Tughra | 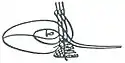 | ||||
Early life
He was born at Edirne Palace on 6 February 1664. He was the son of Sultan Mehmed IV (1648–87) and Gülnuş Sultan, originally named Evmenia,[1] who was of Greek Cretan descent.[2][3][4] Mustafa II abdicated in favor of his brother Ahmed III (1703–30) in 1703.
Born in Edirne, Mustafa's childhood passed here. While he was in Mora Yenişehiri with his father in 1669, he took the first lesson from Mehmed Efendi at the bed-i besinele ceremony. [5] The writing teacher was the famous calligrapher Hafiz Osman. In 1675, He and his brother Ahmed were circumcised and his sisters Hatice Sultan and Fatma Sultan were married. [6] The celebration lasted 20 days. [7]
Reign
Great Turkish War
During his reign the Great Turkish War, which had started in 1683, was still going on. After the failure of the second Siege of Vienna (1683) the Holy League had captured large parts of the Empire's territory in Europe. The Habsburg armies came as far as Niš, modern-day Serbia, before being pushed back across the Danube by 1690. Sultan Mustafa II was determined to recapture the lost territories in Hungary and therefore he personally commanded his armies.
Capture of Chios
First, the Ottoman navy recaptured the island of Chios after defeating the Venetian Fleet twice, in the Battle of the Oinousses Islands (1695) and in the Battle of Chios (1695), in February 1695.[8][9] In June 1695, Mustafa II left Edirne for his first military campaign against the Habsburg Empire. By September 1695 the town of Lipova was captured. On 18 September 1695 the Venetian Navy was again defeated in the naval victory of Zeytinburnu. A few days later the Habsburg army was defeated in the Battle of Lugos. Afterwards the Ottoman Army returned to the capital. Meanwhile, the Ottoman fortress in Azov was successfully defended against the besieging Russian forces.[8]
As Mustafa attempted to realize his thoughts quickly, the island of Chios, which had previously fallen into the hands of the Venetians, was taken back at that time, the Crimean Tatars Shahbaz Giray entered the territory of Poland and proceeded to Lemberg, and returned with many captives and booty. There were reports that the Venetians were influenced by the Ottoman forces on the Herzegovina front in Peloponnese. Especially the recovery of Chios was considered auspicious and was celebrated with great festivities in Edirne. Meanwhile, the tips of the people were distributed to the locals. [10]
Habsburg wars
In April 1696 Mustafa II left Edirne for his second military campaign against the Habsburg Empire. In August 1696 the Russians besieged Azov for the second time and captured the fortress. In August 1696 the Ottoman troops defeated the Habsburg army in the Battle of Ulaş and in the Battle of Cenei. After these victories the Ottoman troops captured Timișoara and Koca Cafer Pasha was appointed as the protector of Belgrade. Afterwards the army returned to the Ottoman capital.[8]
In June 1697 Mustafa II left the capital on his third military campaign against the Habsburg Empire. However, the Ottoman Army suffered a defeat in the Battle of Zenta and Grand Vizier Elmas Mehmed Pasha died in the battle. Afterwards the Ottomans signed a treaty with the Holy League.[8]
The most traumatic event of his reign was the loss of Hungary by the Treaty of Karlowitz in 1699.
Yet even if Ottoman power seemed to wane on one side of the empire, this did not mean that Ottoman efforts at expansion ceased. In 1700, for example, the Grand Vizier Amcazade Hüseyin boasted to a recalcitrant tribe residing in swamps near Baghdad that they ought to abide by the sultan's rule, since his grasp extended even to their marshy redoubts. The Grand Vizier added that, after all, Mustafa II was "the Lord of Water and Mud."[11]
At the end of his reign, Mustafa II sought to restore power to the Sultanate, which had been an increasingly symbolic position since the middle of the 17th century, when Mehmed IV had signed over his executive powers to the Grand Vizier. Mustafa II's strategy was to create an alternative base of power for himself by making the position of timars, the Ottoman cavalrymen, hereditary and thus loyal to him. The timars, however, were at this point increasingly an obsolete part of the Ottoman military machine.
Deposition
The strategem failed, the disaffected troops bound to a Georgian campaign mutinied in the capital (called the "Edirne event" by historians), and Mustafa was deposed on 22 August 1703.
Character
Define as red beard, short neck, medium height and majestic. Mustafa II has a miniature made by Levni. After 1699, like his father, he was interested in hunting and entertainment, engaged in literature and wrote poems with the pseudonym. A curiosity of this sultan, who had lines in the style of Celi, Nesih and Sulus was archery. Silahdar Findiklili Mehmed Agha, who was assigned to write the history of his period. He described Mustafa's reign in his book Nusretname. [12]
Family
- Consorts
- Alicenab Kadın (died 20 April 1699, Edirne Palace, Edirne, buried in Darülhadis Mosque);[13]
- Saliha Sultan[13] (died 21 September 1739, Tırnakçı Palace, Istanbul, buried in Turhan Sultan Mausoleum, New Mosque);
- Şehsuvar Sultan[13] (died 27 April 1756, Topkapı Palace, Istanbul, buried in Nuruosmaniye Mosque);
- Afife Kadın;[13]
- Bahtiyar Kadın;[13]
- Ivaz Kadın;[13]
- Şahin Kadın;[14][13]
- Sons
- Mahmud I (2 August 1696 – 13 December 1754), son with Saliha Sultan;[13]
- Şehzade Suleiman (25 December 1697 – 25 December 1697, Edirne Palace, Edirne, buried in New Mosque), son with Afife Kadın;[13]
- Şehzade Mehmed (22 November 1698 – 5 June 1703, Edirne Palace, Edirne, buried in New Mosque), son with Afife Kadın;[13]
- Osman III (2/3 January 1699 – 30 October 1757), son with Şehsuvar Sultan;[13]
- Şehzade Hasan (16 April 1699 – 25 May 1733), became heir apparent from 1730. [13]
- Şehzade Hüseyn (7 May 1699 – 24 August 1700, Edirne Palace, Edirne, buried in New Mosque);
- Şehzade Selim (16 May 1700 – 8 June 1701, Edirne Palace, Edirne, buried in New Mosque), son with Afife Kadın;[13]
- Şehzade Ahmed (3 March 1703 – 7 September 1703, Edirne Palace, Edirne, buried in Darülhadis Mosque), son with Afife Kadın;[13]
- Daughters
- Ayşe Sultan (30 April 1696 – 26 September 1752, Istanbul, buried in New Mosque);
- Emine Sultan (1 September 1696 – c. 1739, Istanbul, buried in New Mosque);
- Safiye Sultan (13 December 1696 – 15 May 1778, Istanbul, buried in New Mosque);
- Rukiye Sultan (13 November 1697 – 28 March 1698, Edirne Palace, Edirne, buried in Darülhadis Mosque);
- Hatice Sultan (14 February 1698 – died young, Edirne Palace, Edirne, buried in Darülhadis Mosque);
- Fatma Sultan (8 October 1699 – 20 May 1700, Istanbul, buried in New Mosque);
- Ismihan Sultan (23 April 1700 – 1 June 1700);
- Ümmügülsüm Sultan (10 June 1700 – 1 May 1701, Edirne Palace, Edirne, buried in Darülhadis Mosque);
- Zeyneb Sultan (10 June 1700 – 18 December 1705, Istanbul, buried in New Mosque);
- Emetullah Sultan (22 June 1701 – 12 April 1727, Istanbul, buried in New Mosque);
Death
After the new sultan's return to Istanbul, after the Edirne Foundation and the state official. Mustafa and his princes were brought to Istanbul in the Topkapı Palace they were locked up in the Kafes. Mustafa's cage life lasted four months. He died of either sadness or an unknown cause on 29 December 1703. He was buried next to his grandmother, Turhan Hatice Sultan, in the New Mosque, Eminönü, Istanbul, Turkey. [12]
References
- Baker, Anthony E (1993). The Bosphorus. Redhouse Press. p. 146. ISBN 975-413-062-0.
The Valide Sultan was born Evmania Voria, daughter of a Greek priest in a village near Rethymnon on Crete. She was captured by the Turks when they took Rethymnon in 1645.
- Bromley, J. S. (1957). The New Cambridge Modern History. University of California: University Press. p. 554. ISBN 0-521-22128-5.
the mother of Mustafa II and Ahmed III was a Cretan
- Sardo, Eugenio Lo (1999). Tra greci e turchi: fonti diplomatiche italiane sul Settecento ottomano. Consiglio nazionale delle ricerche. p. 82. ISBN 88-8080-014-0.
Their mother, a Cretan, lady named Rabia Gulnus, continued to wield influence as the Walide Sultan - mother of the reigning sultan
- Library Information and Research Service (2005). The Middle East. Library Information and Research Service. p. 91.
She was the daughter of a Cretan (Greek) family and she was the mother of Mustafa II (1664–1703), and Ahmed III (1673–1736).
- Sakaoğlu 2015, p. 285.
- Uluçay 2011, p. 110.
- Sakaoğlu 2015, p. 286.
- Bilgi
- Somel, Selcuk Aksin (13 February 2003). Historical Dictionary of the Ottoman Empire. Scarecrow Press, 2003. p. XIIV chronology. ISBN 0810866064.
- "MUSTAFA II مصطفی (ö. 1115/1703) Osmanlı padişahı (1695-1703)". İslam Ansiklopedisi. Retrieved 12 April 2020.
- Husain, Faisal (October 2014). "In the Bellies of the Marshes: Water and Power in the Countryside of Ottoman Baghdad". Environmental History. 19 (4): 638–664. doi:10.1093/envhis/emu067.
- Sakaoğlu 2015, p. 294.
- Majer, Hans Georg (1992). Osmanlı Araştırmaları XII (The Journal of Ottoman Studies XII): The harem of Mustafa II (1695–1703). pp. 435–7, 438.
- Çalık, Sıddık (1993). 1108 Numaralı Harc-ı Hassa Defterinin Transkripsiyonu ve Değerlendirmesi. pp. 278–79.
Sources
- Abou-El-Haj, R. A. (1974). "The Narcissism of Mustafa II (1695–1703): A Psychohistorical Study". Studia Islamica (40): 115–131. doi:10.2307/1595336. JSTOR 1595336.
- Sakaoğlu, Necdet (2015). Bu Mülkün Sultanları. Alfa Yayıncılık. ISBN 978-6-051-71080-8.
- Uluçay, Mustafa Çağatay (2011). Padişahların kadınları ve kızları. Ankara: Ötüken. ISBN 978-9-754-37840-5.
External links
 Media related to Mustafa II at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Mustafa II at Wikimedia Commons
Mustafa II Born: February 6, 1664 Died: December 29, 1703[aged 39] | ||
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Ahmed II |
Sultan of the Ottoman Empire Feb 6, 1695 – August 22, 1703 |
Succeeded by Ahmed III |
| Sunni Islam titles | ||
| Preceded by Ahmed II |
Caliph of the Ottoman Caliphate Feb 6, 1695 – August 22, 1703 |
Succeeded by Ahmed III |

.svg.png.webp)
