Nelson and Fort Sheppard Railway
The Nelson and Fort Sheppard Railway (N&FS) is a historic railway that operated in the West Kootenay region of southern British Columbia. The railway's name derived from a misspelling of Fort Shepherd, a former Hudson's Bay Company fort, on the west bank of the Columbia River immediately north of the border.
The N&FS connected the city of Nelson with the Canada–United States border at Waneta.
Incursion into BC
In 1890, Daniel Chase Corbin, an American financier, built his Spokane Falls and Northern Railway (SF&N) north to Little Dalles, served by the northern routes of the Columbia and Kootenay Steam Navigation Company (C&KSN). In 1891, the Canadian Pacific Railway (CP) hoped to head off the American incursion into the rich mining areas of the West Kootenay, by opening the Columbia and Kootenay Railway (C&K). This line ran between Robson (near Castlegar) and Nelson, along the unnavigable section of the Kootenay River linking Kootenay Lake and the Arrow Lakes.
The BC government was unsympathetic to any proposal that was merely a feeder for US railroads. Using Canadian businessmen as a front, and promising to connect the railway to the coast, Corbin obtained a provincial charter for the N&FS in 1891.[1] This act made the $750,000 CP investment in the C&K of little value, until further CP expansion began in 1898. In 1893, the N&FS received a federal charter,[2] declaring it to be a work for the greater advantage of Canada.[3] The connection to the coast was never built but the railway reached Nelson in 1893. With an all-rail route to the United States and links to American transcontinental railroads, the N&FS offered better market access than CP.[4]
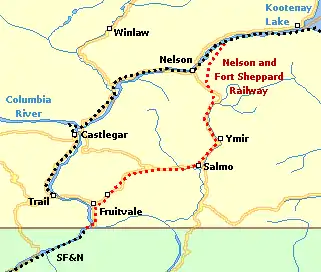
Route
From south to north, the railway joined the SF&N on the east shore of the Columbia River at the US border, and crossed a 500-foot bridge over the Pend-d'Oreille River at Waneta, since repurposed as a highway crossing. The railway ascended the Columbia Valley, the Salmo River valley, and descended to the northeast of Nelson to Troup (also known as Five Mile Point), which became the temporary terminus until 1894.[5][6][4][7]
Nelson train stations
Mountain station was in the current parking area at the south end of Cherry St.[8]
In 1895, a rail loop at Troup, enabled the line to reverse direction, border the west arm of the lake, and terminate by the Cottonwood St. and Maple St. intersection, at what was then Bogustown (now Fairview).[4][8]
In December 1899, the inaugural streetcar (tram) ran southwestward from a terminus at the adjacent Cottonwood St. and First St. intersection to the then Railway St. and Baker St. intersection (now BC Highway 3A)/Baker St.), which served the C&K station at the former foot of Railway.[9] In April 1900, the tramway hill section commenced. This line turned from Kootenay St. northeastward into Houston St, terminating at the Stanley St. intersection,[10] requiring a 0.9-kilometre (0.6 mi) walk from the closest point to the N&FS Mountain station.
To create the Nelson–Procter spur in 1900, CP bought the Nelson–Troup right-of-way from N&FS, which received trackage rights on this section.[4]
In January 1901, on the opening of the new CP C&K station (now the visitor centre), two blocks southwest of the former station, the N&FS terminal moved from Bogustown to share this facility, and the tramway was extended along the Baker St. alignment adjacent to this point. That same day, the final part of the hill route changed, turning northeastward on Observatory St. and south eastward on Stanley St. to the previous terminus.[11] The new CP station became the northwestern terminus for this route. However, from May 1901, unless requested by a passenger, or meeting the 11:35 am or 10:10 pm trains, the tramway terminus became Stanley/Baker streets.[12] In 1902, the tramway extension to the station was abandoned, which was likely the time that the two tramway routes were combined into a single through route.[8]
In November 1910, the final part of the hill section reopened as a loop. Uphill was Stanley St, Latimer St, Hendryx St, Carbonate St, Cedar St, and Innes St, with the downhill return unchanged. The amended route offered a short 0.2-kilometre (0.12 mi) walk from the closest point to the N&FS Mountain station.[13] When the tramway ceased in June 1949, the replacement bus route appears to have been no closer than Josephine St. to this station.[14]
All train stations
| Stations | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1893[15] | Mile | 1905[16] | Mile | 1907[17] | 1913[18] | Mile | 1922[19] | Mile | 1928[20] | Mile | 1933[21] | Mile | 1956[22] |
| Waneta | 140.3 | Waneta | 39.1 | Waneta | Waneta | 39.3 | Waneta | 39.4 | Waneta | 39.4 | Waneta | 126.2 | Waneta |
| 144.2 | Sayward | 43.0 | Sayward | Col. Gdns. | 43.2 | Col. Gdns. | 43.3 | Col. Gdns. | 43.3 | Col. Gdns. | 130.0 | Col. Gdns. | |
| Beaver | 149.5 | Beaver | 48.3 | Fruitvale | Fruitvale | 48.5 | Fruitvale | 48.6 | Fruitvale | 48.6 | Fruitvale | 135.3 | Fruitvale |
| 54.2 | Parks | 140.9 | Parks | ||||||||||
| Meadows | 58.1 | Meadows | 58.3 | Meadows | 58.3 | Meadows | 145.0 | Meadows | |||||
| 162.0 | Erie | 60.8 | Erie | Erie | 61.1 | Erie | 61.1 | Erie | 61.1 | Erie | 147.9 | Erie | |
| Salmon | 164.8 | Salmo | 63.6 | Salmo | Salmo | 63.8 | Salmo | 63.9 | Salmo | 63.9 | Salmo | 150.6 | Salmo |
| 67.0 | Boulder Mill | 67.2 | Boulder Mill | 67.2 | Boulder Mill | 153.9 | Boulder Mill | ||||||
| 172.4 | Ymir | 71.2 | Ymir | Ymir | 71.4 | Ymir | 71.5 | Ymir | 71.5 | Ymir | 158.3 | Ymir | |
| Hall | 179.6 | Hall | 78.4 | Hall | Hall | 78.6 | Hall | 78.6 | Hall | 78.6 | Hall | 165.4 | Hall |
| Summit | 182.9 | Summit | 81.7 | Summit | Apex | 81.9 | Apex | 82.0 | Apex | 82.0 | Apex | 168.7 | Apex |
| Nelson | 189.6 | Mountain | 88.4 | Mountain | Mountain | 88.7 | Mountain | 88.8 | S. Nelson | 88.8 | S. Nelson | 175.5 | S. Nelson |
| Kootenay | 194.5 | Troup Jctn. | 93.3 | Troup Jctn. | Troup Jctn. | 93.5 | Troup Jctn. | 93.6 | Troup Jctn. | 93.6 | Troup Jctn. | 180.3 | Troup Jctn. |
| 200.0 | Nelson | 98.8 | Nelson | Nelson | 98.1 | Nelson | 99.0 | Nelson | 99.0 | Nelson | 185.8 | Nelson | |
About 1961, passenger train service ceased, leaving only Greyhound bus travel via Trail, which followed a completely different route.[23][24]
Operators & abandonment
On July 1, 1898, the Northern Pacific Railway (NP) acquired the SF&N. On June 30 1899, the Great Northern Railway (GN) purchased the NP stock.[25] The GN was consolidated into the Burlington Northern Railroad (BN) in 1970, which merged to become the Burlington Northern and Santa Fe Railway (BNSF) in 1996.
The track was gradually abandoned south from Nelson to Salmo during the 1990s. Forest products are the only significant traffic on the line.[4]
The abandoned section from Salmo to the west arm has been acquired by the provincial government and converted to the Salmo-Troup Rail Trail.
In 2019, the St. Paul & Pacific Northwest Railroad Company assumed operation from OmniTRAX of the track north to Columbia Gardens.[26]
Footnotes
- An Act to incorporate the Nelson and Fort Sheppard Railway Company, SBC 1891, c. 58.
- Canadian Pacific , p. 77, at Google Books
- An Act respecting the Nelson and Fort Sheppard Railway Company, SC 1893, c. 57
- "Great Northern Rail Trail". www.ronperrier.net.
- "The Daily Colonist, 22 Nov 1893". www.archive.org. p. 2.
- "The Daily Colonist, 23 Dec 1893". www.archive.org. p. 1.
- "Fruitvale". www.crowsnest-highway.ca.
- Parker 1992, p. 30.
- Parker 1992, p. 34.
- Parker 1992, p. 41.
- Parker 1992, pp. 30, 47.
- Parker 1992, p. 48.
- Parker 1992, pp. 64, 73–75.
- Parker 1992, pp. 120–122.
- "Nelson Star, 18 Jan 2015". www.nelsonstar.com.
- "1905 timetable" (PDF). www.gn-npjointarchive.org. p. 2.
- "1907 timetable" (PDF). www.gn-npjointarchive.org. p. 3.
- "1913 timetable" (PDF). www.gn-npjointarchive.org. p. 3.
- "1922 timetable" (PDF). www.gn-npjointarchive.org. p. 9.
- "1928 timetable" (PDF). www.gn-npjointarchive.org. p. 5.
- "1933 timetable" (PDF). www.gn-npjointarchive.org. p. 5.
- "1956 timetable" (PDF). www.gn-npjointarchive.org. p. 7.
- "1960 timetable" (PDF). www.streamlinermemories.info. p. 25 (Table 70).
- "1962 timetable" (PDF). www.streamlinermemories.info. p. 17 (Table 25).
- Spokane Falls and Northern Railway , p. 280, at Google Books
- "Railway Age, 11 Dec 2018". www.railwayage.com.
References
- Parker, Douglas V. (1992). Streetcars in the Kootenays: Nelson's Tramways, 1899–1992. Havelock House. ISBN 0-920805-02-7.