Oxyrhynchus
Oxyrhynchus (/ɒksɪˈrɪŋkəs/; Greek: Ὀξύρρυγχος, translit. Oxýrrhynchos, lit. "sharp-nosed"; ancient Egyptian Pr-Medjed; Coptic: ⲡⲉⲙϫⲉ or ⲡⲙ̅ϫⲏ, romanized: Pemdje[1][2]; Egyptian Arabic: البهنسا, romanized: el-Bahnasa) is a city in Middle Egypt located about 160 km south-southwest of Cairo in Minya Governorate. It is also an archaeological site, considered one of the most important ever discovered. Since the late 19th century, the area around Oxyrhynchus has been excavated almost continually, yielding an enormous collection of papyrus texts dating from the Ptolemaic Kingdom and Roman Egypt. Among the texts discovered at Oxyrhynchus are plays of Menander, fragments from the Gospel of Thomas, and fragments from Euclid's Elements. They also include a few vellum manuscripts, and more recent Arabic manuscripts on paper (for example, the medieval P. Oxy. VI 1006[3]).
Oxyrhynchus
البهنسا | |
|---|---|
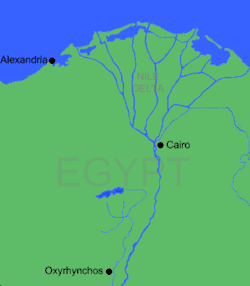 Location of Oxyrhynchus in Egypt | |
 Oxyrhynchus | |
| Coordinates: 28.531°N 30.647°E | |
| Country | |
| Governorate | Minya |
| Time zone | UTC+2 (EST) |
History

Ancient Egyptian Era
| pr mjḏ[1] in hieroglyphs |
|---|
| pr mꜣḏꜣ[2] in hieroglyphs |
|---|
Oxyrhynchus lies west of the main course of the Nile on the Bahr Yussef, a branch that terminates in Lake Moeris and the Faiyum oasis. In ancient Egyptian times, there was a city on the site called Per-Medjed,[4] named after the medjed, a species of elephantfish of the Nile worshipped there as the fish that ate the penis of Osiris. It was the capital of the 19th Upper Egyptian Nome.
Ptolemaic Era

After the conquest of Egypt by Alexander the Great in 332 BC, the city was reestablished as a Hellenistic town called Oxyrrhynchoupolis (Koinē Greek: Ὀξυρρύγχου Πόλις, lit. 'town of the sharp-snouted fish'). In the Hellenistic period, Oxyrhynchus was a prosperous regional capital, the third-largest city in Egypt. After Egypt was Christianized, it became famous for its many churches and monasteries.[4]
Roman Era
Oxyrhynchus remained a prominent, though gradually declining, town in the Roman and Byzantine periods. From 619 to 629, during the brief period of Sasanian Egypt, three Greek papyri from Oxyrhynchus include references to large sums of gold that were to be sent to the emperor.[5]
Arab Era
After the Muslim conquest of Egypt in 641, the canal system on which the town depended fell into disrepair, and Oxyrhynchus was abandoned. Today the town of el Bahnasa occupies part of the ancient site. Bahnasa is known for having 5,000 Sahaba buried in it following several major battles against the Roman army and fortifications.
For more than 1000 years, the inhabitants of Bahnasa dumped garbage at a series of sites out in the desert sands beyond the town limits. The fact that the town was built on a canal rather than on the Nile itself was important, because this meant that the area did not flood every year with the rising of the river, as did the districts along the riverbank. When the canals dried up, the water table fell and never rose again. The area west of the Nile has virtually no rain, so the garbage dumps of Oxyrhynchus were gradually covered with sand and were forgotten for another 1000 years.
Because Egyptian society under the Greeks and Romans was governed bureaucratically, and because Oxyrhynchus was the capital of the 19th nome, the material at the Oxyrhynchus dumps included vast amounts of papyri. Accounts, tax returns, census material, invoices, receipts, correspondence on administrative, military, religious, economic, and political matters, certificates and licenses of all kinds—all these were periodically cleaned out of government offices, put in wicker baskets, and dumped out in the desert. Private citizens added their own piles of unwanted papyri. Because papyrus was expensive, papyri were often reused: a document might have farm accounts on one side, and a student's text of Homer on the other. The Oxyrhynchus Papyri, therefore, contained a complete record of the life of the town, and of the civilizations and empires of which the town was a part.
The town site of Oxyrhynchus itself has never been excavated, because the modern Egyptian town is built on top of it, but it is believed that the city had many public buildings, including a theatre with a capacity of 11,000 spectators, a hippodrome, four public baths, a gymnasium, and two small ports on the Bahr Yussef. It is also likely that there were military buildings, such as barracks, since the city supported a military garrison on several occasions during the Roman and Byzantine periods. During the Greek and Roman periods, Oxyrhynchus had temples to Serapis, Zeus-Amun, Hera-Isis, Atargatis-Bethnnis and Osiris. There were also Greek temples to Demeter, Dionysus, Hermes, and Apollo; as well as Roman temples to Jupiter Capitolinus and Mars. In the Christian era, Oxyrhynchus was the seat of a bishopric, and the modern town still has several ancient Coptic Christian churches.
When Flinders Petrie visited Oxyrhynchus in 1922, he found remains of the colonnades and theatre. Now only part of a single column remains: everything else has been scavenged for building material for modern housing.[6]
Excavation
In 1882, Egypt, while still nominally part of the Ottoman Empire, came under effective British rule, and British archaeologists began the systematic exploration of the country. Because Oxyrhynchus was not considered an Ancient Egyptian site of any importance, it was neglected until 1896, when two young excavators, Bernard Pyne Grenfell and Arthur Surridge Hunt, both fellows of The Queen's College, Oxford, began to excavate it. "My first impressions on examining the site were not very favourable," wrote Grenfell. "The rubbish mounds were nothing but rubbish mounds."[7] However, they very soon realized what they had found. The unique combination of climate and circumstance had left at Oxyrhynchus an unequalled archive of the ancient world. "The flow of papyri soon became a torrent," Grenfell recalled. "Merely turning up the soil with one's boot would frequently disclose a layer."[8]
Being classically educated Englishmen, Grenfell and Hunt were mainly interested in the possibility that Oxyrhynchus might reveal the lost masterpieces of classical Greek literature. They knew, for example, that the Constitution of Athens by Aristotle had been discovered on Egyptian papyrus in 1890. This hope inspired them and their successors to sift through the mountains of rubbish at Oxyrhynchus for the next century. Their efforts were amply rewarded: it has been estimated that over 70% of all the literary papyri so far discovered come from Oxyrhynchus, both copies of well-known standard works (many in versions significantly closer to the originals than those that had been transmitted in medieval manuscripts) and previously unknown works by the greatest authors of antiquity.
However, from the many thousands of papyri excavated from Oxyrhynchus, only about 10% were literary. The rest consisted of public and private documents: codes, edicts, registers, official correspondence, census-returns, tax-assessments, petitions, court-records, sales, leases, wills, bills, accounts, inventories, horoscopes, and private letters. Still, Grenfell and Hunt found enough texts of more general interest to keep them going in the hope of finding more. In their first year of digging alone, they found parts of several lost plays of Sophocles, such as the Ichneutae and many other books and fragments, including parts of what appeared to be an unknown Christian gospel. These discoveries captured the public imagination, and Grenfell and Hunt sent articles and photos to newspapers in Britain, arguing the importance of their work and seeking donations to keep it going.
Aside from the years of World War I, Grenfell and Hunt devoted their lives to work on the material from Oxyrhynchus. For ten years, from 1896 to 1906, every winter, when the Egyptian climate was mild, Grenfell and Hunt supervised hundreds of Egyptian workers, excavating the rubbish mounds, digging up tightly packed layers of papyrus mixed with earth. The finds were sifted, partially cleaned and then shipped to Grenfell and Hunt's base at Oxford. During the summer, Grenfell and Hunt cleaned, sorted, translated and compared the year's haul, assembling complete texts from dozens of fragments and extracts. In 1898, they published the first volume of their finds. They worked closely together, each revising what the other wrote, and publishing the result jointly. In 1926, however, Grenfell died, leaving Hunt to continue the work with other collaborators until his own death in 1934. Meanwhile, Italian excavators had returned to the site: their work, from 1910 to 1934, brought to light many further papyri, including additional pieces of papyrus rolls of which parts had already been discovered by Grenfell and Hunt.
In May 2020, an Egyptian-Spanish archaeological mission headed by Esther Ponce revealed a unique cemetery consisting of one room built with glazed limestone dating back to the 26th Dynasty (so-called the El-Sawi era). Archaeologists also uncovered bronze coins, clay seals, Roman tombstones and small crosses.[9][10][11]
Finds
Although the hope of finding all the lost literary works of antiquity at Oxyrhynchus was not realized, many important Greek texts were found at the site. These include poems of Pindar, fragments of Sappho and Alcaeus, along with larger pieces of Alcman, Ibycus, and Corinna.
There were also extensive remains of the Hypsipyle of Euripides, fragments of the comedies of Menander, and a large part of the Ichneutae of Sophocles.[12] Also found were the oldest and most complete diagrams from Euclid's Elements. Another important find was the historical work known as the Hellenica Oxyrhynchia, whose author is unknown but may be Ephorus or, as many currently think, Cratippus. A life of Euripides by Satyrus the Peripatetic was also unearthed, while an epitome of seven of the 107 lost books of Livy was the most important literary find in Latin.
The classical author who has most benefited from the finds at Oxyrhynchus is the Athenian playwright Menander (342–291 BC), whose comedies were very popular in Hellenistic times and whose works are frequently found in papyrus fragments. Menander's plays found in fragments at Oxyrhynchus include Misoumenos, Dis Exapaton, Epitrepontes, Karchedonios, Dyskolos and Kolax. The works found at Oxyrhynchus have greatly raised Menander's status among classicists and scholars of Greek theatre.
Among the Christian texts found at Oxyrhynchus, were fragments of early non-canonical Gospels, Oxyrhynchus 840 (3rd century AD) and Oxyrhynchus 1224 (4th century AD). Other Oxyrhynchus texts preserve parts of Matthew chapter 1 (3rd century: P2 and P401), 11–12 and 19 (3rd to 4th century: P2384, 2385); Mark chapters 10–11 (5th to 6th century: P3); John chapter 1, and 20 (3rd century: P208); Romans chapter 1 (4th century: P209); the First Epistle of John (4th-5th century: P402); the 3 Baruch (chapters 12–14; 4th or 5th century: P403); the Gospel of the Hebrews (3rd century AD: P655); The Shepherd of Hermas (3rd or 4th century: P404), and a work of Irenaeus, (3rd century: P405). There are many parts of other canonical books as well as many early Christian hymns, prayers, and letters also found among them.
There is an on-line table of contents briefly listing the type of contents of each papyrus or fragment.[13]
Today


Since the 1930s, work on the papyri has continued. For many years it was under the supervision of Professor Peter Parsons of Oxford. Eighty large volumes of the Oxyrhynchus Papyri have been published,[16][17] and these have become an essential reference work for the study of Egypt between the 4th century BC and the 7th century AD. They are also extremely important for the history of the early Christian Church, since many Christian documents have been found at Oxyrhynchus in far earlier versions than those known elsewhere. At least another forty volumes are anticipated.
Since the days of Grenfell and Hunt, the focus of attention at Oxyrhynchus has shifted. Modern archaeologists are less interested in finding the lost plays of Aeschylus, although some still dig in hope, and more in learning about the social, economic, and political life of the ancient world. This shift in emphasis had made Oxyrhynchus, if anything, even more important, for the very ordinariness of most of its preserved documents makes them most valuable for modern scholars of social history. Many works on Egyptian and Roman social and economic history and on the history of Christianity rely heavily on documents from Oxyrhynchus.
In 1966, the publication of the papyri was formally adopted as a Major Research Project of the British Academy, jointly managed by Oxford University and University College London and headed by Parsons. The project's chief researcher and administrator is Dr Nikolaos Gonis. The Academy provided funding until 1999; the project then enjoyed a grant from the Arts and Humanities Research Board, which funded ongoing work until 2005. Today some 100,000 papyrus fragments are housed at the Sackler Library, Oxford, with their indexes, archives and photographic record; it is the biggest hoard of classical manuscripts in the world. About 2,000 items are mounted in glass — the rest are conserved in 800 boxes.
The focus of the project is now mainly on the publication of this vast archive of material: by 2003 4,700 items had been translated, edited and published. Publication continues at the rate of about one new volume each year. Each volume contains a selection of material, covering a wide range of subjects. The editors include senior professionals but also students studying papyrology at the doctoral or undergraduate level. Thus recent volumes offer early fragments of the Gospels and of the Book of Revelation, early witnesses to the texts of Apollonius Rhodius, Aristophanes, Demosthenes, and Euripides, previously unknown texts of Simonides and Menander and of the epigrammatist Nicarchus. Other subjects covered include specimens of Greek music and documents relating to magic and astrology.
A joint project with Brigham Young University using multi-spectral imaging technology has been extremely successful in recovering previously illegible writing. With multi-spectral imaging, many pictures of the illegible papyrus are taken using different filters, finely tuned to capture certain wavelengths of light. Thus, researchers can find the optimum spectral portion for distinguishing ink from paper in order to display otherwise completely illegible papyri. The amount of text potentially to be deciphered by this technique is huge. A selection of the images obtained during the project and more information on the latest discoveries has been provided on the project's website.[18]
On June 21, 2005 the Times Literary Supplement published the text and translation of a newly reconstructed poem by Sappho,[19] together with discussion by Martin L. West.[20] Part of this poem was first published in 1922 from an Oxyrhynchus papyrus, no. 1787 (fragment 1).[21] Most of the rest of the poem has now been found on a papyrus kept at Cologne University.[22]
In 1992, upon the discovery of an important necropolis with a period of use from the Saite period through to the Christian era (664 BC − 640 AD) a joint action by the University of Barcelona and the Egyptian Antiquities Service began with the aim of initiating a research program: The Archaeological Mission Oxyrhynchus. In 2004 the first program agreement was signed to enhance the Mission between the University of Barcelona, the current driver of the mission together with the Department of Culture and Media of the Generalitat of Catalonia, but since 2011 it is only financed by the University of Barcelona, the Spanish Ministry and the Catalan Society of Egyptology. The aim of the mission is to give continuity to the historical archaeological studies of previous expeditions while promoting research at Oxyrhynchus and conserve and enhance structures discovered on the site. In addition to the publication of several articles in professional journals, excavations carried out by the Mission have resulted in a sample, presented at the Egyptian Museum and the Greco-Roman Museum in Alexandria with paintings of late antiquity and various objects belonging to a necropolis Osireion located 1.5 km northwest of the urban area; and various publications of the Catalan Institute of Classical Archaeology.
See also
References
- E. A. Wallis Budge (1920). An Egyptian hieroglyphic dictionary: with an index of English words, king list and geological list with indexes, list of hieroglyphic characters, coptic and semitic alphabets, etc. Vol II=. John Murray. p. 987
- Gauthier, Henri (1925). Dictionnaire des Noms Géographiques Contenus dans les Textes Hiéroglyphiques Vol .2. p. 83.
- "Oxyrhynchus Online Image Database". Oxyrhynchus Online Project Metadata. Retrieved 27 March 2017. Document Location: The Egyptian Museum, Cairo, Egypt. Material: Paper. Image: Unavailable.
- "Where is Oxyrhynchus?". Oxyrhynchus Online. Retrieved 1 June 2007.
- EGYPT iv. Relations in the Sasanian period at Encyclopædia Iranica
- Parsons, Peter J. (2012). City of the Sharp-Nosed Fish: Greek Lives in Roman Egypt. Orion Publishing Group. ISBN 978-1-78022-530-2.
- Quoted in A.M. Luijendijk, "Sacred Scriptures as Trash: Biblical Papyri from Oxyrhynchus" Vigiliae Christianae, 2010.
- Grenfell, Bernard (1898). "Oxyrhynchus and Its Papyri". In Griffith, F.L. (ed.). Archaeological Report: 1896-1897. Egypt Exploration Fund. pp. 1–12, (7). Retrieved October 1, 2016.
- "StackPath". dailynewsegypt.com. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- "Unique cemetery dating back to el-Sawi era discovered in Egypt amid coronavirus crisis". Zee News. 2020-05-28. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- Mahmoud, Rasha (2020-05-26). "Egypt makes major archaeological discovery amid coronavirus crisis". Al-Monitor. Retrieved 2020-09-09.
- Sophocles' Ichneutae was adapted, in 1988, into a play entitled The Trackers of Oxyrhynchus, by British poet and author Tony Harrison, featuring Grenfell and Hunt as main characters.
- Search by table of contents; "Oxyrhynchus Online Image Database". Imaging Papyri Project. Retrieved 25 May 2007. A listing of what each fragment contains.
- "Artifact Record Details: Oxyrhynchus Papyrus, No. 932: Letter, Thaius to Tigrius (Fragment)". Spurlock Museum at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. 2001. Retrieved 30 May 2007. "Artifact of the Month: Letter from Thaius to Tirius, Oxyrhynchus Papyrus, No. 932". Spurlock Museum. 2002. Retrieved 30 May 2007.
- Bill Casselman. "One of the oldest extant diagrams from Euclid". Department of Mathematics, University of British Columbia. Retrieved 30 May 2007.
- "Publications: Full List". Egypt Exploration Society. Archived from the original on 28 January 2008. Retrieved 30 March 2008.
- "Publications" (PDF). The Egypt Exploration Society. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 August 2016. Retrieved 2 August 2016.
- "Multispectral imaging". Oxyrhynchos online. Retrieved 1 June 2007.
- Martin West (24 June 2005). "A New Sappho Poem". Times Online. Archived from the original on 28 June 2007. Retrieved 1 June 2007.
- Discussion by Martin West Archived September 29, 2006, at the Wayback Machine
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-03-25. Retrieved 2006-03-23.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)see the third pair of images on this page
- "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2007-03-17. Retrieved 2006-03-23.CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link)Image of papyrus fragment
Further reading
- The Oxyrhynchus Logia and the Apocryphal Gospels. (2007). Gardners Books. ISBN 978-1-4304-5596-7
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Oxyrhynchus. |
- Official website of the Archaeological Mission in Oxyrhynchus
- Oxyrhynchus Online
- PBS NOVA scienceNOW feature on papyrus imaging (streaming video)
- Report on the recent Egyptian-Spanish archaeological mission to the site
- Oxford University Classics Department Oxyrhynchus Project
- Oxyrhynchus and the Gospel of Thomas
- Article on new discoveries in the papyri from The Independent on Sunday, April 17, 2005
- University of Michigan Collection
- Joint Egyptian/Spanish archaeological mission in Oxyrhynchus
Oxyrhynchus papyri volumes
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. I, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. II, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. III, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt Cornell University Library Historical Monographs Collection. Reprinted by Cornell University Library Digital Collections
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. IV, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. V, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. VI, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. VII, edited with translations and notes by Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. VIII, edited with translations and notes by Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. IX, edited with translations and notes by Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. X, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt Cornell University Library Historical Monographs Collection. Reprinted by Cornell University Library Digital Collections
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. X, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. XI, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. XII, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. XIII, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. XIV, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive
- The Oxyrhynchus papyri vol. XV, edited with translations and notes by Bernard P. Grenfell and Arthur S. Hunt at the Internet Archive