Names of India in its official languages
India has many official names, expressing its linguistic diversity. Hindi in the Devanagari script is the sole official language of India as per Article 343 of the Constitution of India and there is no national language for the country.[1][2] English has the status of a "subsidiary official language".[1][3] Hindi romanisation uses Hunterian transliteration, which is the "national system of romanisation in India" and the one officially used by the Government of India. It takes into account the rules of schwa deletion in Indo-Aryan languages. The Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution lists 22 languages,[4] which have been referred to as scheduled languages and given recognition, status, and official encouragement.
| Part of a series on the |
| Constitution of India |
|---|
 |
| Preamble |
Hindi and English
| Language | Official short form | Official full form | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hindi (official) |
Devanagari | भारत | भारत गणराज्य |
| Hunterian transliteration | Bhārat | Bhārat Gaṇrājya | |
| English (subsidiary official) | India | Republic of India | |
Eighth Schedule Languages
| Language | Official short name for India [upper-alpha 1] | Official full name for The Republic of India [upper-alpha 1] | Details | "Republic (of)" | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Official Name | Script Name [upper-alpha 2] | Indian script [upper-alpha 3] | Transliteration | Indian script | Transliteration or IPA | Transliteration system shown | Dialect details or script status | Indian script | Transliteration or IPA |
| Assamese | Bengali‑Assamese | ভাৰত | Bhārôt | ভাৰত গণৰাজ্য | Bhārôt Gônôrāzyô | গণৰাজ্য | Gônôrāzyô | ||
| Bengali | Bengali‑Assamese | ভারত | Bhārot | ভারতীয় প্রজাতন্ত্র | Bhārotiyo Projātôntro | প্রজাতন্ত্র | Projātôntro | ||
| Bodo | Devanagari | भारत | Bhārôt | भारत गणराज्य | Bhārôt Gônôrājyô | गणराज्य | Gônôrājyô | ||
| Dogri | Devanagari | भारत | Bhārat | भारत गणराज्य | Bhārat Ganrājya | गणराज्य | Ganrājya | ||
| Gujarati | Gujarati | ભારત | Bhārat | ભારતીય ગણતંત્ર | Bhārtiya Gaṇtāntrā | ISO 15919 | ગણતંત્ર | Gaṇtāntrā | |
| Hindi | Devanagari | भारत | Bhārat | भारत गणराज्य | Bhārat Ganrājya | Hunterian | गणराज्य | Ganrājya | |
| Kannada | Kannada | ಭಾರತ | Bhārata | ಭಾರತ ಗಣರಾಜ್ಯ | Bhārata Gaṇarājya | ISO 15919 | ಗಣರಾಜ್ಯ | Gaṇarājya | |
| Kashmiri | Perso‑Arabic in the Nasta'liq style | ہِنٛدوستان | Hindōstān | جۆمہوٗرِیَہ ہِنٛدوستان | Jomhūriyah Hindōstān | shown on bank notes | جۆمہوٗرِیَہ | Jomhūriyah | |
| Konkani | Devanagari | भारत | Bharot | भारत गणराज्य | Bhārat Gaṇrājya | गणराज्य | Gaṇrājya | ||
| Maithili | Devanagari | भारत | Bhārat | भारत गणराज्य | Bhārat Gaṇarājya | गणराज्य | Gaṇarājya | ||
| /bʱaːrət̪ᵊ gɐɳᵊraːd͡ʑjə/ | IPA | /gɐɳᵊraːd͡ʑjə/ | |||||||
| Malayalam | Malayalam | ഭാരതം | Bhāratam | ഭാരതമഹാരാജ്യം | Bhāratamahārājyam | ISO 15919 | മഹാരാജ്യം | Mahārājyam | |
| Marathi | Devanagari in the Balbodh style | भारत | Bhārat | भारतीय प्रजासत्ताक | Bhārtīya Prajāsattāk | प्रजासत्ताक | Prajāsattāk | ||
| Meitei (Manipuri) | Bengali‑Assamese | ভারত | Bharôt | ভারত গণরাজ্য | Bharôt Gôṇôrajyô | গণরাজ্য | Gôṇôrajyô | ||
| Meitei script | ꯏꯟꯗꯤꯌꯥ [upper-alpha 4] | Indiyā | |||||||
| Nepali | Devanagari | भारत | Bhārat | गणतन्त्र भारत | Gaṇatantra Bhārat | गणतन्त्र | Gaṇatantra | ||
| Odia | Odia | ଭାରତ | Bhārata | ଭାରତ ଗଣରାଜ୍ୟ | Bhārata Gaṇarājya | ଗଣରାଜ୍ୟ | Gaṇarājya | ||
| Punjabi | Gurmukhi | ਭਾਰਤ | Bhārat | ਭਾਰਤ ਗਣਰਾਜ | Bhārat Gaṇrāj | Perso-Arabic script is used for Pakistani dialects but has no official status in India. | ਗਣਰਾਜ | Gaṇrāj | |
| Sanskrit | Devanagari | भारतम् | Bhāratam | भारतमहाराज्यम् | Bhāratamahārājyam | ||||
| Santali | Ol Chiki | ᱥᱤᱧᱚᱛ [upper-alpha 5] | Siñôt | ᱥᱤᱧᱚᱛ ᱨᱮᱱᱟᱜ ᱟᱹᱯᱱᱟᱹᱛ | Siñôt Renāg Ăpnăt | Mahali is a dialect of Santali.[5] | ᱨᱮᱱᱟᱜ ᱟᱹᱯᱱᱟᱹᱛ | Renāg Ăpnăt | |
| Devanagari | भारोत[6] | Bharot | |||||||
| Sindhi | Devanagari | भारत | Bhārat | भारत गणतन्त्र | Bhārat Gaṇtantra | गणतन्त्र | Gaṇtāntrā | ||
| Perso‑Arabic | ڀارت | جمھوريا ڀارت | Jamhūriyā Bhārat | جمھوريا | Jamhūriyā | ||||
| Tamil | Tamil | இந்தியா | Indhiyā | இந்தியக் குடியரசு | Indhiyā Kudiyarasu | குடியரசு | Kudiyarasu | ||
| Telugu | Telugu | భారత | Bhārata | భారత గణతంత్ర రాజ్యము | Bhāratha Gaṇathanthra Rājyamu | ISO 15919 | గణతంత్ర రాజ్యము | Gaṇathanthra Rājyamu | |
| Urdu | Perso‑Arabic in the Nasta'liq style | بھارت | Bhārat | جمہوریہ بھارت | Jamhūriyah Bhārat | جمہوریہ (Naskh) جمہوریہ (Nastaliq) |
Jamhūriyah | ||
- Footnotes:
- Colours: the names are colour-coded by similarity.
- Official writing system(s) or script(s) are shown first for each language. (If they don't display on your device, most are available for Windows in the Microsoft font family Nirmala UI, or for all systems in the free fonts from Google's Noto fonts.)
- The short names link to the Wikipedia page about India in that language if available.
- Image of the text in the font Noto Sans Meetei Mayek. The script is also available in the Microsoft font family Nirmala UI.
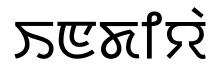 "Indiyā" ꯏꯟꯗꯤꯌꯥ in Meitei script.
"Indiyā" ꯏꯟꯗꯤꯌꯥ in Meitei script. - Image of the text in the font Noto Sans Ol Chiki. The script is also available in the Microsoft font family Nirmala UI.
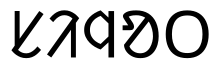 "Siñôt" ᱥᱤᱧᱚᱛ in Ol Chiki script.
"Siñôt" ᱥᱤᱧᱚᱛ in Ol Chiki script.
See also
References
- "Constitution of India". Archived from the original on 2 April 2012. Retrieved 21 March 2012.
- "Department of official Language | Government of India". Archived from the original on 1 October 2014.
- Salzmann, Zdenek; Stanlaw, James; Adachi, Nobuko (8 July 2014). Language, Culture, and Society: An Introduction to Linguistic Anthropology. Westview Press. ISBN 9780813349558 – via Google Books.
- Languages Included in the Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constution Archived 2016-06-04 at the Wayback Machine
- "Glottolog 4.2.1 - Mahali (Santali)". glottolog.org. Retrieved 5 June 2020.
- "Internationalized Domain Names (IDNs) | Registry.In". www.registry.in. Retrieved 22 March 2020.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.